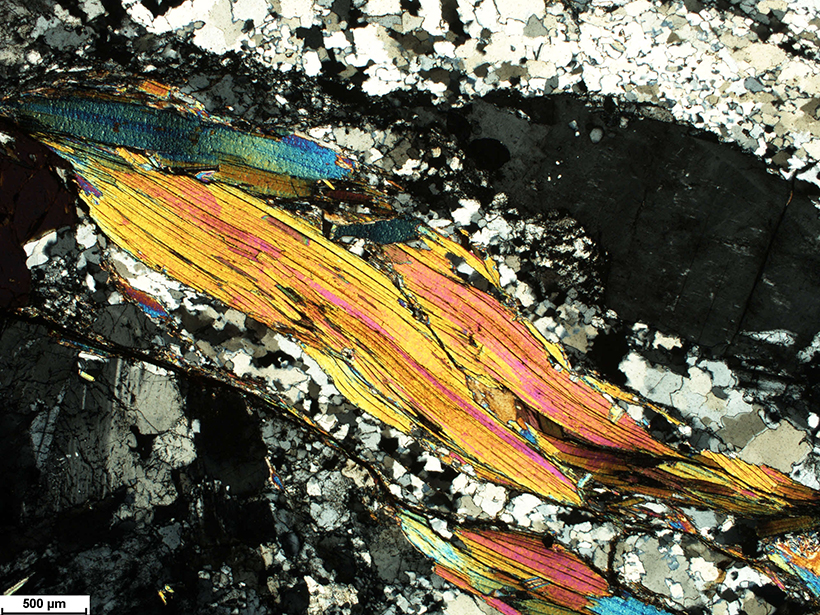
By studying the chemical signatures of 300-million-year-old precipitation, researchers find evidence that the supercontinent Pangea contained peaks as tall as the European Alps.
CC BY-NC-ND 2019
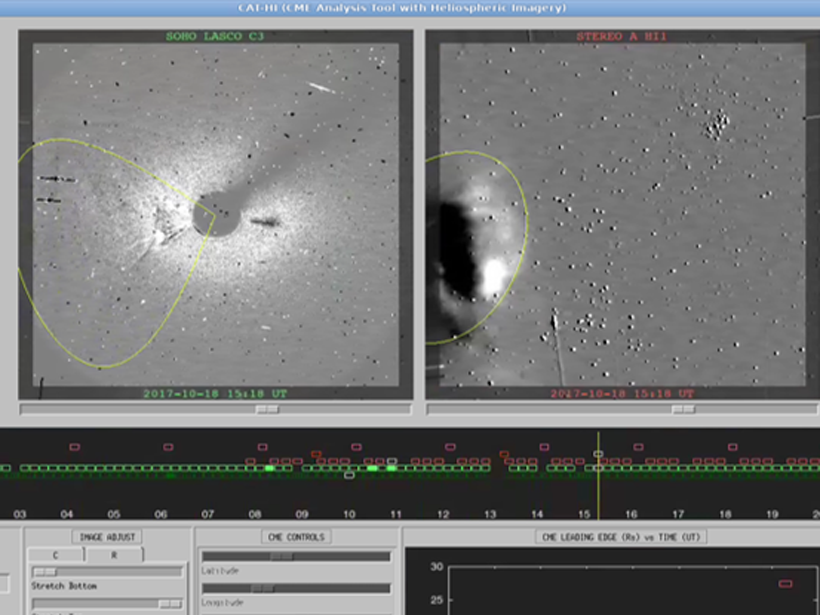
Looking Away from the Sun: Improved Tracking of Solar Storms
A new tool for tracking coronal mass ejections away from the Sun opens a path toward more accurate warnings for operators who have to cope with adverse space weather.
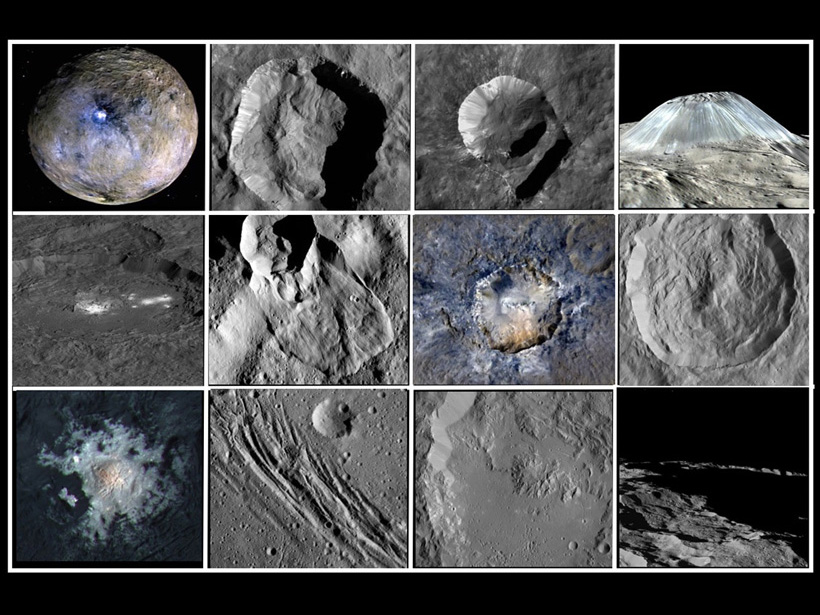
Ceres: Evolution of the Asteroid Belt’s Icy Giant
A new special collection in JGR: Planets explores how ice has played a key role in the development of the landscape on the surface of Ceres.
A New Proxy for Past Precipitation
Researchers used luminescence signals from marine sediment cores to bolster estimates of precipitation levels on land over the past 30,000 years.
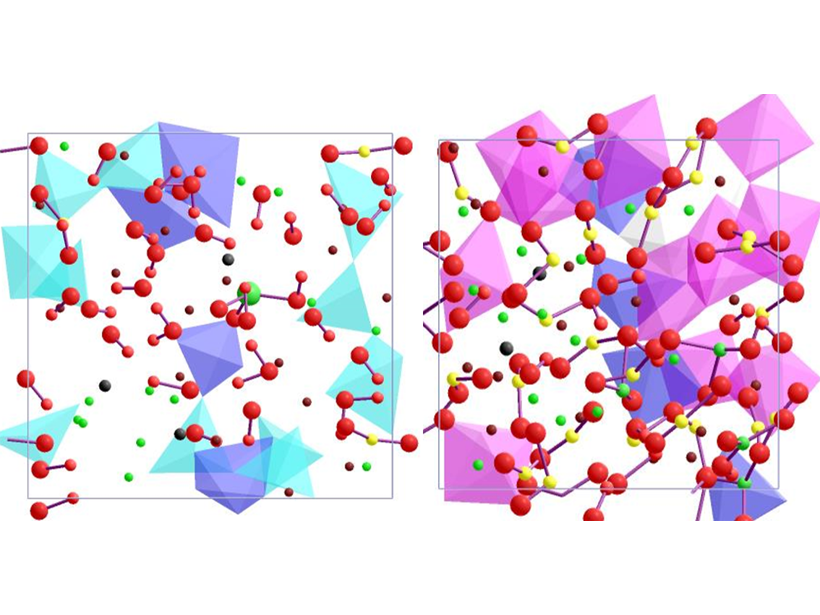
Hiding Deep Hydrous Melts at the Core-Mantle Boundary
Silicate melts containing H2O in the lowermost mantle are surprisingly dense and may stagnate there, trapping primordial volatiles and potentially causing some of the ultra-low velocity zones.
Massive Collision Cracked Young Jupiter’s Core
The gas giant’s interior reveals evidence of an ancient impact.
Finding Faces in Hailstorms
Machine learning technology helps scientists recognize severe weather patterns.
How Volcanic Mountains Cool the Climate
Though coastal plutons spew greenhouse gases into the atmosphere as they form, they also pull some of those gases back out of the atmosphere as they break down over time.
Ocean Observations for Everyone
As the ocean observation community expands its research enterprise, it needs to better engage the end users of its data.
Solar Spike Suggests a More Active Sun
Radio waves are providing a new way to probe the Sun and suggest that the magnetic field of its corona may be stronger than long thought.