A study directly comparing waterways of different sizes revealed important differences in nitrogen dynamics across seasons.
Research Spotlights
Research spotlights are plain-language summaries of recent articles published in AGU’s suite of 24 journals.
Marine Snow Grows Faster and Fluffier as It Sinks
New observations highlight how abiotic and biotic processes influence the tiny oceanic particles.
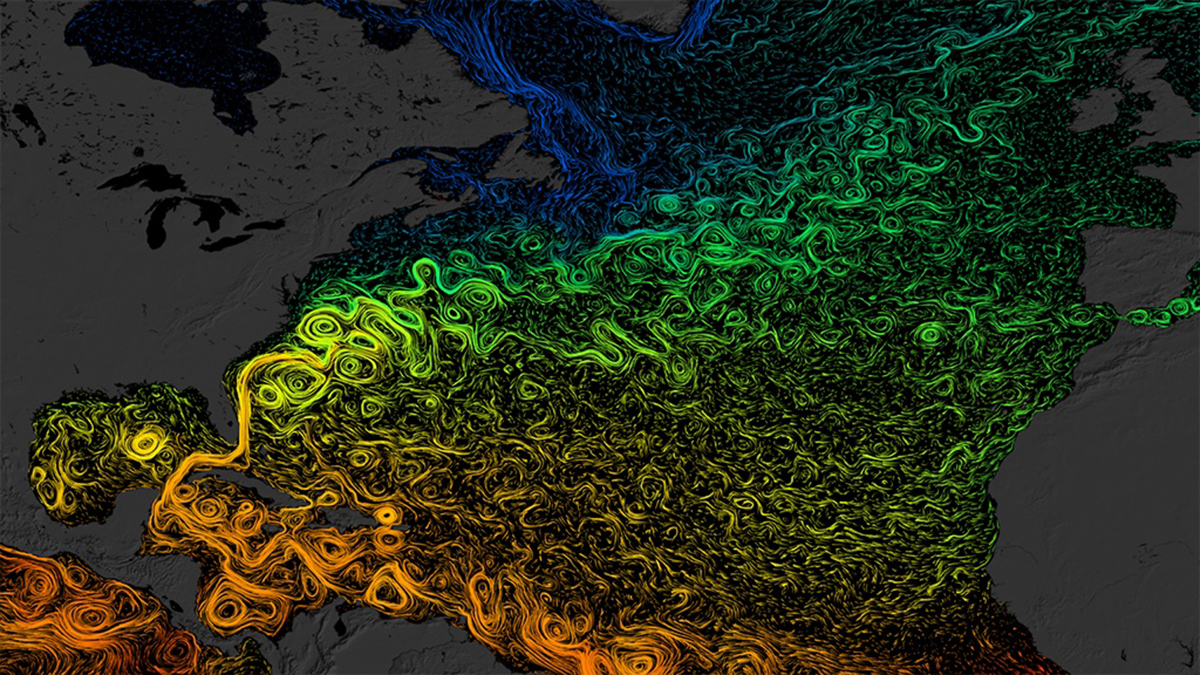
AI Sheds Light on Hard-to-Study Ocean Currents
The Maluku Strait is a key predictor of conditions in the Indonesian Throughflow, modeling shows.
Melting Glaciers Mix Up Waters More Than We Thought
Existing theory underestimates the mixing of freshwater and seawater by up to 50%.
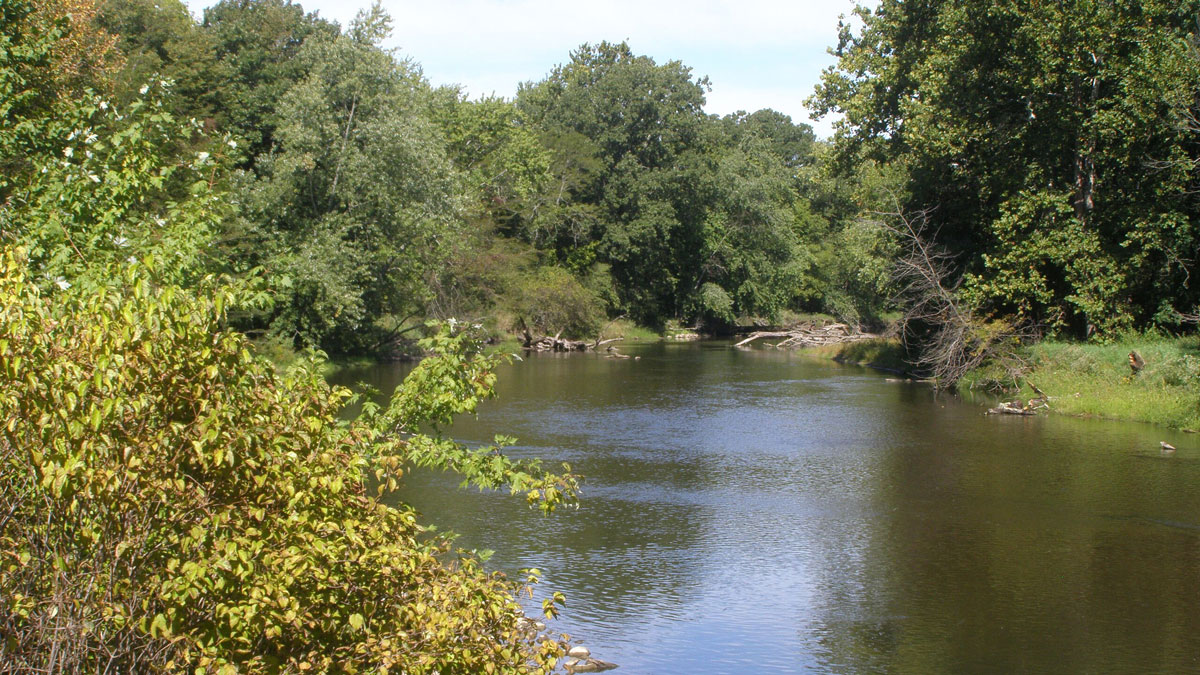
Microbial Genes Could Improve Our Understanding of Water Pollution
New research in Germany’s Ammer floodplain examines microbial biomarkers to help improve modeling of denitrification.
New River Chemistry Insights May Boost Coastal Ocean Modeling
By more realistically accounting for river inputs, researchers reduced overestimation of the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by coastal waters.
Temperatures Are Rising, but What About Humidity?
Humid heat extremes are less frequently studied, but no less important, than those of dry heat.
What Could Happen to the Ocean’s Carbon If AMOC Collapses
Mass glacier melting may have led this influential ocean current system to collapse at the end of the last ice age. A pair of modeling studies examines how such a collapse could affect dissolved inorganic carbon and carbon isotopes in Earth’s oceans.
How a Move to the Shallows 300,000 Years Ago Drove a Phytoplankton Bloom
And what that could mean for today’s ocean.
Marine Heat Waves Can Exacerbate Heat and Humidity over Land
Researchers found the unprecedented 2023 East Asian marine heat wave increased land temperatures and humidity by up to 50%.