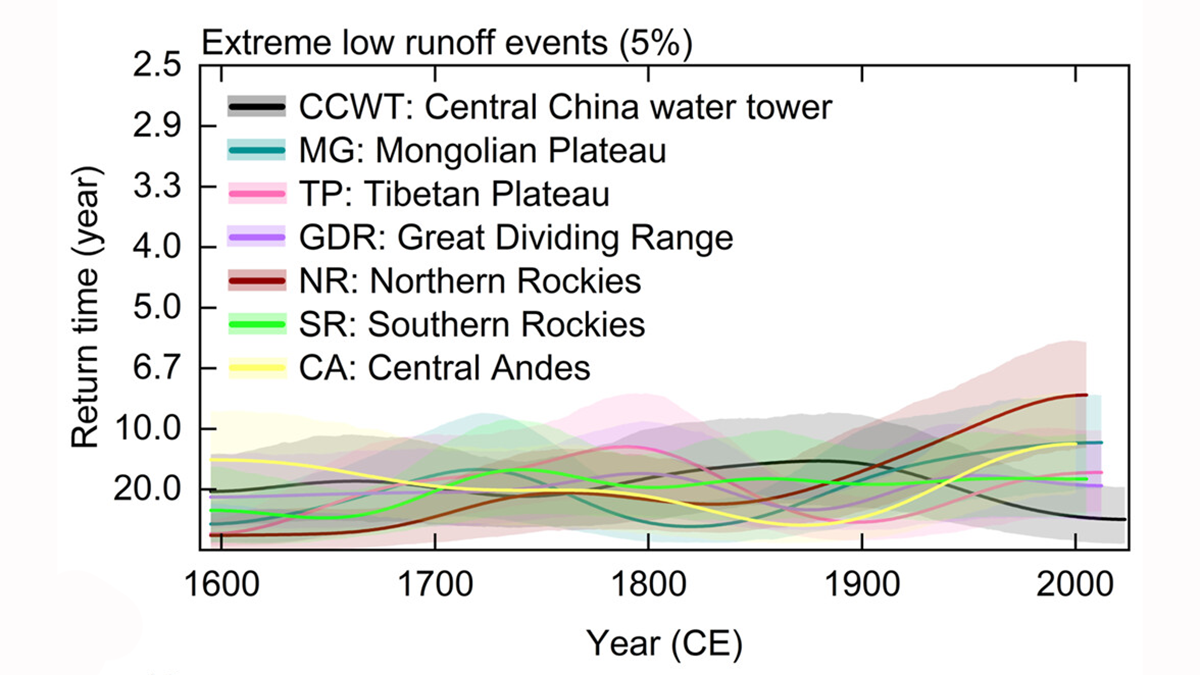
A new reconstruction of river runoff from 1595 shows that Central China water towers deliver the most stable water supply from the high mountain ranges of the Pacific Rim.
Editors’ Highlights
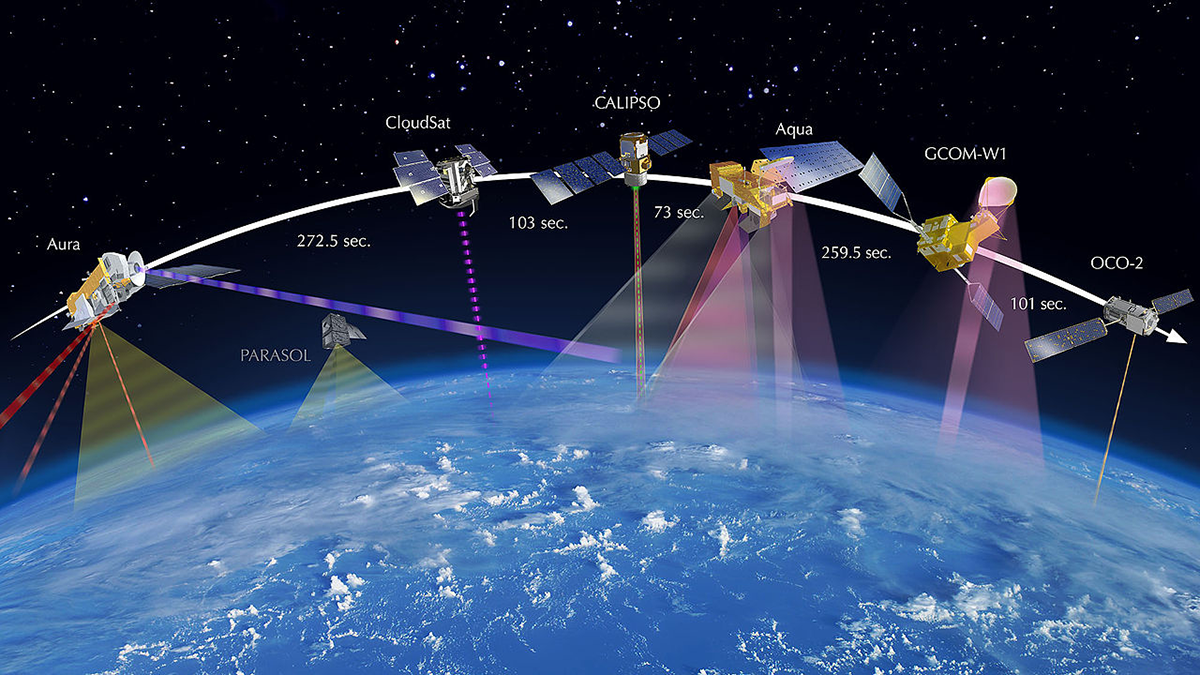
Managing Carbon Stocks Requires an Integrated View of the Carbon Cycle
The carbon cycle community calls for an integrated carbon observing system leveraging near-surface partial-column data to better resolve finer spatial scales where key processes and decisions occur.
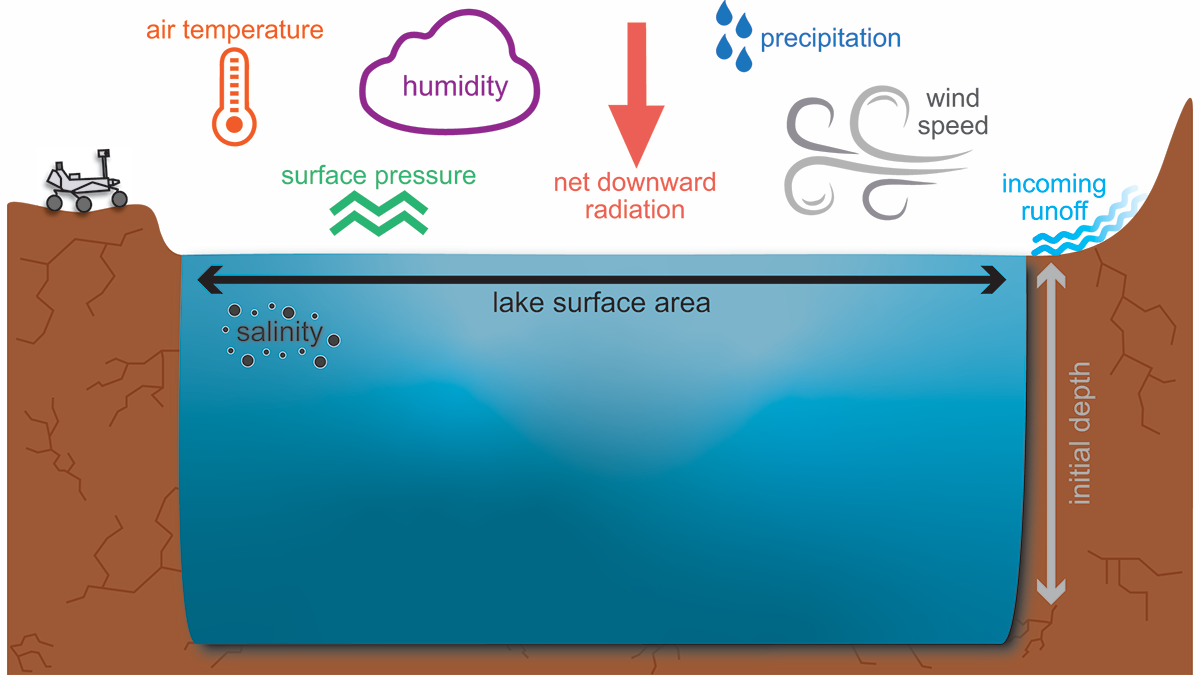
Successful Liquid Lake Conditions in a Cold Martian Paleoclimate
Simulations from a new lake model explain how liquid water could have been maintained over Mars in a cold climate, thus resolving a critical scientific gap in our understanding of Mars’ early history.
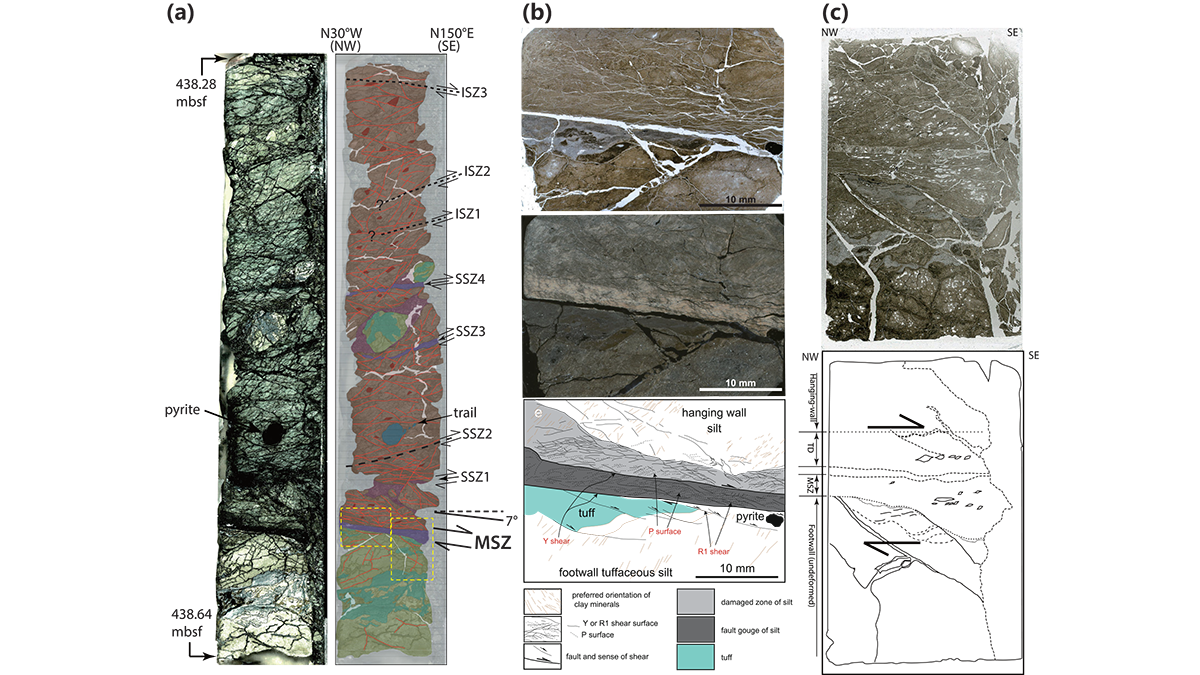
Frictional Properties of the Nankai Accretionary Prism
A database of frictional properties from IODP drilling materials explores the range of slip spectrum and the generation of slow to fast earthquakes in the Nankai subduction zone in light of mineralogy.
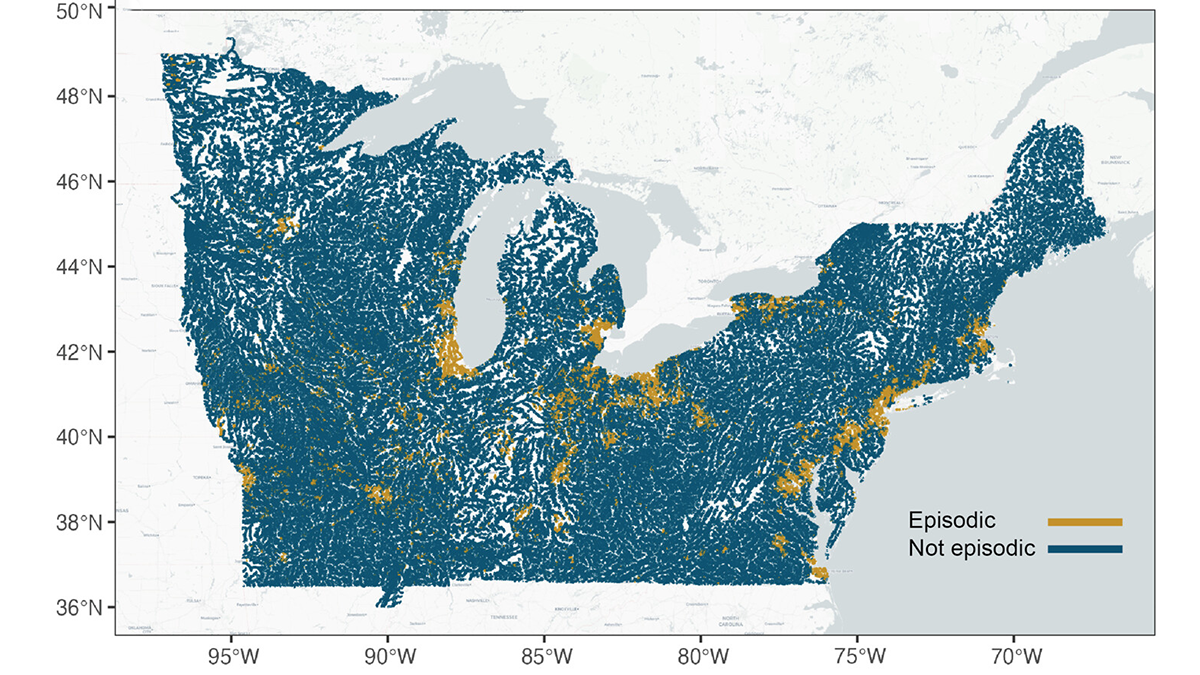
Episodic Tales of Salt
When episodic pulses of road salt hit after a winter storm, the impact can be like a lightning strike for the environment.
Is Convection Wobbling Venus?
Venus’s rotation axis is not where it should be – but atmospheric torques, not mantle convection, are likely responsible.
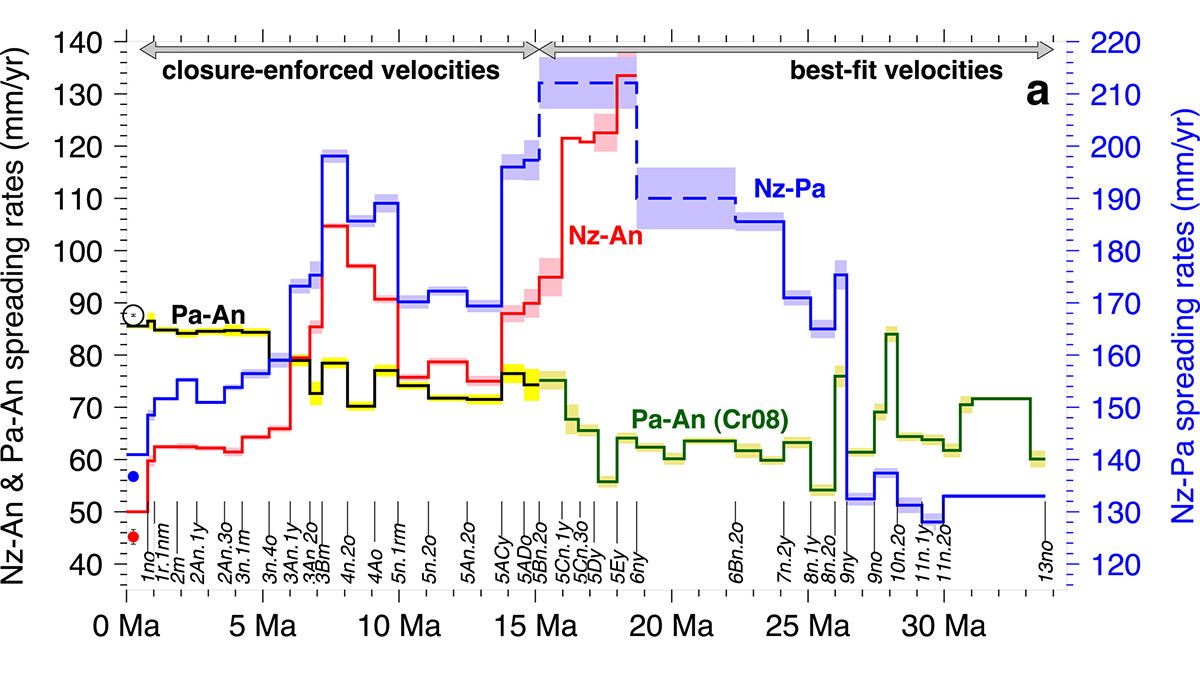
Changes in Slab Dip Cause Rapid Changes in Plate Motion
Periods of slab shallowing in the South American subduction zone appear to cause decelerations in Nazca plate motion.
Using Lightning-Induced Precipitation to Estimate Electron Belt Decay Times
A long-term study of MeV electron burst events detected in the inner radiation belt and slot region was used to determine the electron belt decay times.
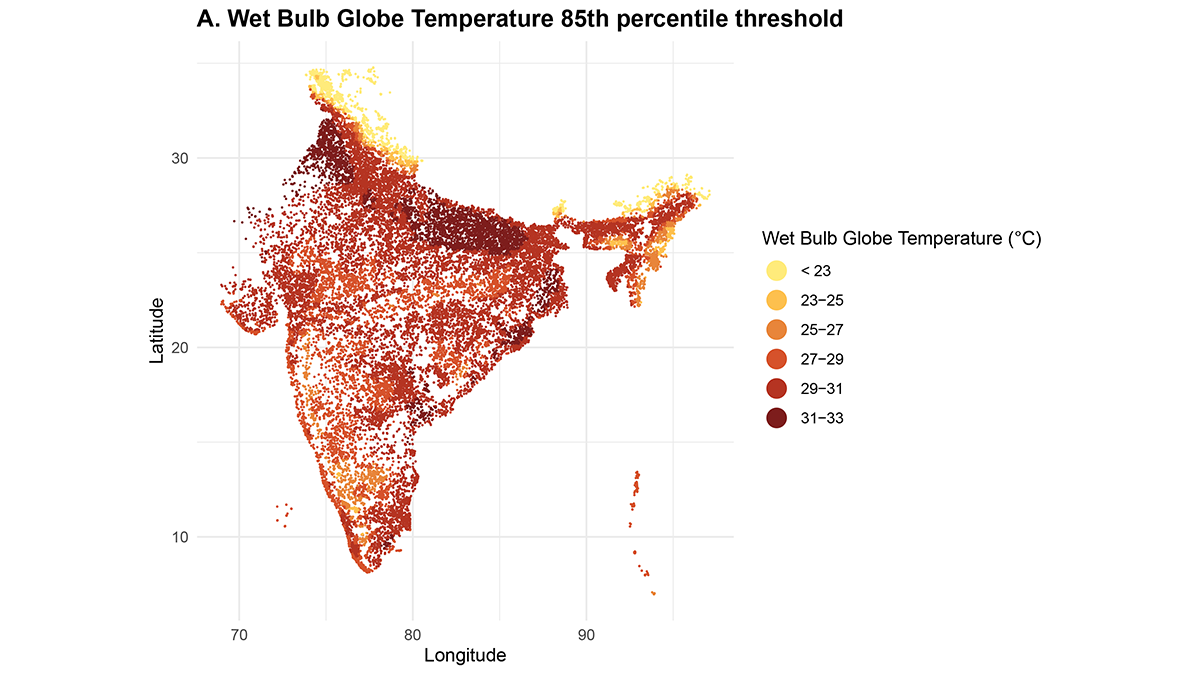
Heatwaves Increase Home Births in India
Heatwaves in India are associated with increased home births, with differential susceptibilities across regions and populations, threatening maternal and newborn health.
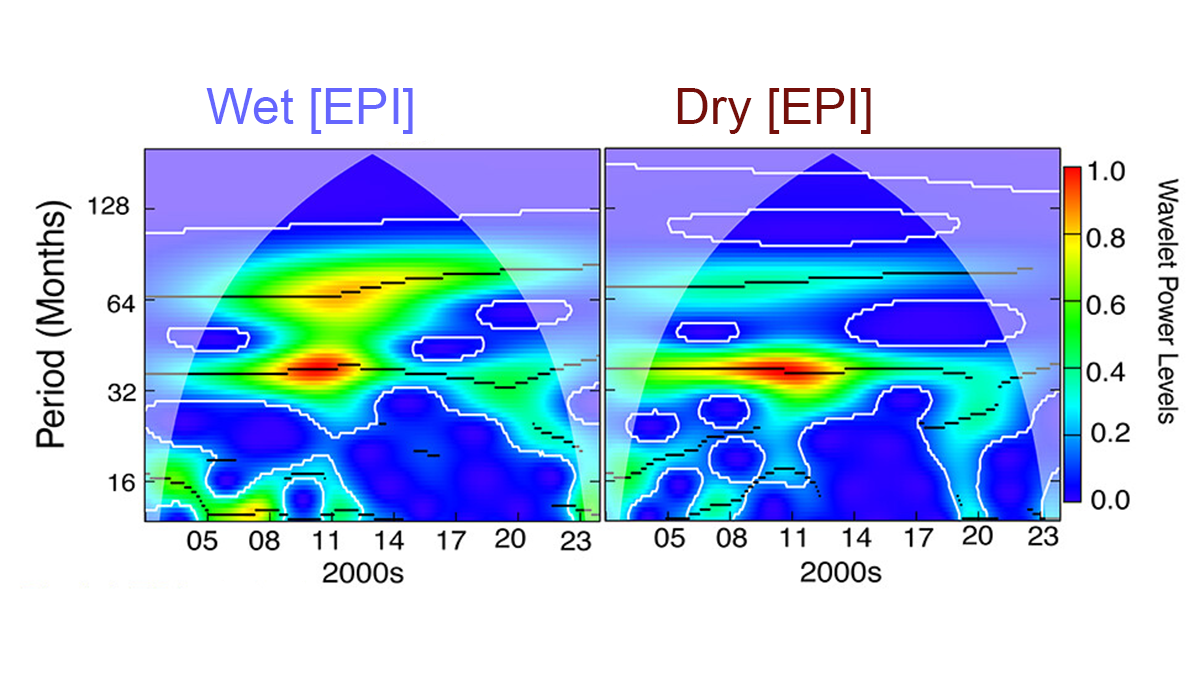
Climate Variations in Tropical Oceans Drive Primarily Extreme Events
Severe droughts and floods are primarily driven by climate variations in tropical oceans, with interannual and decadal patterns playing key roles.