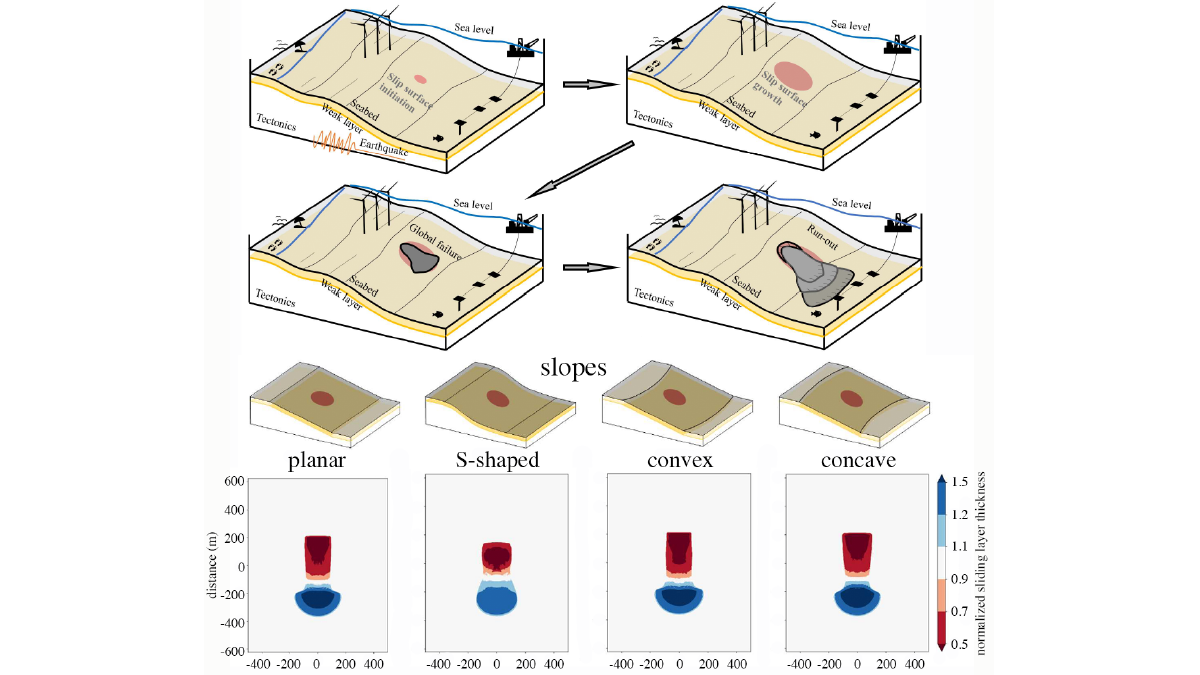
A new study reveals how small cracks turn into gigantic submarine slides.
Editors’ Highlights
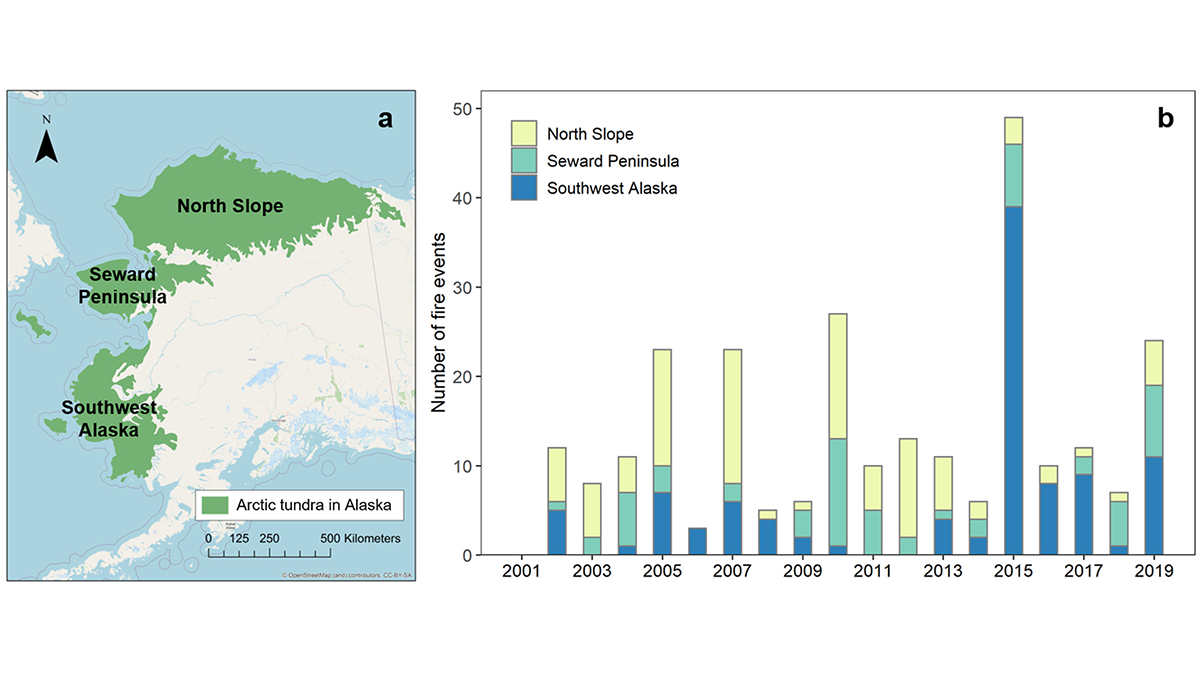
Lightning in Alaskan Tundra Ignites Most Fires
Cloud-to-ground lightning is found to be the most important controller of wildfire occurrence in the Artic tundra of Alaska from 2001 to 2019.
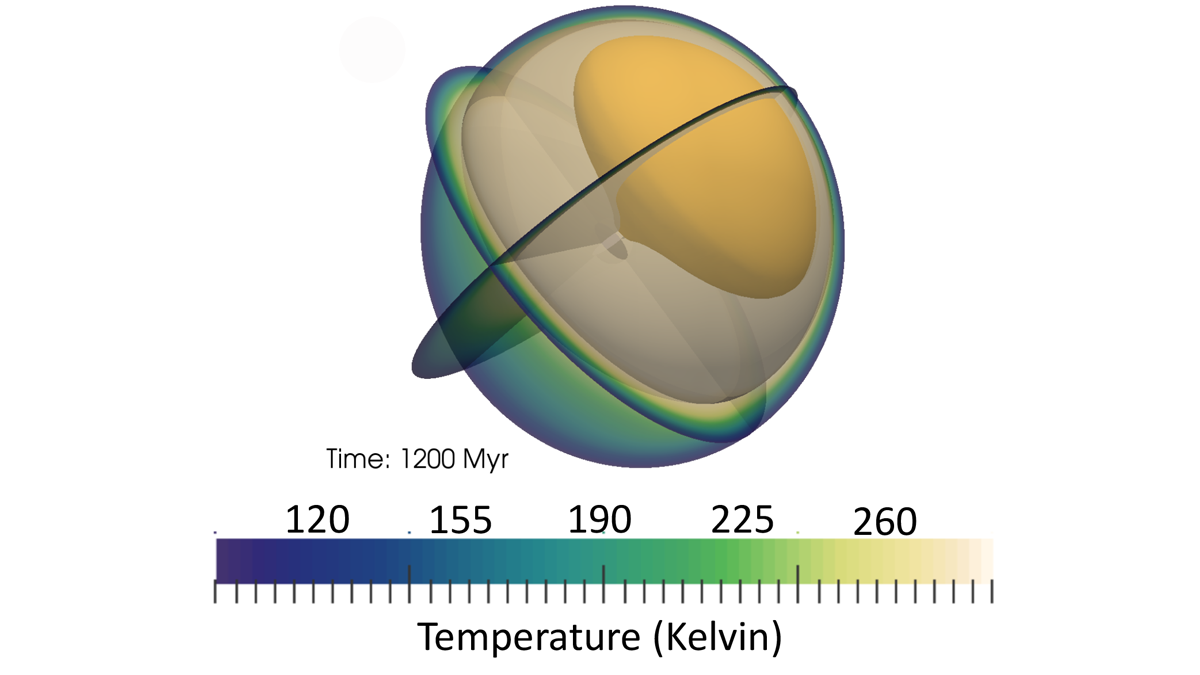
Ceres: Missing Craters, Crust Thickness Variation by Interior Convection
Models show that several puzzling features about Ceres’ topography, gravity anomalies, and crater size distribution may be explained by asymmetric hemispherical convection due to radiogenic heating.
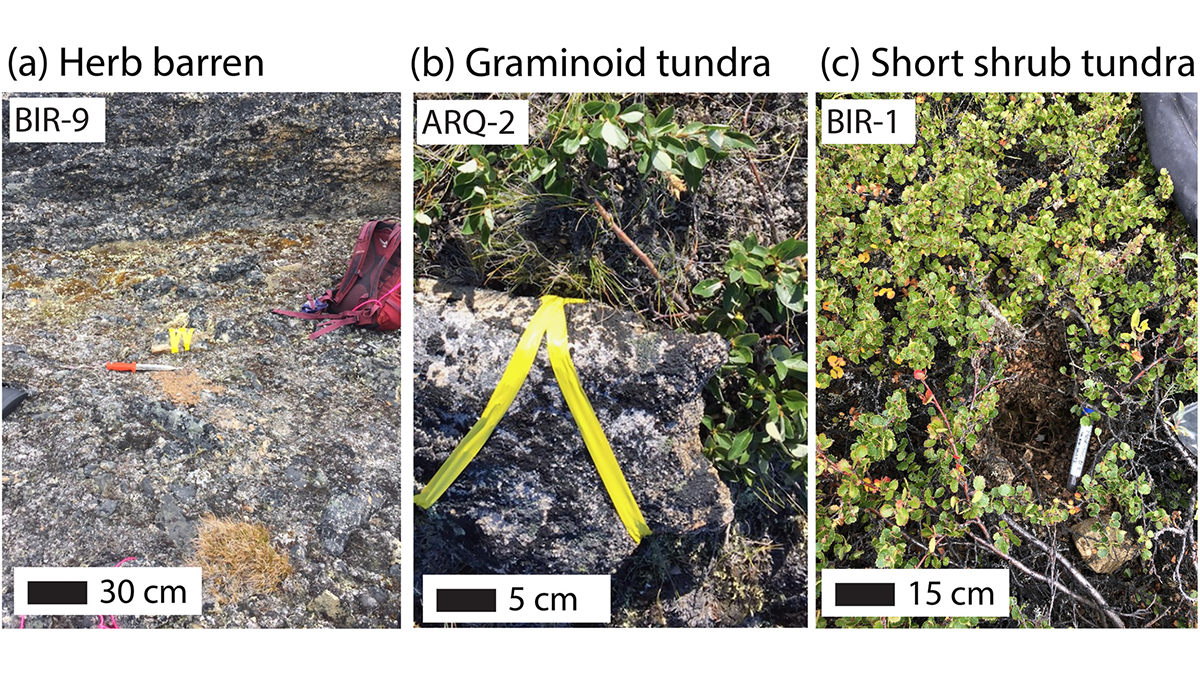
It’s Cool to be Short When You’re in the Arctic Permafrost
Extensive ground temperature measurements complicate our understanding of how vegetation cover, snow duration, and microtopography influence the pace of permafrost thaw in a changing climate.
More Accurately Modeling Rain Formation
Rain and cloud droplets are treated as distinct categories in most models yet lie on a continuous droplet size spectrum in nature. Representing them as part of a continuous spectrum improves models.
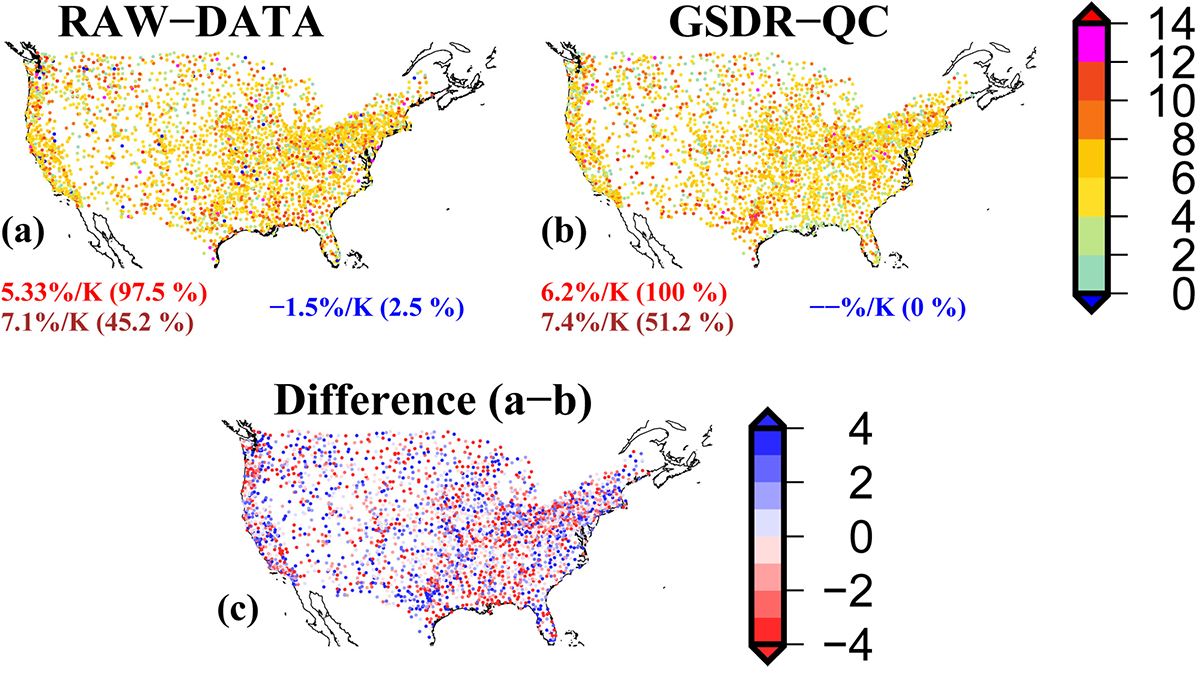
Explaining Uncertainty in Estimates of Rain Response to Warming
Humidity increases with warming. Theory and observations about how increased humidity translates into more extreme rainfall can be reconciled if attention is paid to data and methods.
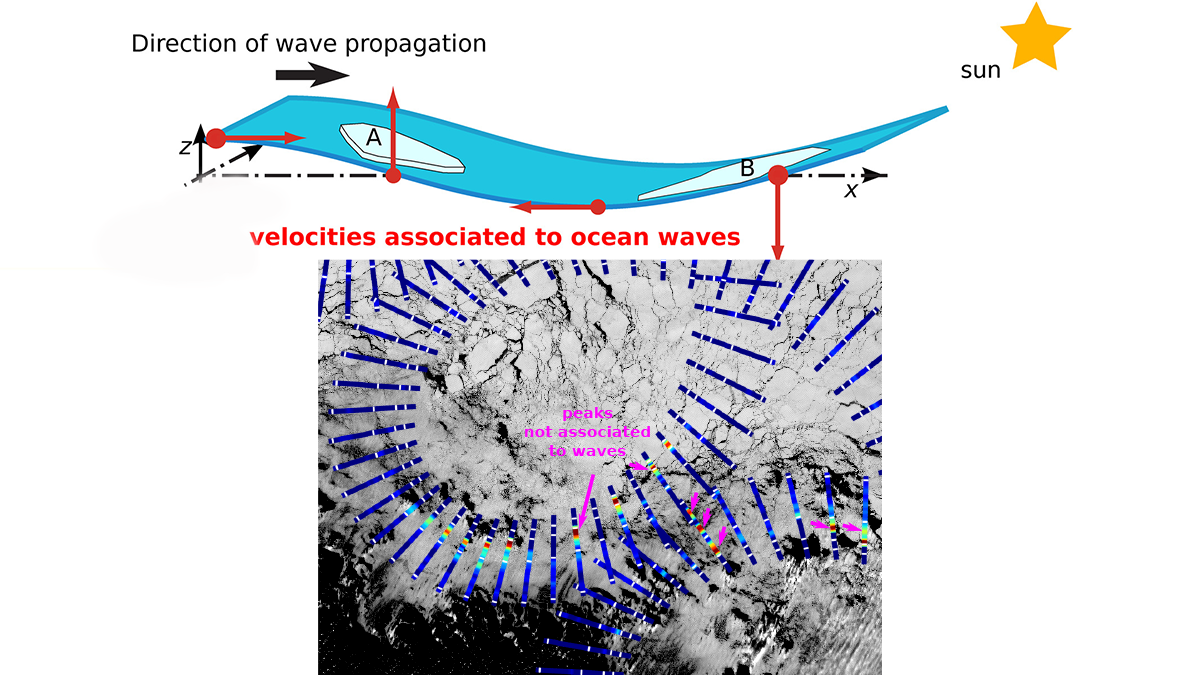
Satellites Remotely Measure Ocean Waves and Sea Ice Interactions
A new method for using satellite observations from multiple sensors improves measurements of ocean waves as they propagate through and interact with sea ice.
An Ocean Surface Layer with Potential
The depth of the ocean’s surface mixed layer is typically defined based on density thresholds. However, a more physically appealing definition can be constructed from potential energy considerations.
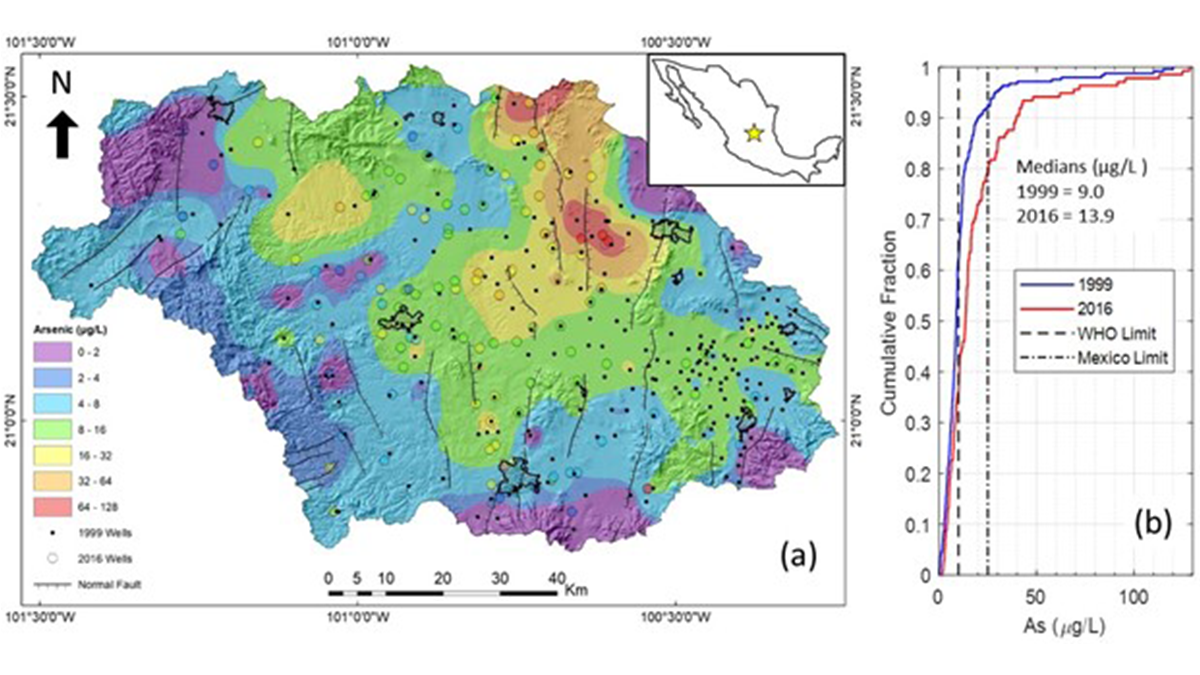
Protecting Children’s Health Can Benefit the Economy
A new study presents an integrated approach to predicting the human health impacts, economic implications, and remediation solutions for using contaminated groundwater in Central Mexico.
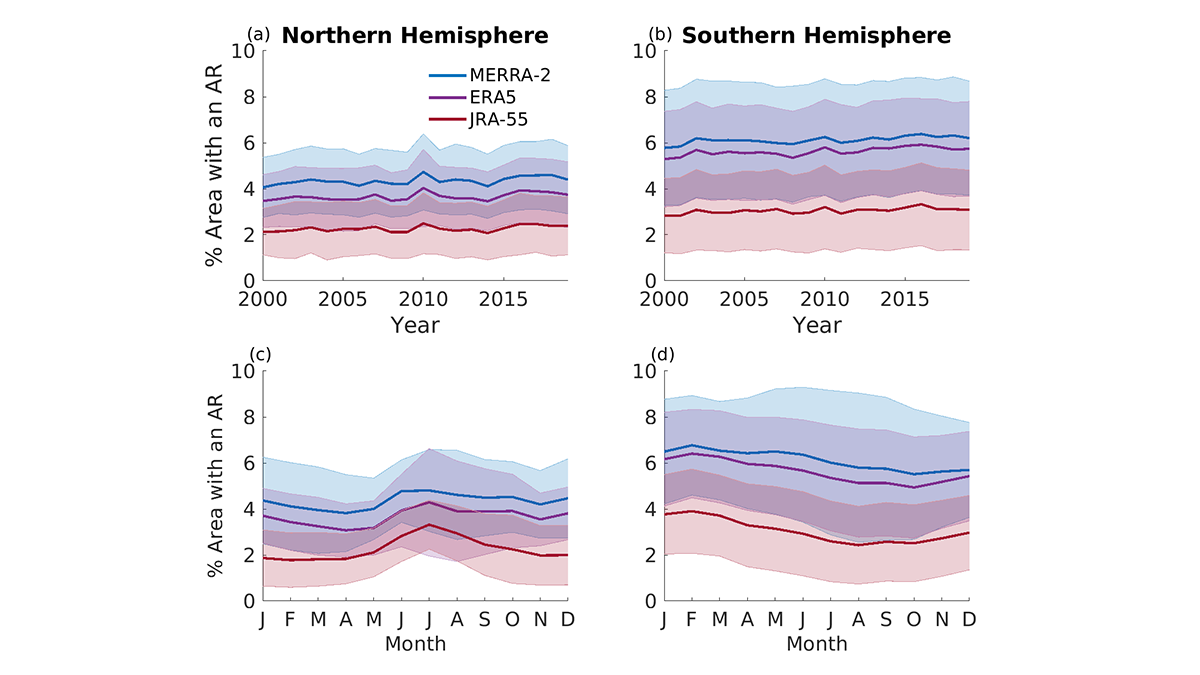
Comparing Methods for Analysis of Atmospheric Rivers
Results from the Atmospheric River Tracking Method Intercomparison Project (ARTMIP) describe the similarity and difference of using eleven detection algorithms and three reanalysis products.