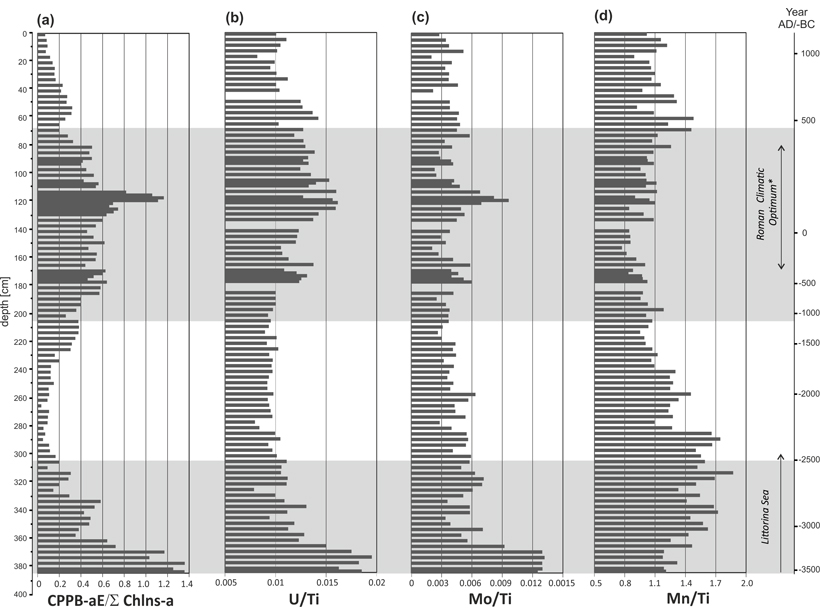
Eutrophication not only is a present-day anthropogenic phenomenon in the southern Baltic but also occurred over the past few millennia, with cyanobacterial blooms during times of climate warming.
Editors’ Highlights
Real Time Probing of Shale Cracks in Double Torsion Experiments
Imaging crack propagation in shales using twin optical cameras and fast X-ray radiograph acquisition.
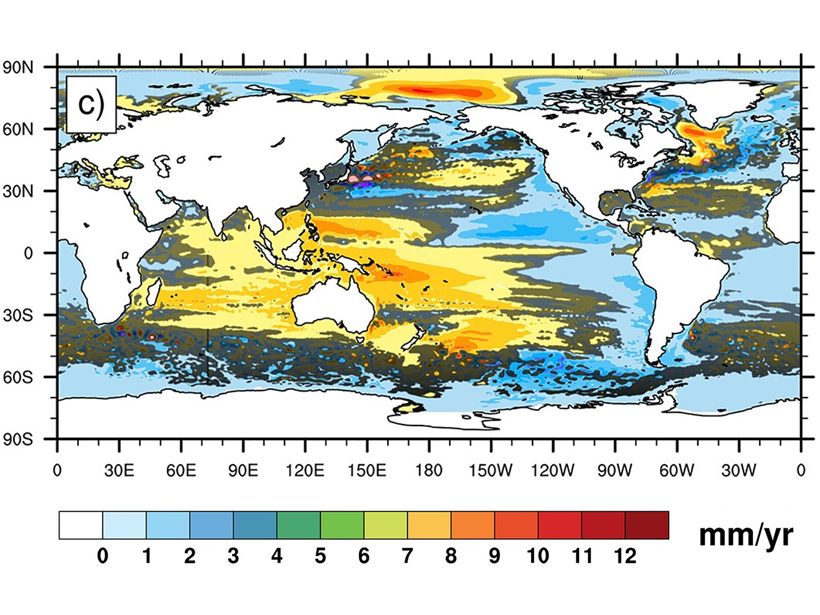
An Inherently Noisy Ocean Can Disguise Regional Sea Level Trends
Sea level trends in different regions of the ocean caused by both natural and man-made changes in the atmosphere can be partially hidden by internal random processes intrinsic to the ocean.
Capturing the Dynamism of Plant Roots in Models
Simulating the dynamic nature of plant root profiles in Earth system models improves the representation of the carbon and water cycles.
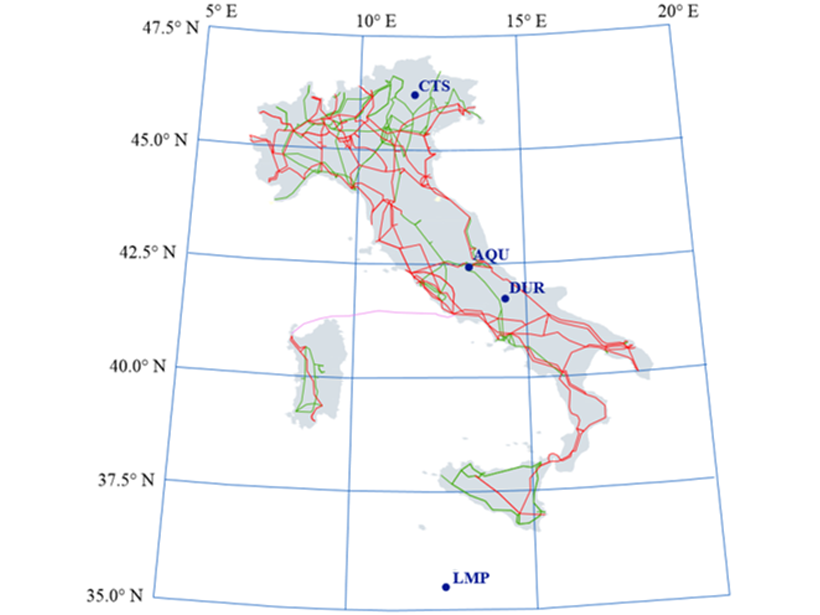
A Space Weather Threat in the Mediterranean Region?
The impact of space weather on power grids in Mediterranean countries, such as Italy, needs deeper assessment, including consideration of coastal effects, ground conductivity, and failure reports.
Thermal Signature of Martian River Deposits Suggests Cementation
Are there indications of extended aqueous processes beyond the period of widespread fluvial activity on Mars?
Radionuclide Data from GEOTRACES Improve Particle Flux Estimates
New measurements of multiple radionuclides in the Atlantic Ocean offer a robust constraint on the sinking flux of particles and associated vertical fluxes of biogeochemically important elements.
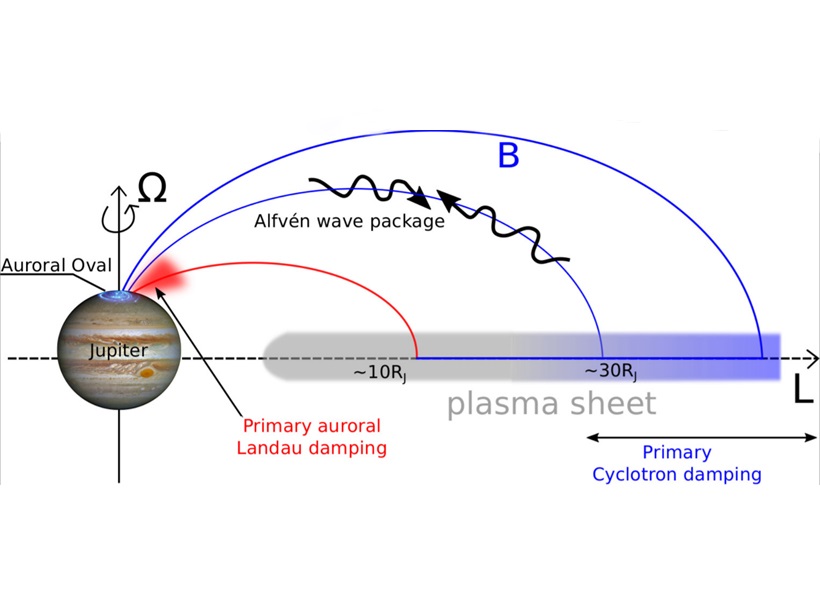
Jupiter’s Stressed Out Magnetosphere Causes Aurora and Heating
Force imbalance between Jupiter’s ionosphere and magnetosphere leads to wave generation to release this stress, but the waves also accelerate particles, causing aurora and heating.
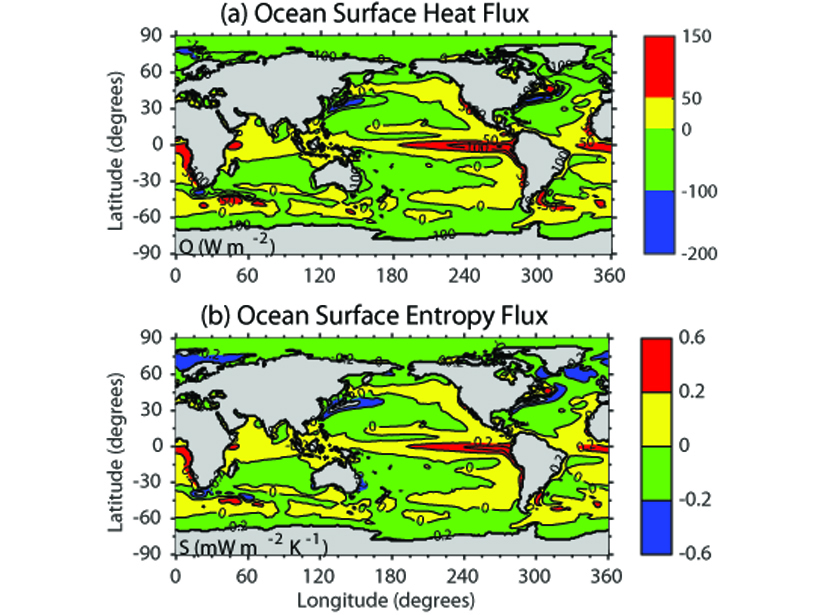
A Comprehensive Estimate on the Entropy Budget in the Ocean
An analysis of the energy budget in the ocean estimates the Carnot work to be 110 terawatts and the ocean’s Carnot efficiency to be 0.86%.
First Multi-Decade Simulation of the Earth’s Radiation Belt
A new simulation of the Earth’s electron radiation belts captures large-scale variations over nearly three solar cycles, and replicates primary cyclical features and extreme behaviors.