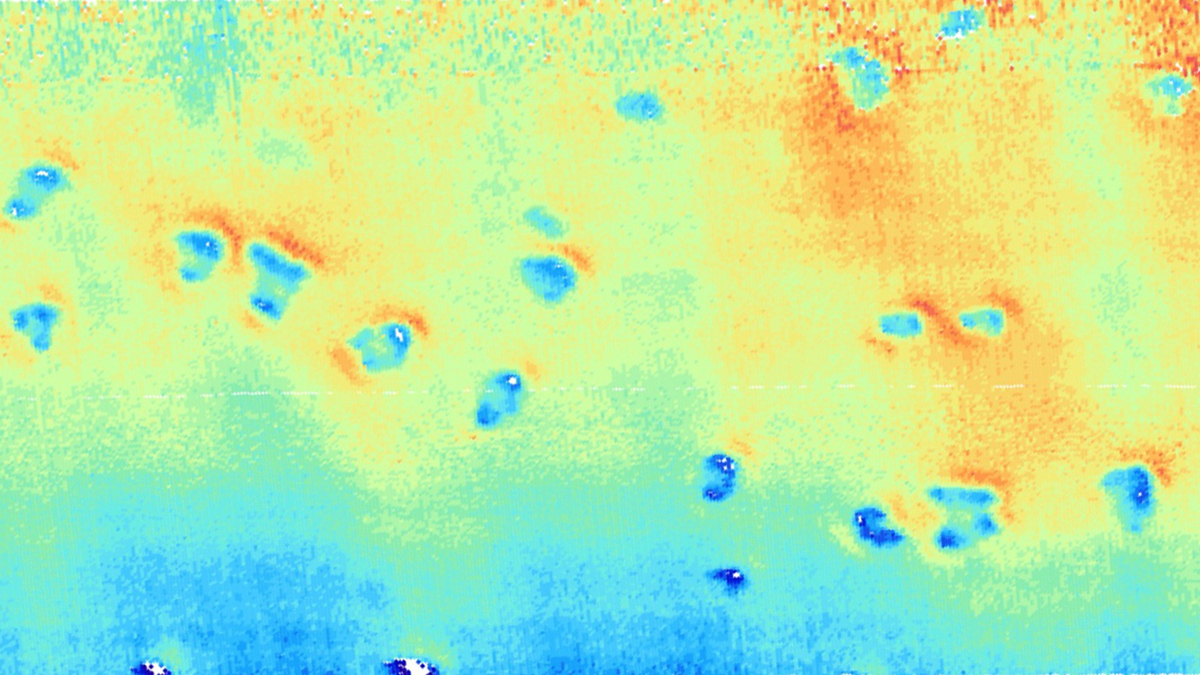
Some shallow seafloor depressions off the coast of Germany that look like those associated with methane might instead be the work of porpoises.
ENGAGE
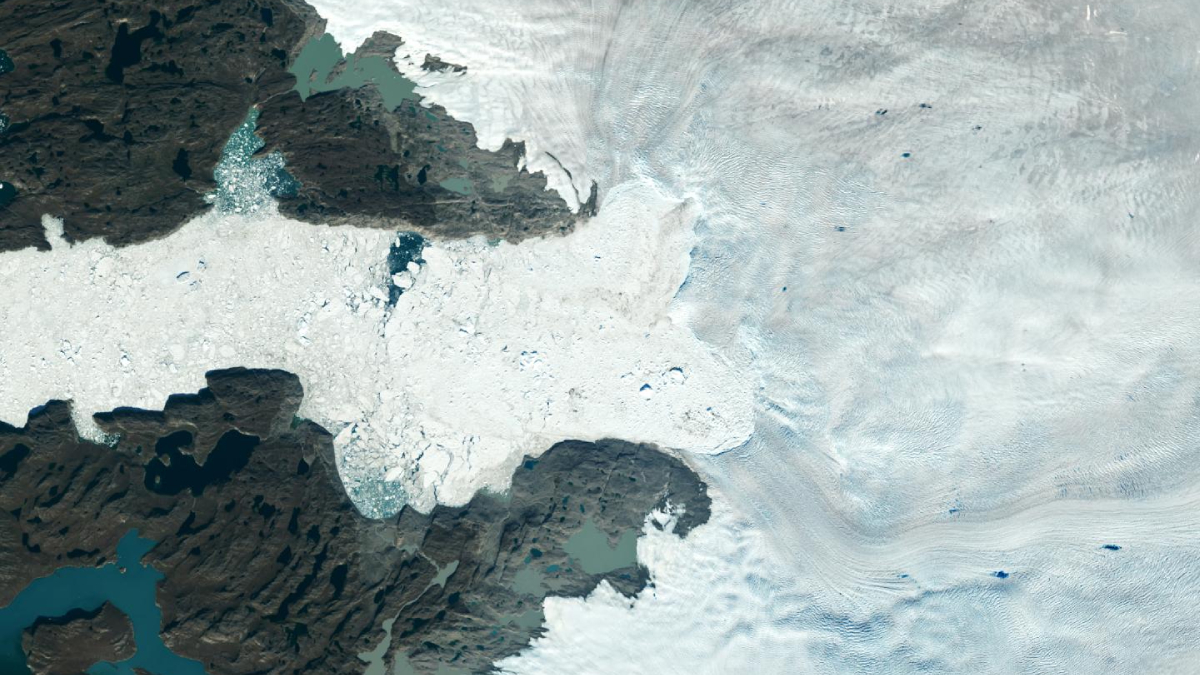
How Did We Miss 20% of Greenland’s Ice Loss?
The ice loss was hidden in places existing monitoring methods can’t reach, such as hard-to-map fjords. Machine learning helped scientist revise mass loss estimates and uncover patterns in glacial retreat.
Amateur Astronomer Finds a Possible Crater on Io
The most volcanically active body in the solar system may have an impact crater, a discovery spotted by a curious nonprofessional scientist.
Ocean Warming Is Wiping Out Southern California’s Mussel Beds
Historic photographs reveal the dramatic retreat of mollusks as warmer waters take a toll on the health of the intertidal zone.
Microbe Goo Could Help Guide the Search for Life on Mars
Sticky substances secreted by microbes may help create landforms on Earth. And new research shows that these substances are more preserved in iron-rich sediment. Mars is decidedly iron-rich (it’s the Red Planet, after all), so the new study adds to evidence that microbe goo could help researchers explain landform creation there. “I think this is […]
El estallido de burbujas acelera el deshielo de los glaciares
Tener en cuenta el efecto burbuja podría mejorar las estimaciones sobre el deshielo de los glaciares submarinos y prever mejor su contracción a medida que se calientan los océanos.
Future Supercontinent Will Be Inhospitable for Mammals
Pangea returns in 250 million years, and it’s not looking good for us.
Five Martian Mysteries That Have Scientists Scratching Their Heads
Despite centuries of study and many spacecraft visits, the Red Planet still holds secrets. Here are just a few.
Millions Likely Live in Areas Contaminated by Mining Runoff
Heavy metal contaminants from mining can live in ecosystems for centuries. A new global database shows where the problem is worst.
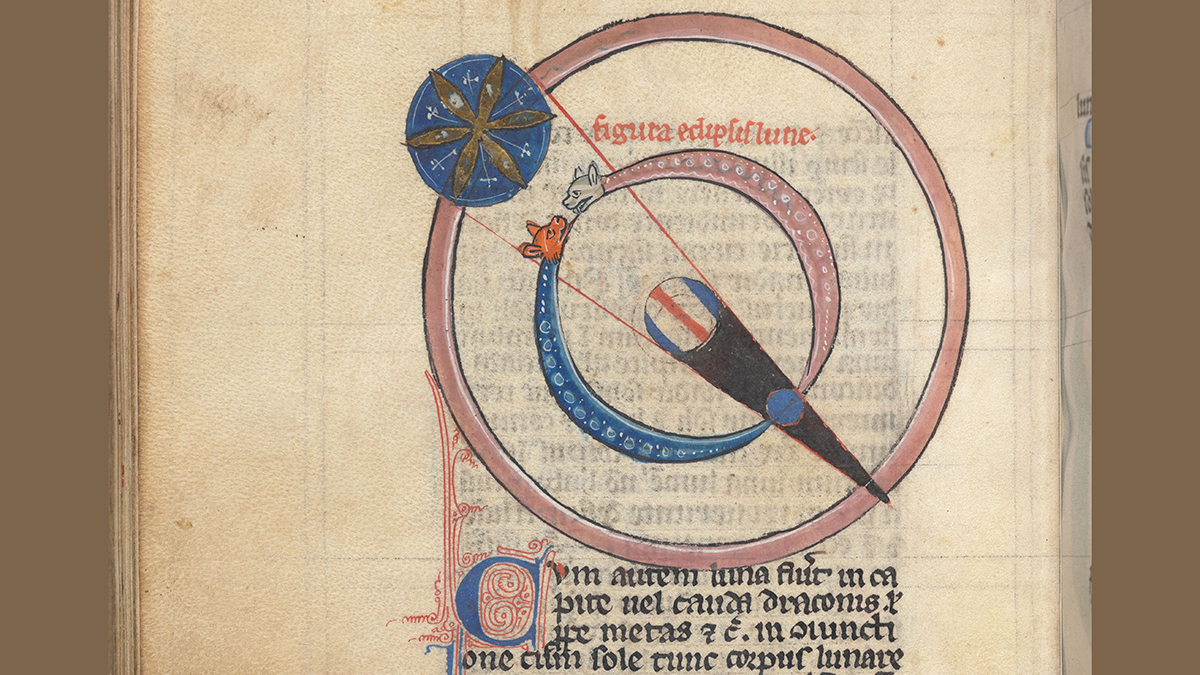
Registros de eclipses fechan erupciones volcánicas de los siglos XII y XIII
Registros antiguos de lunas oscuras y lunas de sangre ayudan a los científicos a vislumbrar erupciones pasadas y sus efectos en el clima global.