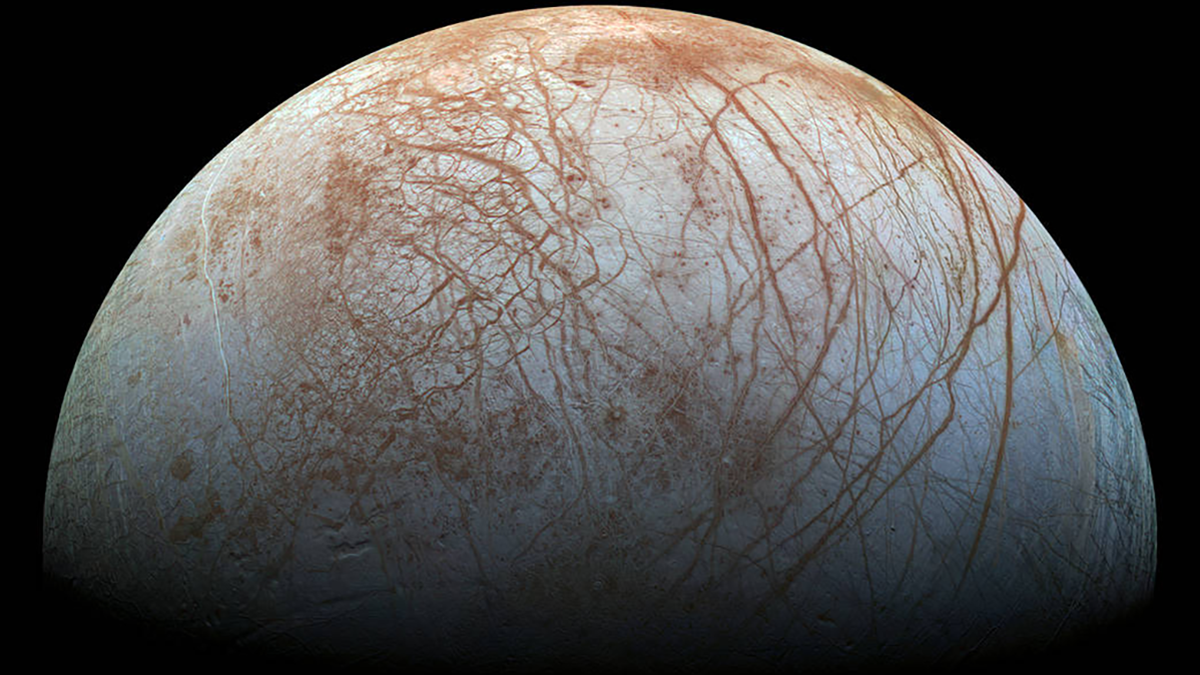
A model using currents in the deep ocean to drive rotation of Europa’s ice shell from below can explain why its surface may drift despite being tidally locked.
AGU Advances
New Theory Explains Radiative Cooling of the Lower Atmosphere
The shape of radiative cooling in lower atmosphere is controlled by the lapse rate in the water vapor path according to a new theory and observations from subsidence regimes in the tropical Atlantic.
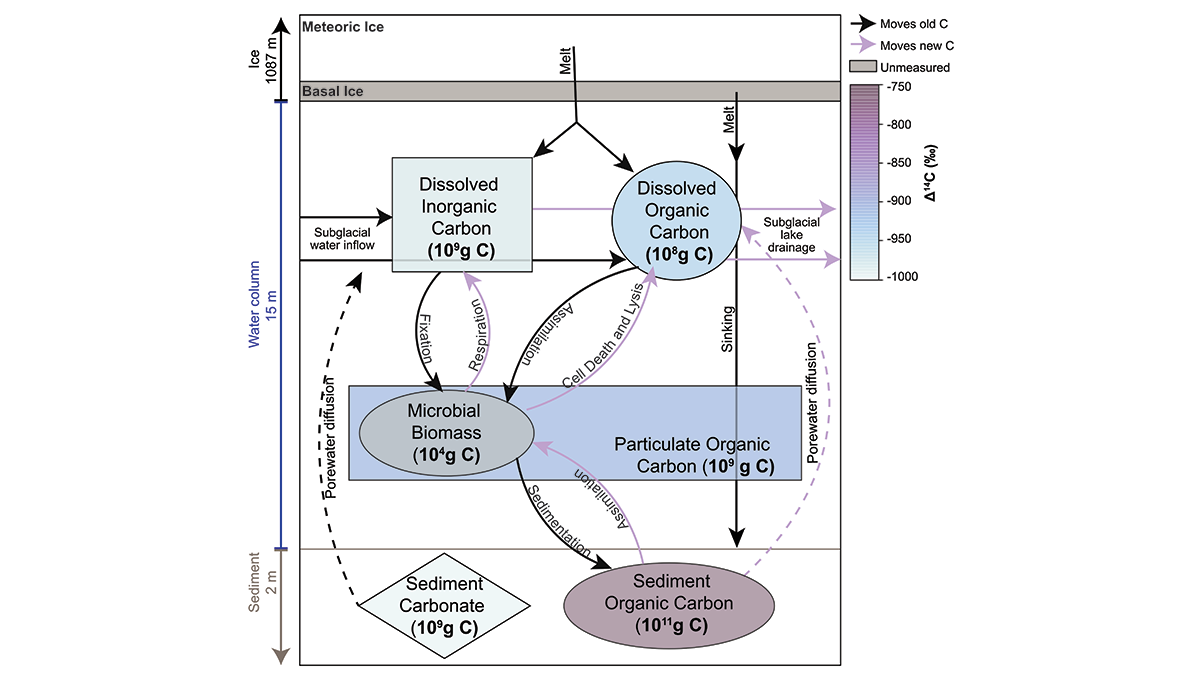
Clues from a Subglacial Lake for Holocene Grounding Line Change
Organic carbon sampled in the lake contained radiocarbon, indicating connection to the ocean in the mid-Holocene, when the grounding line was up to 260 kilometers inland of its current position.
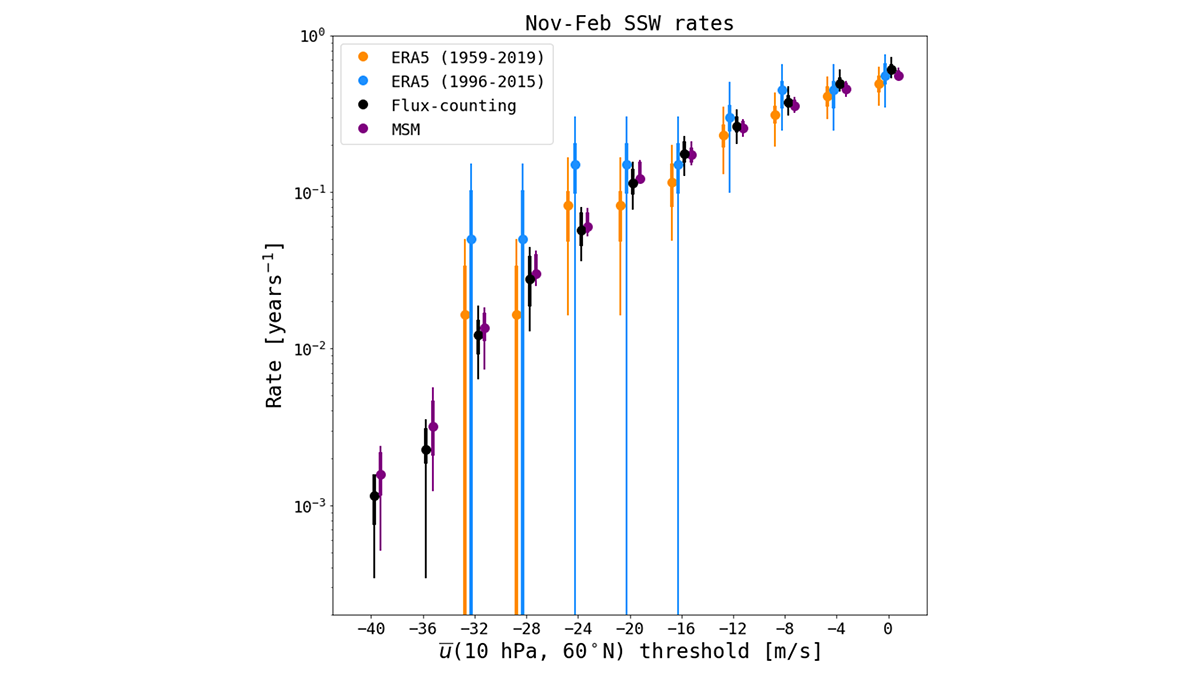
Quantifying Extreme Events from Short Weather Forecast Data
Subseasonal weather forecast ensembles are a useful tool for overcoming the inherent difficulty of quantifying extreme weather risk caused by data scarcity.
The Depleted Mantle Merry-Go-Round
Abyssal peridotites show through their isotopic composition a complex history. From differences we can infer the existence of ultra depleted mantle and an uneven contribution to ridge magmatism.
A Deeper Dive into Wintry, Carbon-Absorbing Antarctic Waters
Cold surface water in the Southern Ocean is a critical component in ocean carbon uptake. A new study profiles it using state-of-the-art research techniques.
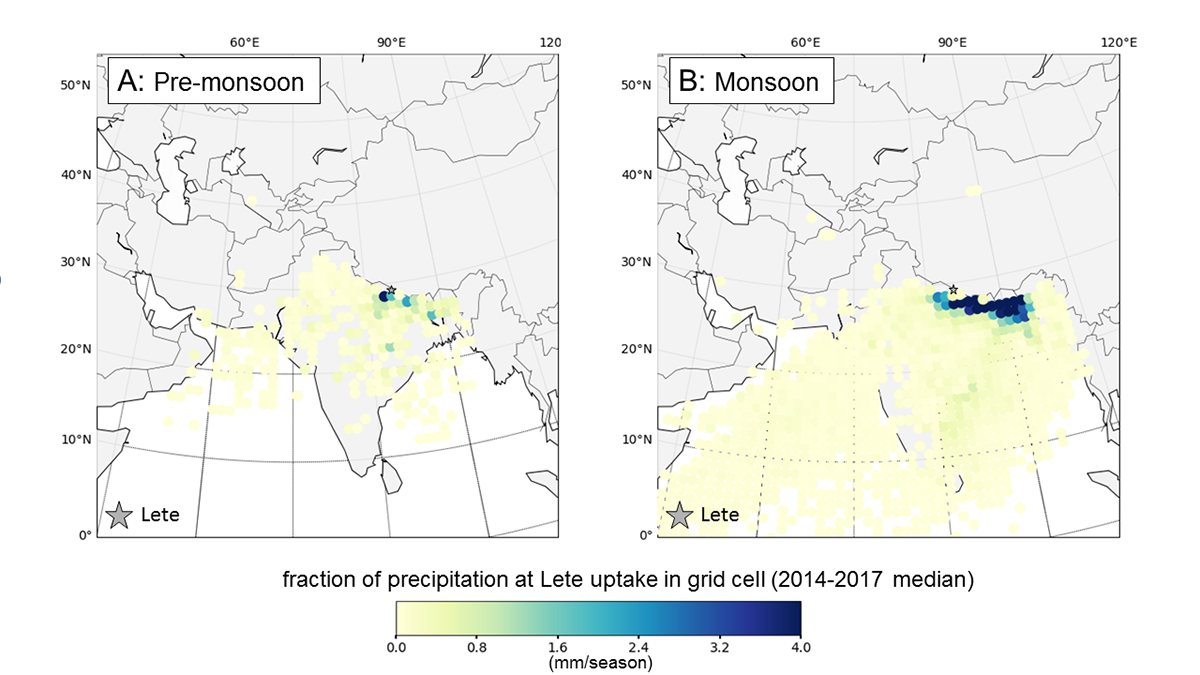
Source of Precipitation Moisture Feeding Himalayan Rivers
Isotope study showing the partitioning of moisture into snow, ice, and groundwater allows an understanding of the relative contribution to river flow to show where Himalayan river water comes from.
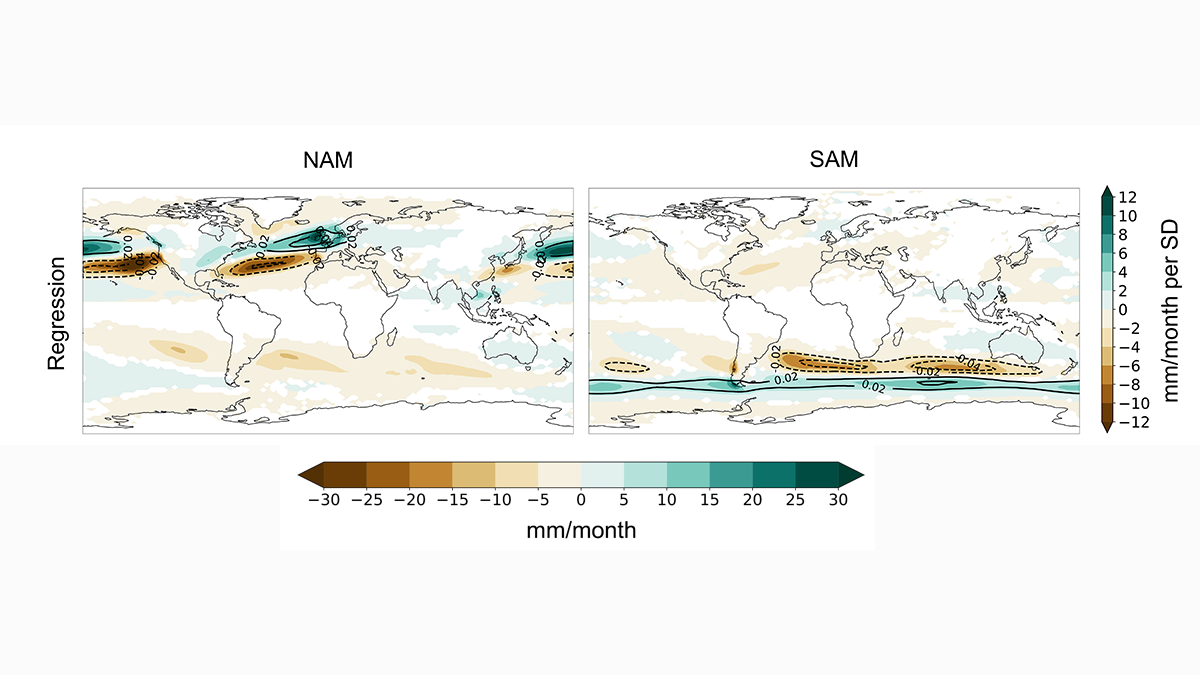
How Do Atmospheric Rivers Respond to Extratropical Variability?
Atmospheric river variability over the last millennium is primarily driven by north-south displacements in zonal winds induced by the annular modes.
How Can We Sample More Ethically?
Ryan-Davis and Scalice describe a path towards sampling more ethically, going beyond legal permitting requirements to engagement of Indigenous expertise and respect of peoples’ relationship to place.
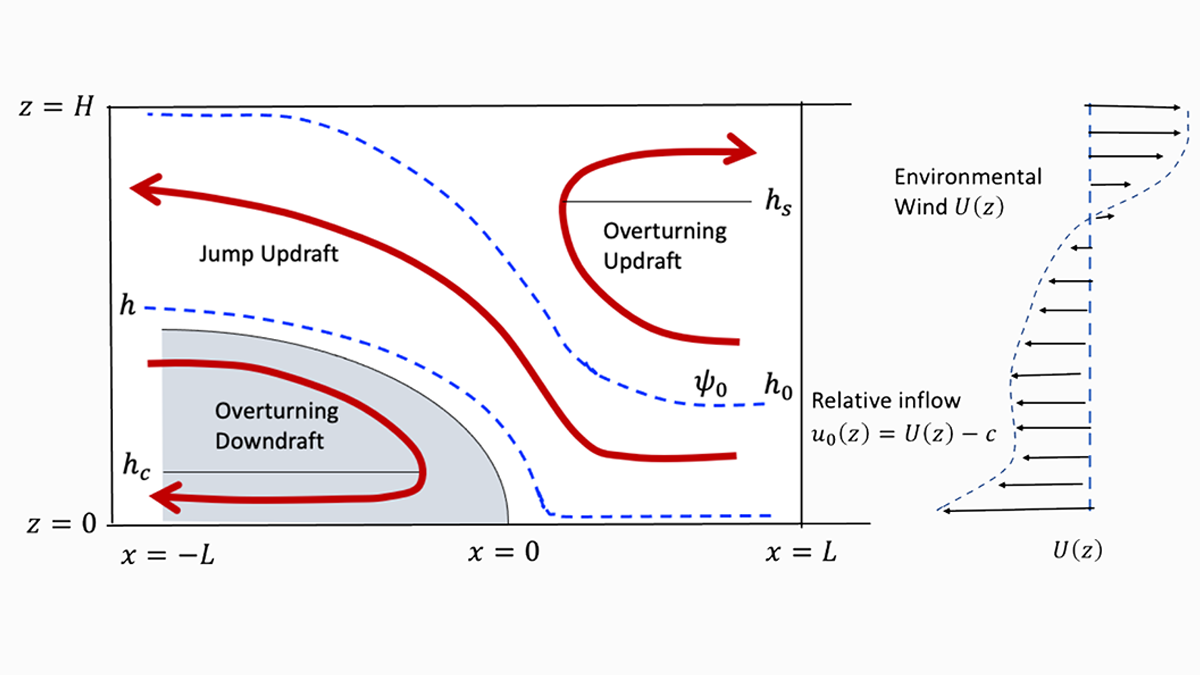
A Theory of Squall Lines
About 50 years ago, vorticity thinking helped unveil basic properties of squall lines. Zhang now provides a closed theory, demystifying one of nature’s most important forms of convective organization.