A study of deformed and metamorphosed rocks exposed in Tibet’s Lopu Range suggests that episodes of crustal shortening and extension during the evolution of the Himalaya are related to subduction processes.
Research Spotlights
Research spotlights are plain-language summaries of recent articles published in AGU’s suite of 24 journals.
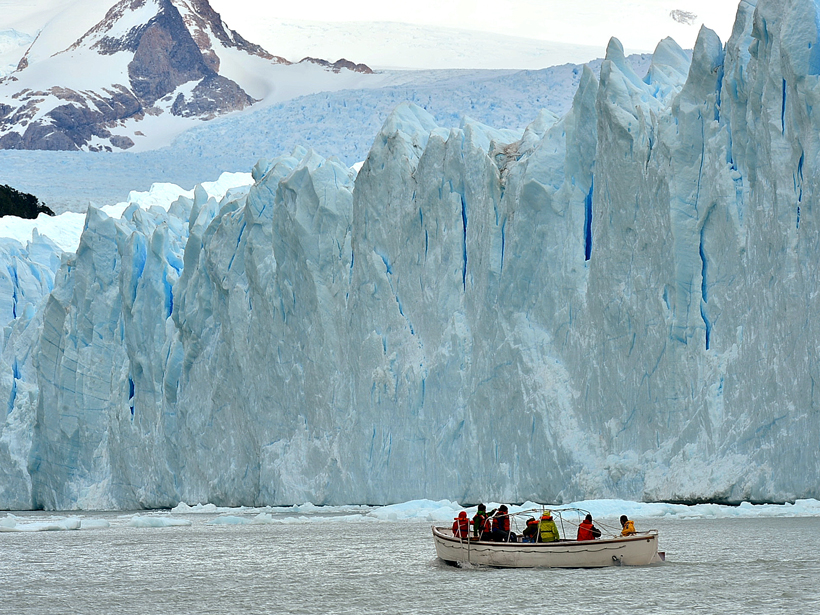
In Patagonian Lakes, Glacial Meltwater Lies Low
A new study reveals key differences in ice-water interactions between glaciers that flow into lakes and glaciers that end in the sea.
Autonomous Floats Shed New Light on the Ocean’s Many Hues
Argo float data reveal regional deviations from existing models of the relationship between ocean color and biogeochemistry.
New Explanation for “Meandering” Electrons Orbiting Earth
A new study proposes a simpler theory to explain a class of electrons zipping around Earth, propelled by magnetic explosions.
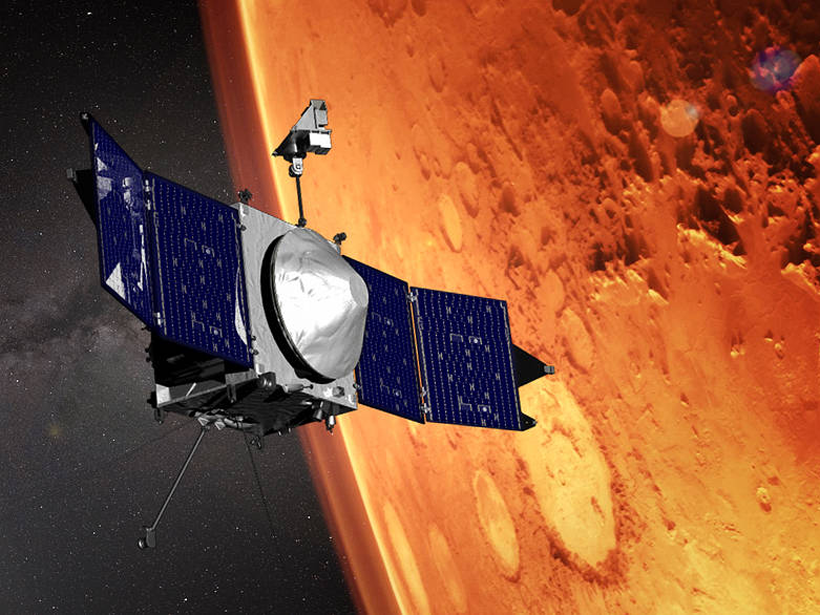
Spacecraft Returns Its First Data on Martian Solar Irradiance
Scientists demonstrate the capabilities and limitations of the mathematical model used to calculate solar irradiance using measurements from NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN).
Diagnosing Cryptic Remagnetization in Sedimentary Rocks
To understand the ancient movement of Earth’s tectonic plates, comprehensive magnetic and petrographic studies are needed to detect secondary magnetization in carbonates and other sedimentary rocks.
How Do Rivers Flow over Bedrock?
A study questions whether the hydraulics of rivers that lack loose sediments along their bottoms can be accurately depicted by standard equations for flow over sediment.
When Ocean and Atmosphere Couple, the Climate Wobbles
Every 25–30 years, the ocean and atmosphere conspire to produce an enhanced North Atlantic Oscillation
Catching Glimpses of Centuries-Old Earthquakes
Researchers in the western United States survey the earthquakes that have torn up California for the past millennium.
Reinterpreting the Age and Origins of Taiwan’s Yuli Belt Terrane
Uranium-lead dating of zircons from Taiwan’s east central metamorphic belt offers robust evidence that this uplifted terrane is some 90 million years younger than previously thought.