Unusual ground motion associated with the deepest major earthquake in the seismological record is due to both its great depth and its origin away from the subducting slab.
Terri Cook
Terri Cook is an award-winning freelance writer whose career has focused on exploring and explaining the 4.5-billion-year-history of the remarkable planet we live on. Cook, who has an M.S. degree in Earth science from the University of California, Santa Cruz, writes about geology, ecology, and the environment—as well as wine, tea, hiking, and biking—for a diverse group of publications, including Eos, Scientific American, NOVA Next, Science News, and EARTH magazine, as well as Avalon Travel and numerous other travel-related publications. Her reporting has taken her to 25 states and 20 countries scattered across 5 continents, from the depths of the Grand Canyon to the sandy Australian Outback to the mist-shrouded summit of Bali’s Mount Batur. As the coauthor of three popular guidebooks, including Hiking the Grand Canyon’s Geology and Geology Underfoot Along Colorado’s Front Range, Cook gives frequent presentations about geology and science communication. She is the recipient of a 2016 European Geosciences Union Science Journalism Fellowship and is based in beautiful Boulder, Colo.
Probing the Grain-Scale Processes That Drive Plate Tectonics
New experimental data suggest that rock composition may play a critical role in forming and perpetuating shear zones.
Resolving a Mystery of the Ages
High-precision radiometric dates shed new light on the puzzling 600,000-year disparity in the timing of one of Earth’s most pivotal timescale boundaries.
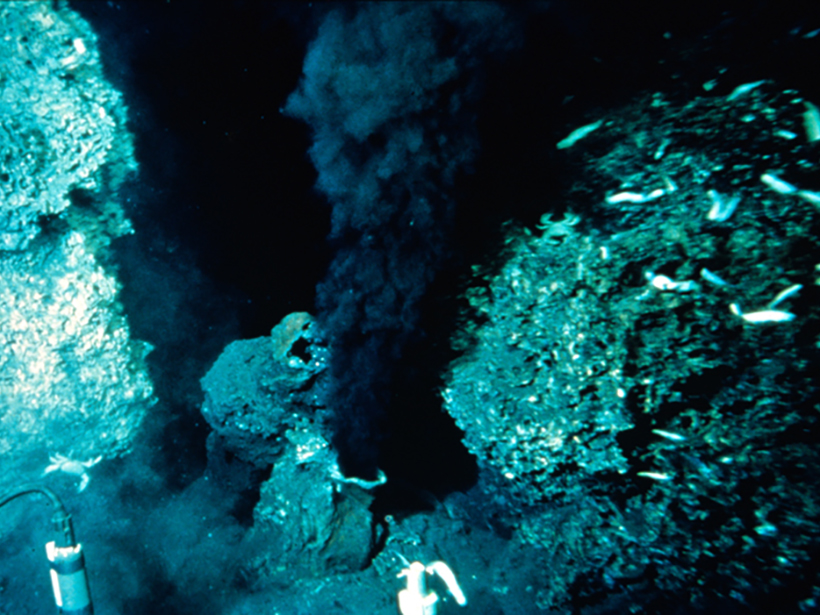
Is the Lower Crust Convecting Beneath Mid-Ocean Ridges?
The first attempt to couple models of hydrothermal circulation and magmatic convection along fast-spreading ridges may explain the spacing of hydrothermal vent fields along the East Pacific Rise.
Cosmic Ray Neutrons Reveal Mountain Snowpacks
The first application of aboveground neutron sensing to evaluate alpine snowpacks indicates that this method can reliably detect average snow depth and water content across intermediate distances.
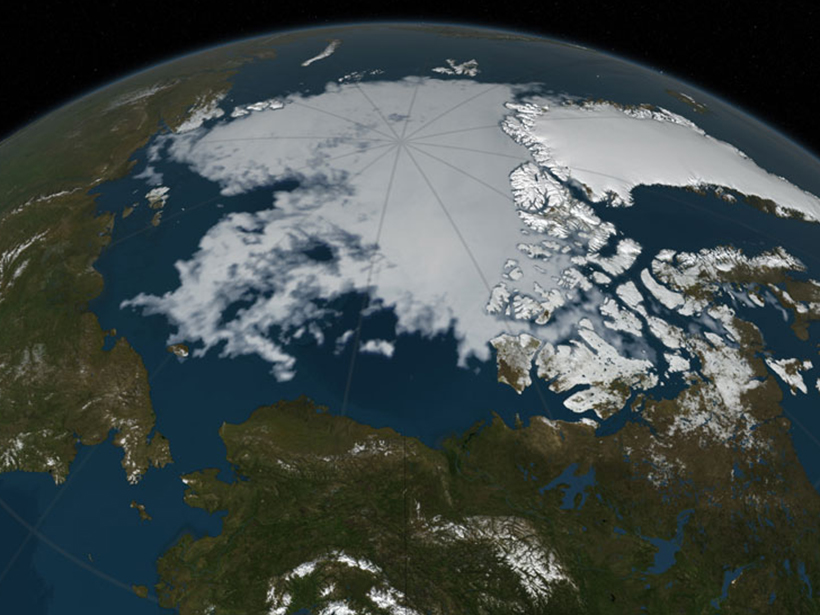
New Baseline for Understanding Arctic Oxygen and Nutrient Fluxes
Significant spatial and temporal patterns emerge from the first pan-Arctic comparison of oxygen demand in marine sediments.
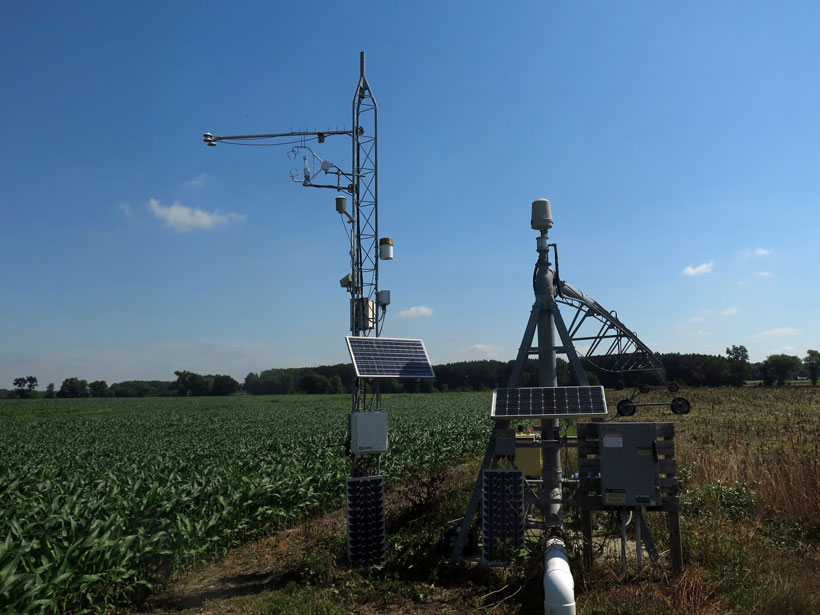
Blending Satellite Data to Monitor Agricultural Water Use
A new technique that merges data gathered by multiple satellites can be used to monitor agricultural water use and improve water quality assessments around the globe.
A Promising New Tool for Forecasting Volcanic Hazards
A new model that simulates the behavior of surging ash clouds may help scientists to better predict the hazards associated with the deadliest type of volcanic flows.
The Competing Climate Effects of Elevation and Albedo
Variations in surface reflectivity are as important as surface elevation changes in determining regional climate at nonpolar latitudes, according to a new modeling study.
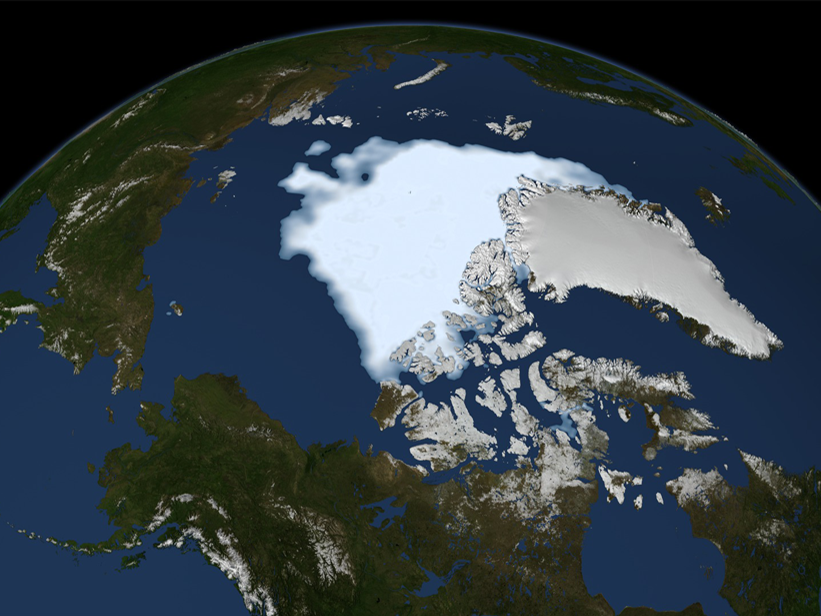
A Benchmark for Trace Greenhouse Gases in the Arctic Ocean
Samples of seawater from the North American Arctic show that the region is neither a major source nor sink of methane and nitrous oxide to the overlying atmosphere.