Editors’ Highlights are summaries of recent papers by AGU’s journal editors.
Source: AGU Advances
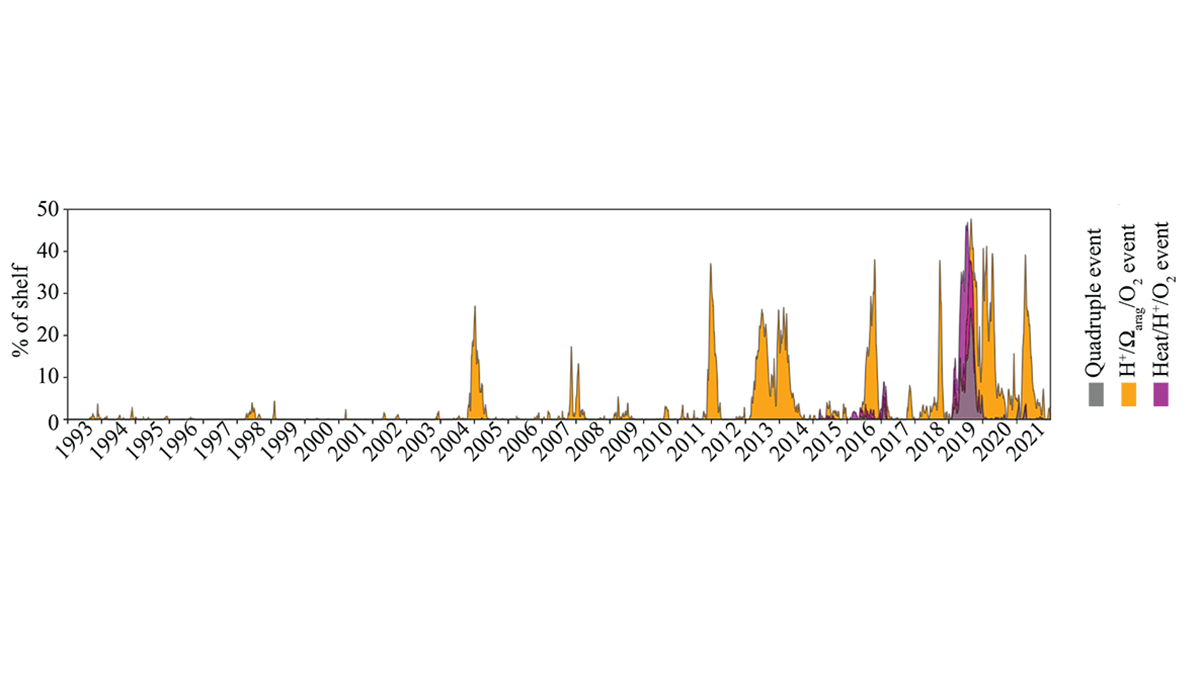
The stressors imposed by warming ocean temperatures, low oxygen, and ocean acidification can be compounded by short term marine heat wave extreme events with devastating effects on marine ecosystems.
Hauri et al. [2024] use hindcasts from a regional ocean biogeochemical model to assess the occurrence and causes of extreme and compound extreme events in the Gulf of Alaska. Their analysis show that marine heat waves exacerbate the stressors imposed by climate change and that these compound extreme events are becoming more frequent and intense in the Gulf of Alaska, with important consequences for the regional ecosystem.
Citation: Hauri, C., Pagès, R., Hedstrom, K., Doney, S. C., Dupont, S., Ferriss, B., & Stuecker, M. F. (2024). More than marine heatwaves: A new regime of heat, acidity, and low oxygen compound extreme events in the Gulf of Alaska. AGU Advances, 5, e2023AV001039. https://doi.org/10.1029/2023AV001039
—Eileen Hofmann, Editor, AGU Advances