The finding, which focuses on lower-income countries, could help inform plans to shrink the global climate knowledge gender gap.
News
Blending Science and Indigenous Knowledge to Tell an Estuary’s Story
A new study of nutrient levels in soil cores supports oral Indigenous history, informing future estuary restoration efforts.
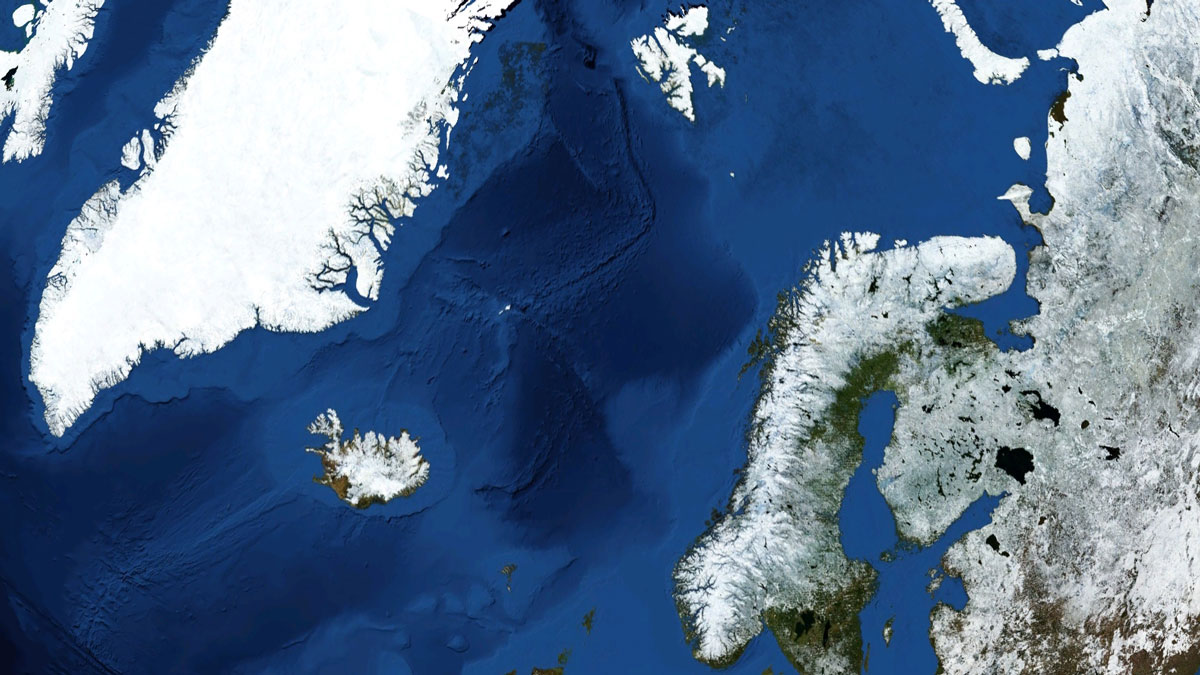
New Eyes on One of the Planet’s Largest Submarine Landslides
Researchers have mapped the ancient Stad Slide off the coast of Norway to better understand what triggered it, and the hunt is on for the tsunami it might have unleashed.
What Okinawan Sailor Songs Might Teach Us About the Climate
New work bridges the worlds of Ryukyuan classical music and the geosciences.
Climate Change Could Drive Butterflies and Plants Apart
Insects and the plants they depend on are migrating in response to climate change, but not always in the same way.
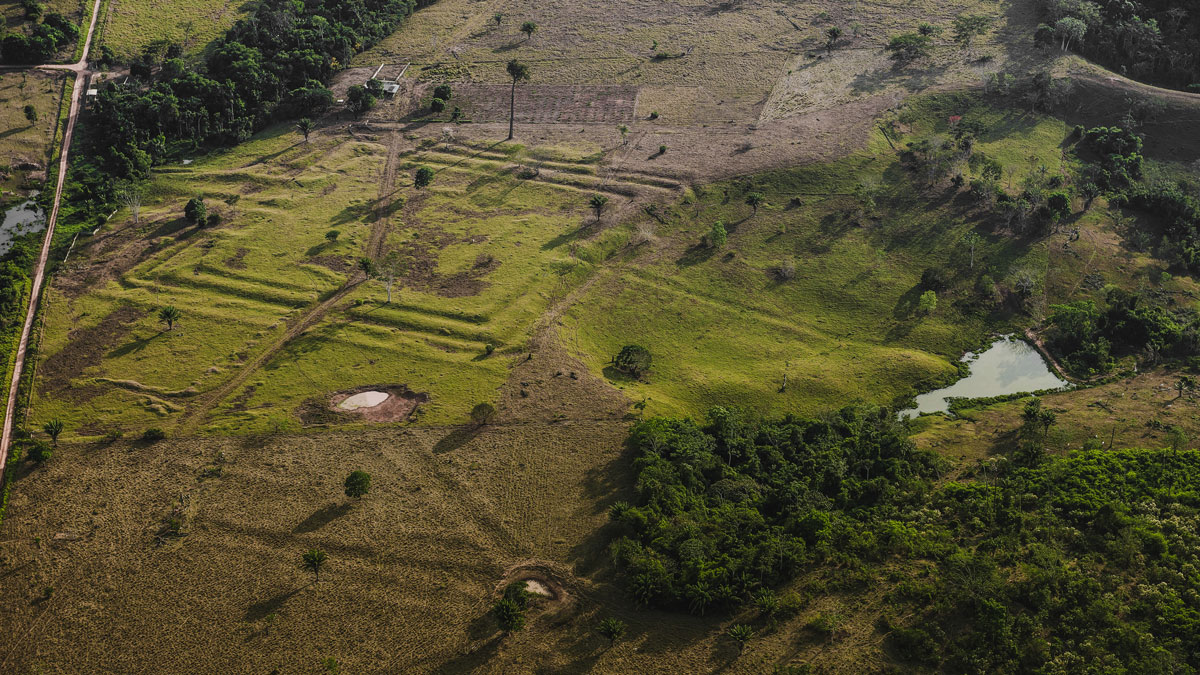
How Ancient Indigenous Societies Made Today’s Amazon More Resilient
Portions of the forest managed by pre-Columbian populations hold higher biomass and are more able to withstand climate change.
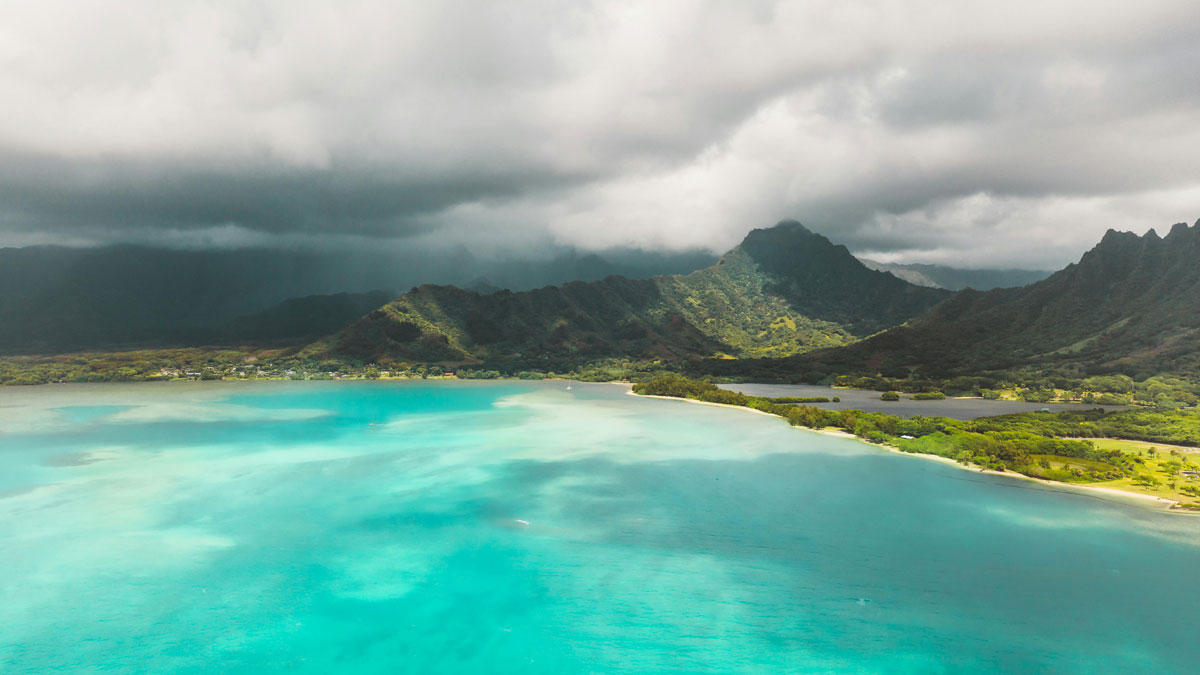
Globe-Trotting Weather Pattern Influences Rainfall in Hawaii
Isolated islands that depend on rainfall could benefit from improved forecasting of near-future events, and understanding the Madden-Julian Oscillation could hold an important key.
Crystal Clusters Contain Clues to Magma’s Past and Future Eruptions
It’s now become easier to forecast the next eruption of Alaska’s Bogoslof volcano. New research led by Pavel Izbekov, a volcanologist at the Alaska Volcano Observatory, is applying the foundations of diffusion chronometry—the study of chemical change in crystals over time—to a new eruption forecasting approach. Izbekov’s team used crystal clusters and their collective records […]
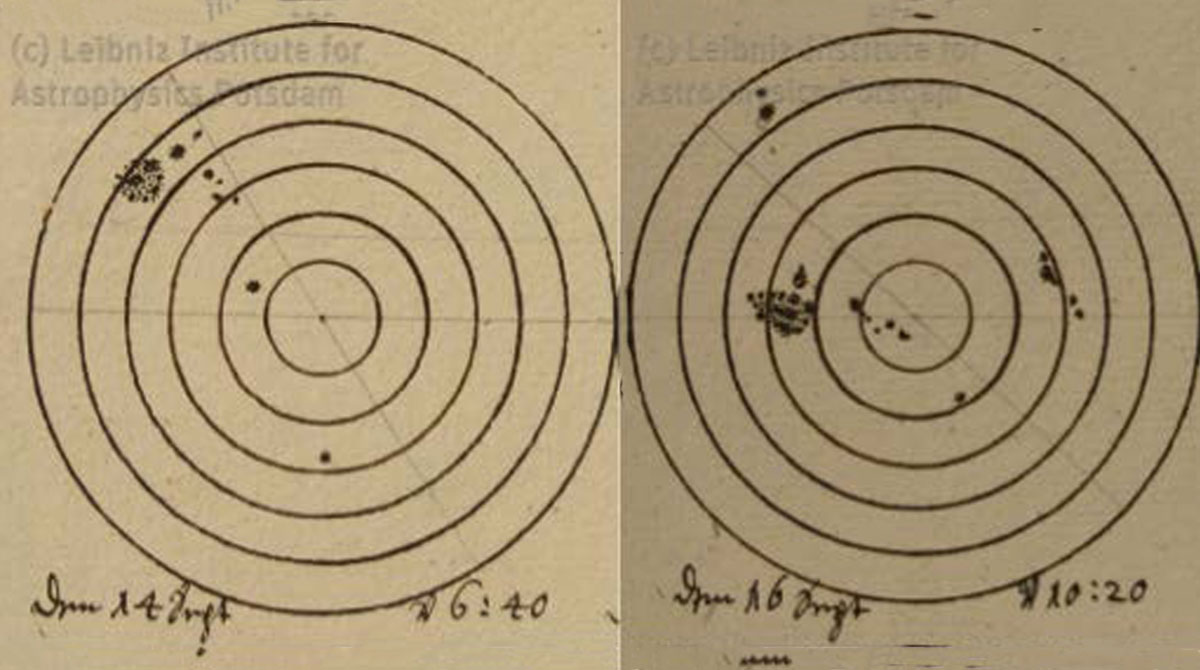
Sunspot Drawings Illuminate 400 Years of Solar Activity
A new computational framework is helping scientists sift through centuries of scientific illustration of the Sun’s spotty surface.
Amid the Arctic’s Hottest Year, Arctic Science Faces a Data Deficiency
The 20th annual Arctic Report Card reveals new highs in temperature and new lows in sea ice, as well as an uncertain outlook for the availability of federal data.