Editors’ Highlights are summaries of recent papers by AGU’s journal editors.
Source: AGU Advances
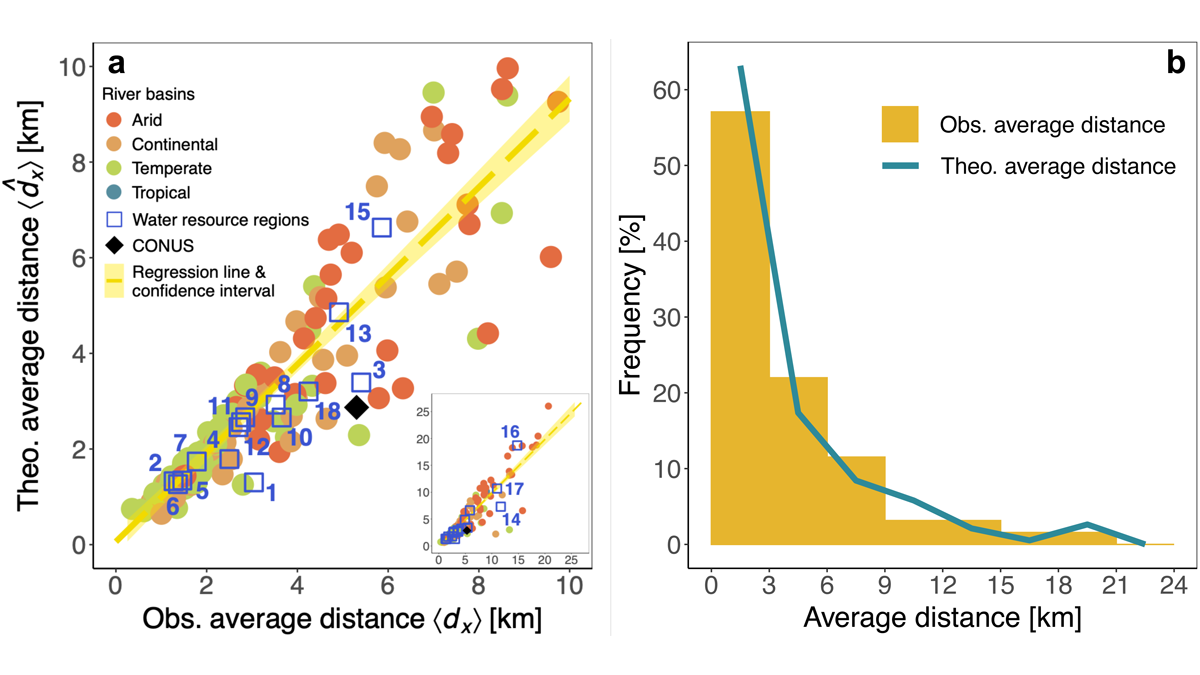
The impact of urbanization on surface water loss is expected due to the increase in built and manipulated surfaces as well as roads and other infrastructure, thus changing the spatial distribution of infiltration and recharge, evapotranspiration, and runoff production, and hydrologic connectivity. Palazzoli et al. [2021]processed surface water extent from existing remote sensing data and quantified the changes between 1984 and 2018. They successfully fitted an exponential distance-decay model for USGS Water Resource Regions and for urbanized basins. The model parameters exhibit sensitivity to climate, with more widespread spatial surface water loss in continental and arid climates. These models can be used in regional planning to quantify the distance over which urbanization will impact surface water availability for people and for ecosystems.
Citation: Palazzoli, I., Montanari, A. & Ceola, S. [2021]. Influence of Urban Areas on Surface Water Loss in the Contiguous United States. AGU Advances, 2, e2021AV000519. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021AV000519
—Ana P. Barros, Editor, AGU Advances