A novel interface allows users of MATLAB and GMT, two software packages widely used by the geoscience community, to simultaneously harness the capabilities of both products.
CC BY-NC-ND 2017
Algorithm Discerns Where Tweets Came from to Track Disasters
New pilot system that analyzed more than 35 million flood-related Twitter posts to determine their geographic origin might help first responders locate and react more quickly to calamities.
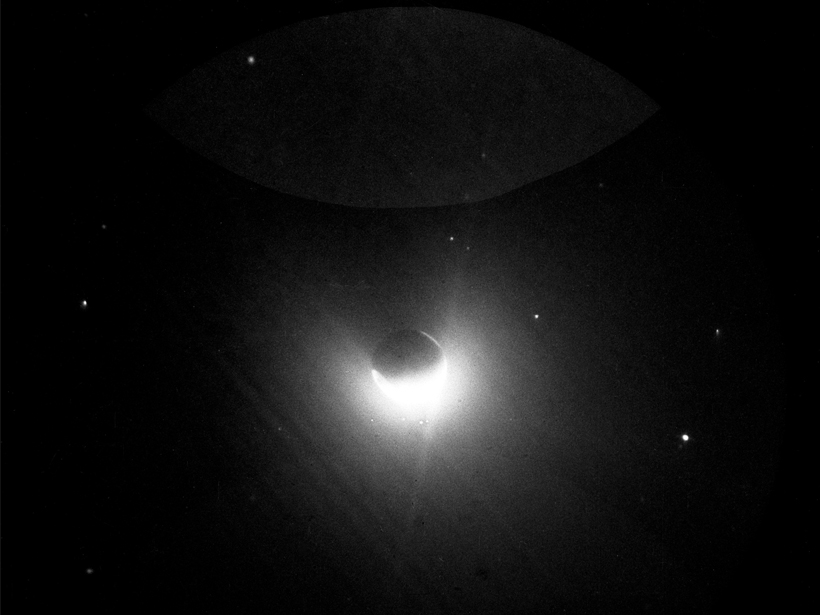
How Geomagnetic Storms Light Up the Geocorona
After geomagnetic storms, Earth’s corona abruptly increases in hydrogen density. For the first time, serendipitous observations have allowed researchers to investigate why.
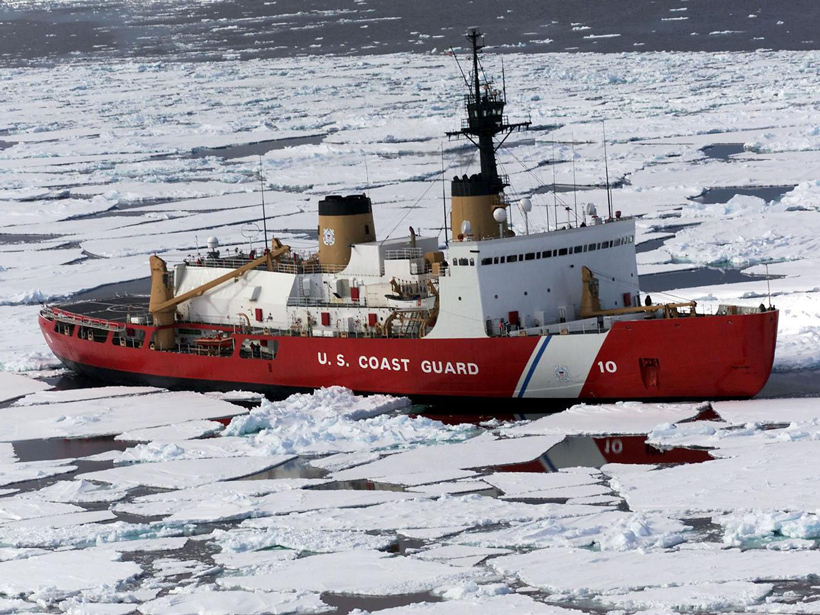
Build Four New U.S. Polar Icebreakers, Report Urges
All of the ships should be “science ready,” whereas one should be “fully science capable,” according to new recommendations from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine.
How Does Changing Climate Bring More Extreme Events?
The editors of a new book describe how and why weather and climate phenomena are intensifying with climate change.
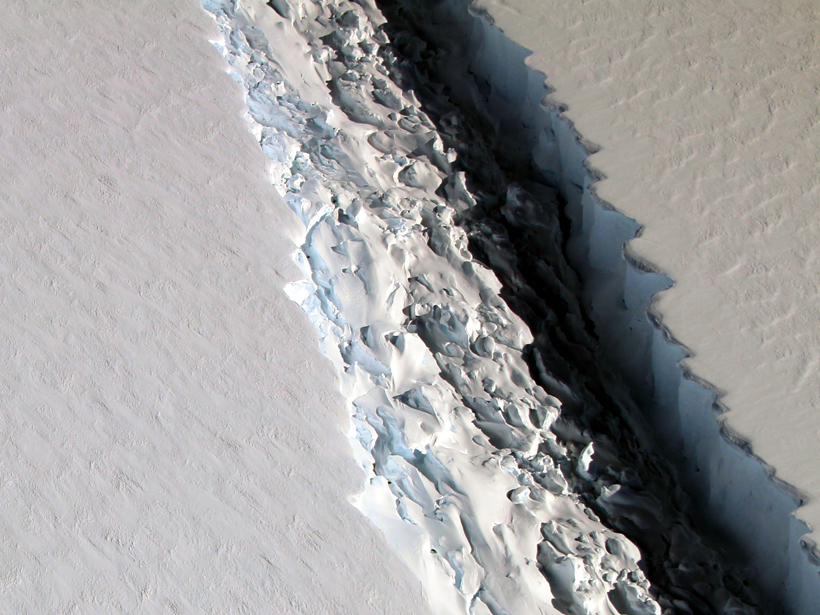
Six Points of Perspective on Larsen C’s Huge New Iceberg
A Delaware-sized slab of ice just broke off Antarctica. Now what?
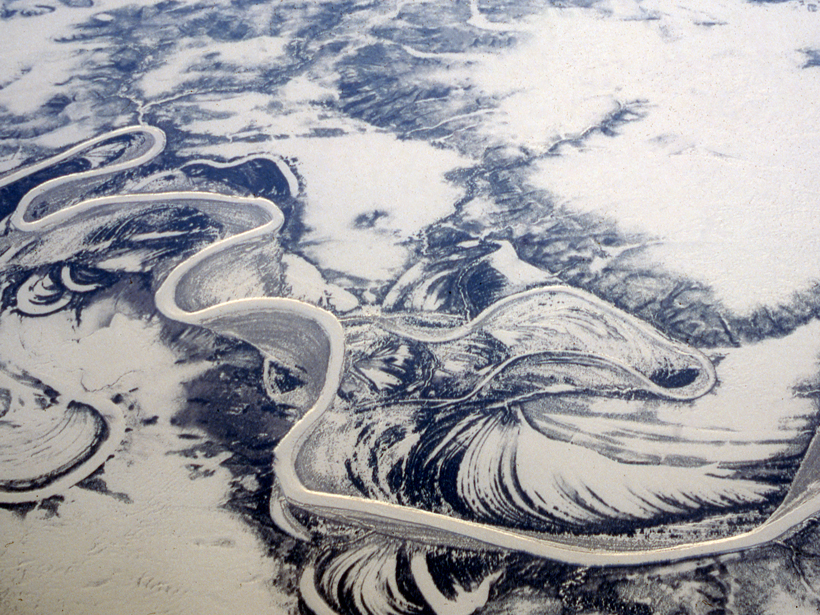
Climate Change Could Make Siberia an Attractive Place to Live
Although anticipated warmer temperatures promise to render the region more comfortable for people, the transformation might turn permafrost areas into inhospitable bogs.
New Technique Could Help Scientists Track Nitrous Oxide Sources
A long-term study in Switzerland reveals the promise of a new method to determine isotopic composition of the potent greenhouse gas.
Modeling Ocean Waves over Rocky Reefs
A field survey in Australia links rugged seafloor terrain to erosion-causing waves.
Communities and Experts Collaborate for Climate Resilience
The Resilience Dialogues program provides resources and expertise to help communities build individualized plans for resilience in the face of climate change.