Scientists link vegetation mosaics in California to patterns of weathered bedrock.
CC BY-NC-ND 2019
Gauging in the Rain
Measuring how much water falls from the sky is more complicated than it seems. To improve measurements, researchers are looking at umbrellas, hydrophones, and gamma ray detectors.
Pacific Carbon Uptake Accelerating Faster Than Expected
A new study suggests that shifting ocean currents drive faster carbon dioxide uptake.
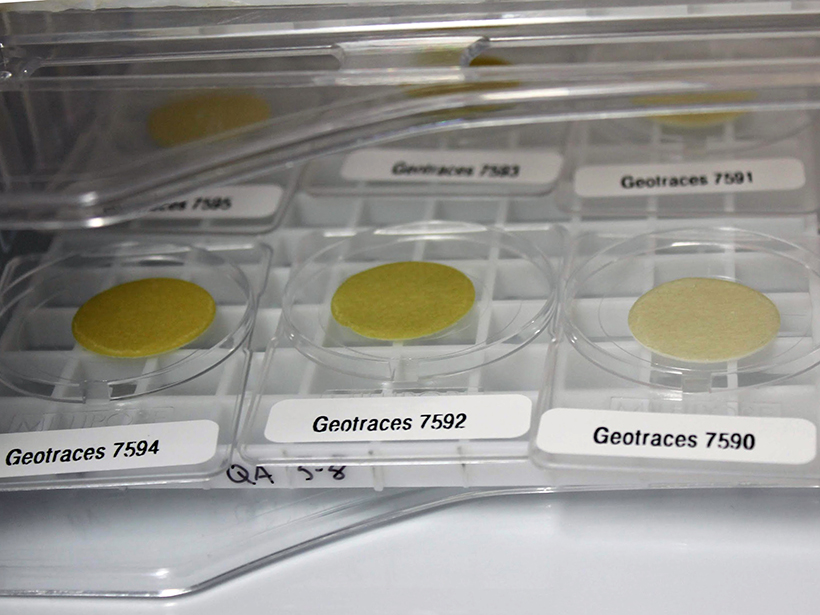
Big Data Help Paint a New Picture of Trace Element Cycling
A new framework for understanding the suite of processes acting on marine particulate trace metals exemplifies how alternative analyses can maximize the information that large data sets provide.
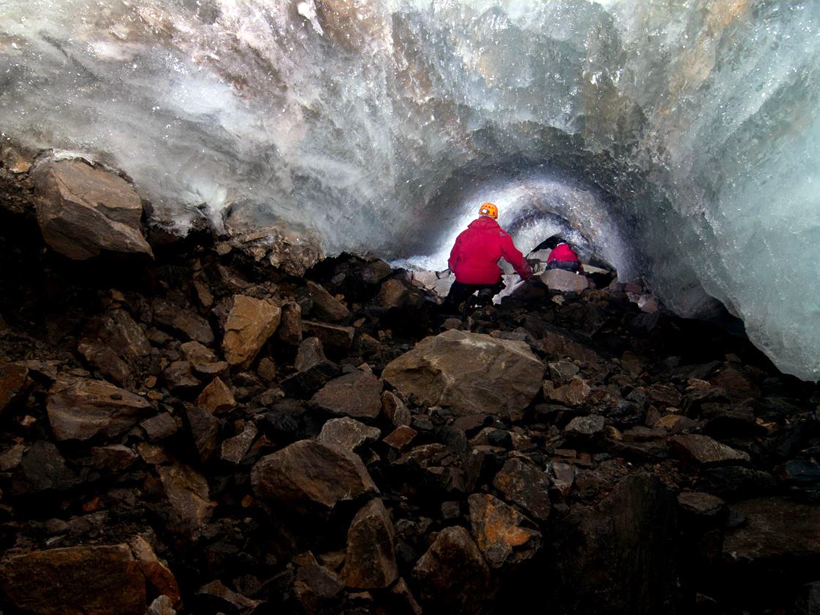
Mapping Subglacial Meltwater Channels
Researchers find that past studies underestimate the friction meltwater channels exert on glaciers by orders of magnitude.
Hiroshima Bomb Created Asteroid Impact–Like Glass
The glass rained from the sky as the bomb annihilated the Japanese city.
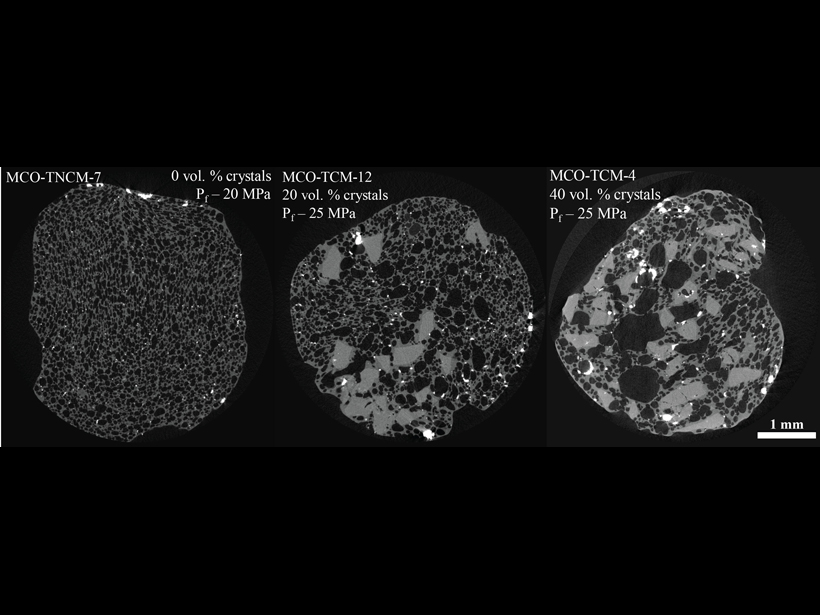
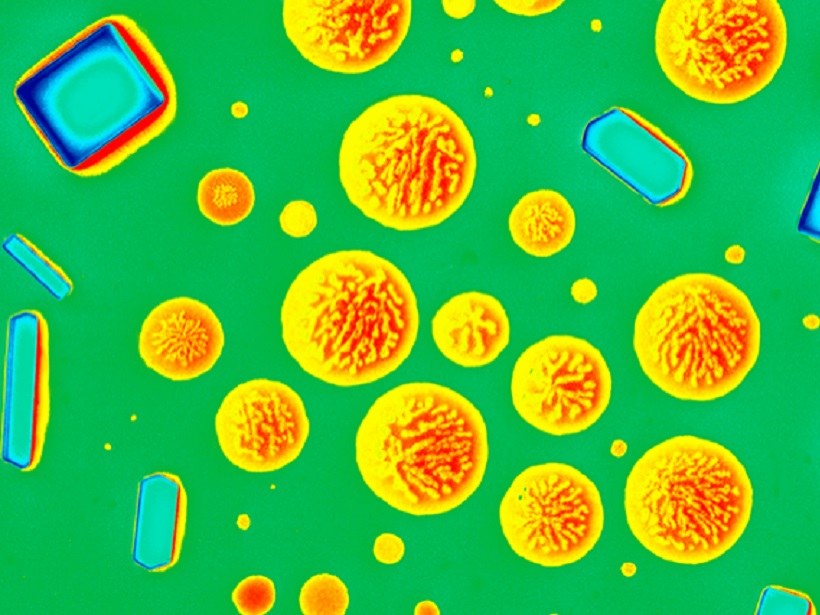
Crystals Connect Bubbles in Explosive Magmas
Hydrous silica-rich magmas can degas through connected bubble pathways when as little as 20% crystals are present, influencing transitions from explosive, Vulcanian-style eruptions to lava effusion.
The Diversity and Complexity of Atmospheric Aerosol
The variability in composition of individual aerosol particles and the way in which they mix in the atmosphere is complex and has significant impacts on Earth’s climate.
Shifting Winds Drive Ocean Temps Along South African Coast
A new study could help manage sardine populations in coastal waters.
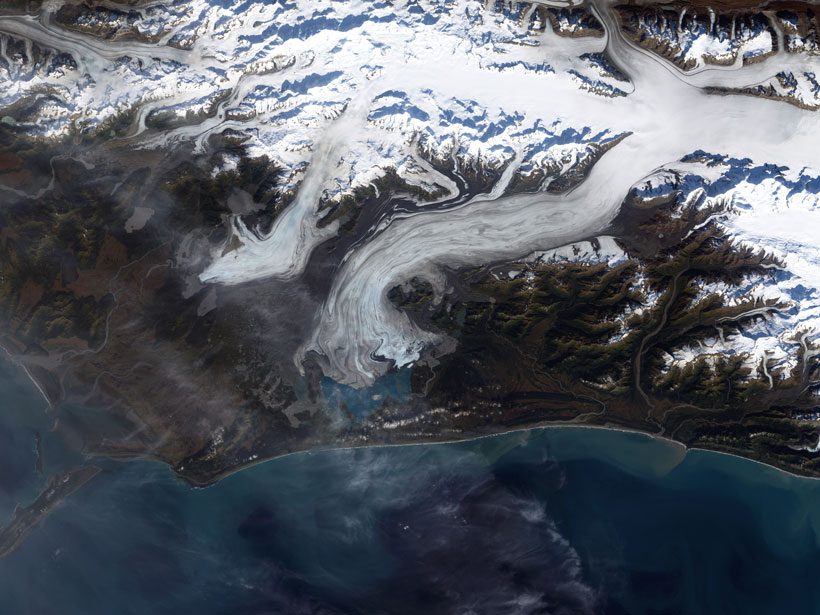
Seismic Clues to Surging Glaciers
Measuring seismic waves passing through a glacier suggests that not only is liquid water playing a role in periodic surging but the water is channeled into cracks from across the ice.