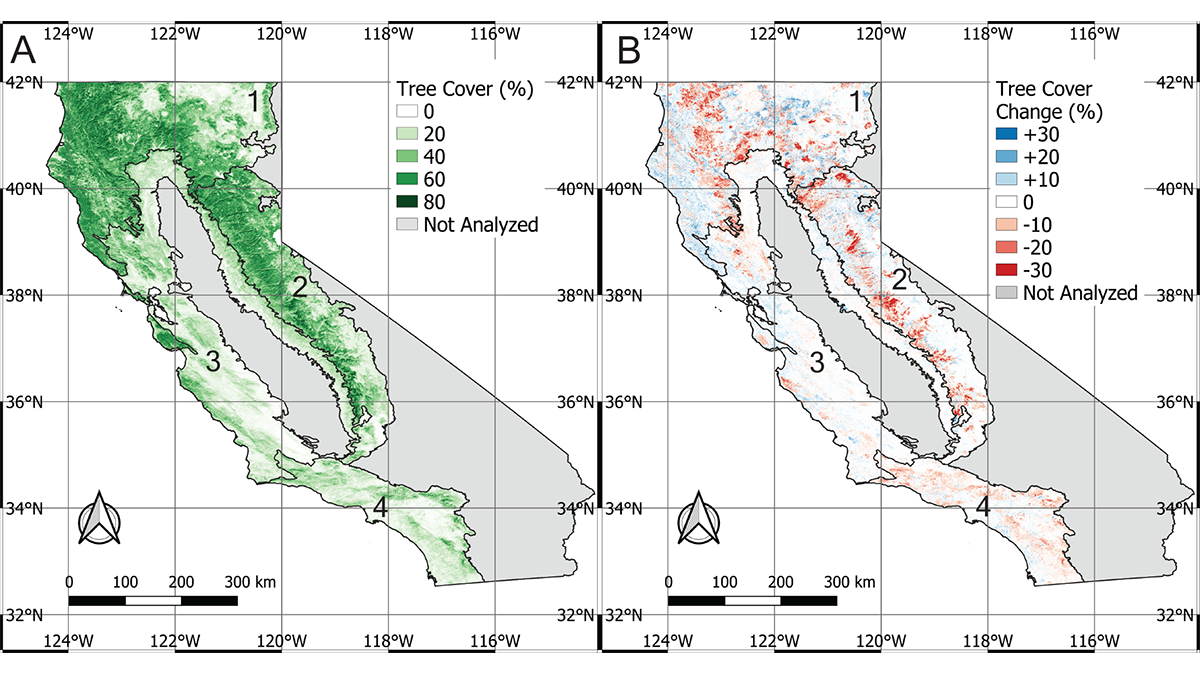
California has lost 7% of its forest cover to climate change over the past 25 years.
AGU Advances
Ceres: Missing Craters, Crust Thickness Variation by Interior Convection
Models show that several puzzling features about Ceres’ topography, gravity anomalies, and crater size distribution may be explained by asymmetric hemispherical convection due to radiogenic heating.
Zircons and Plate Tectonics
New data on ancient zircons points to a transition from stagnant lid to subduction style tectonics at 3.6 Ga ago.
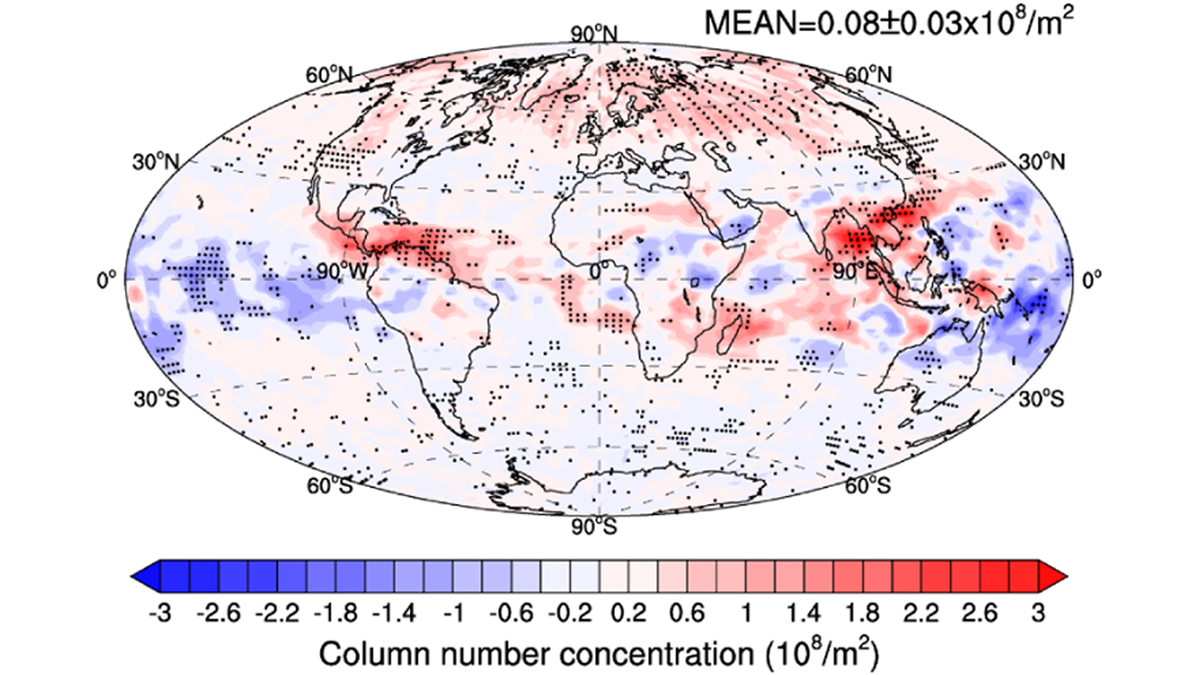
Less Air Travel May Partially Contribute to Global Warming
Decrease in aircraft soot emission, as shown by COVID-19 lockdown, leads to a significant increase in ice crystal number in cirrus clouds, and results in a small global positive radiative effect.
Ice Begets Ice in the Clouds of the Southern Ocean
Poorly understood ice multiplication processes, not aerosols, may determine the microphysical properties of climatologically important clouds over the Southern Ocean.
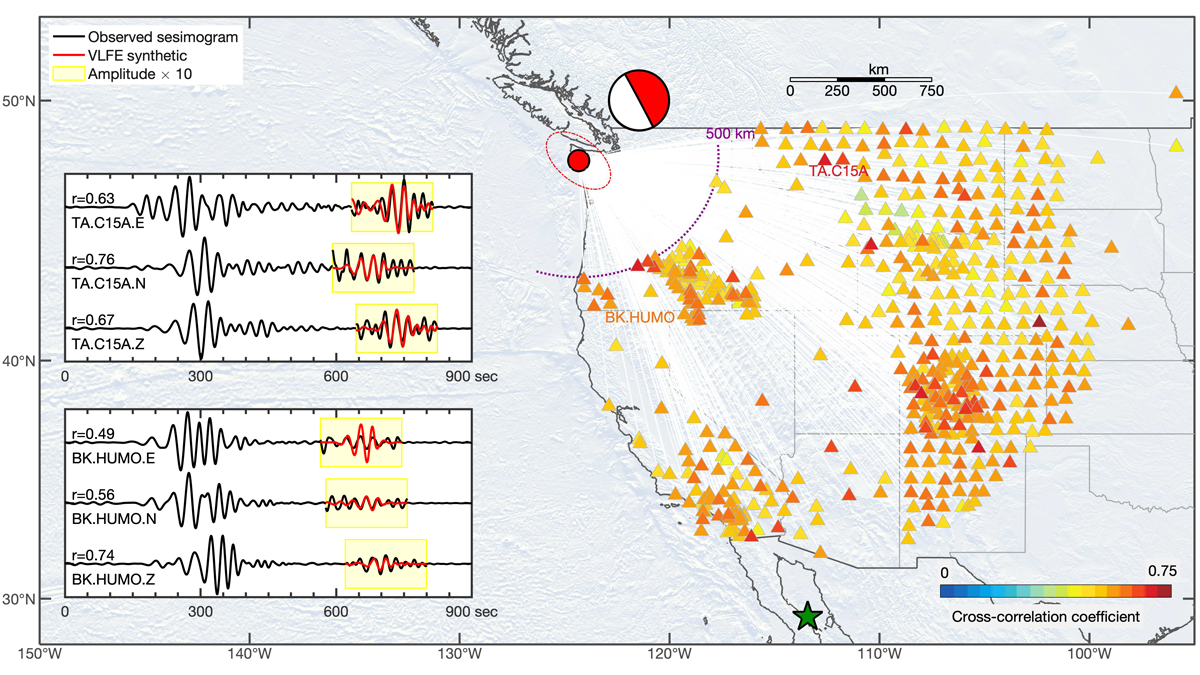
Continent-Scale Detection of Triggered Low Frequency Earthquakes
Very low frequency events in the gap zone of Cascadia illustrate how stress evolves on megathrusts, advancing our understanding of rupture dynamics.
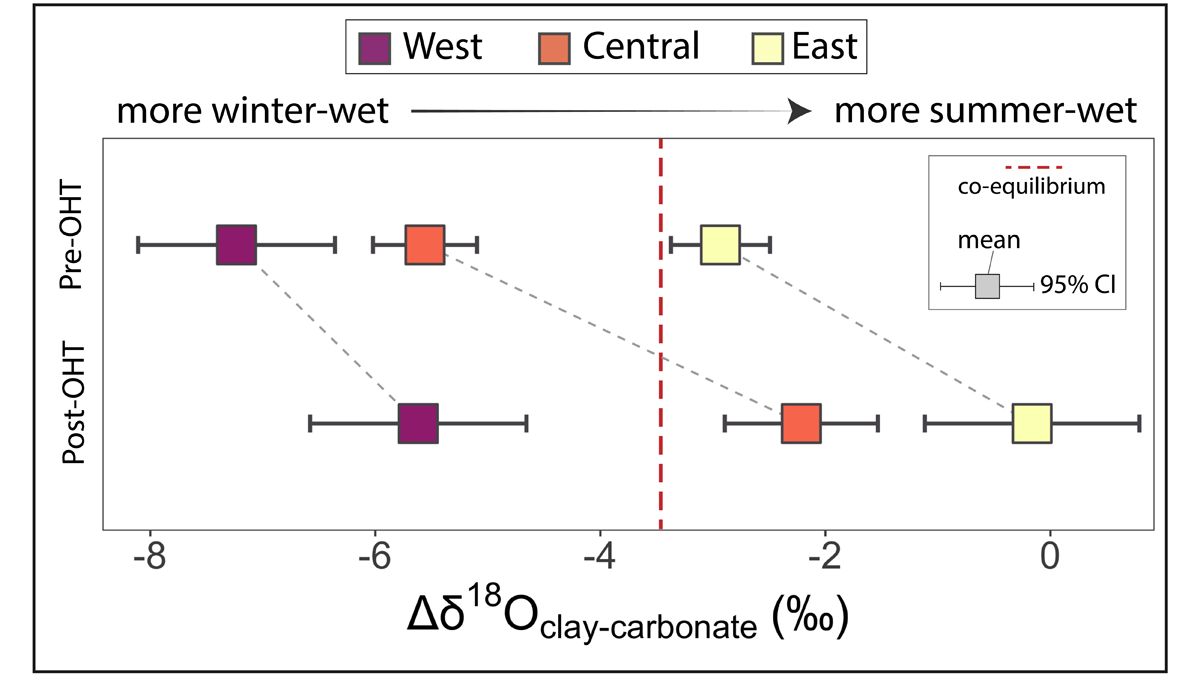
What Caused the Open Habitat Transition in the West-Central U.S.?
Between 26-15 My ago, forests covering west-central North America gave way to open, grassy habitats. Now, oxygen isotope records suggest this shift is owed to drier winters and increased aridity.
Air Pollution Was Reduced During the COVID-19 Pandemic
A decrease in emissions of ozone precursor gases during the COVID-19 economic downturn likely explains the unusual reduction in ozone concentrations observed during the spring and summer of 2020.
Reef-Building Corals at Risk from Ocean Warming, Acidification
Physiological limitations on regulating internal chemistry restricts corals’ ability to deal with ocean acidification and warming, thereby reducing resilience to continued environmental change.
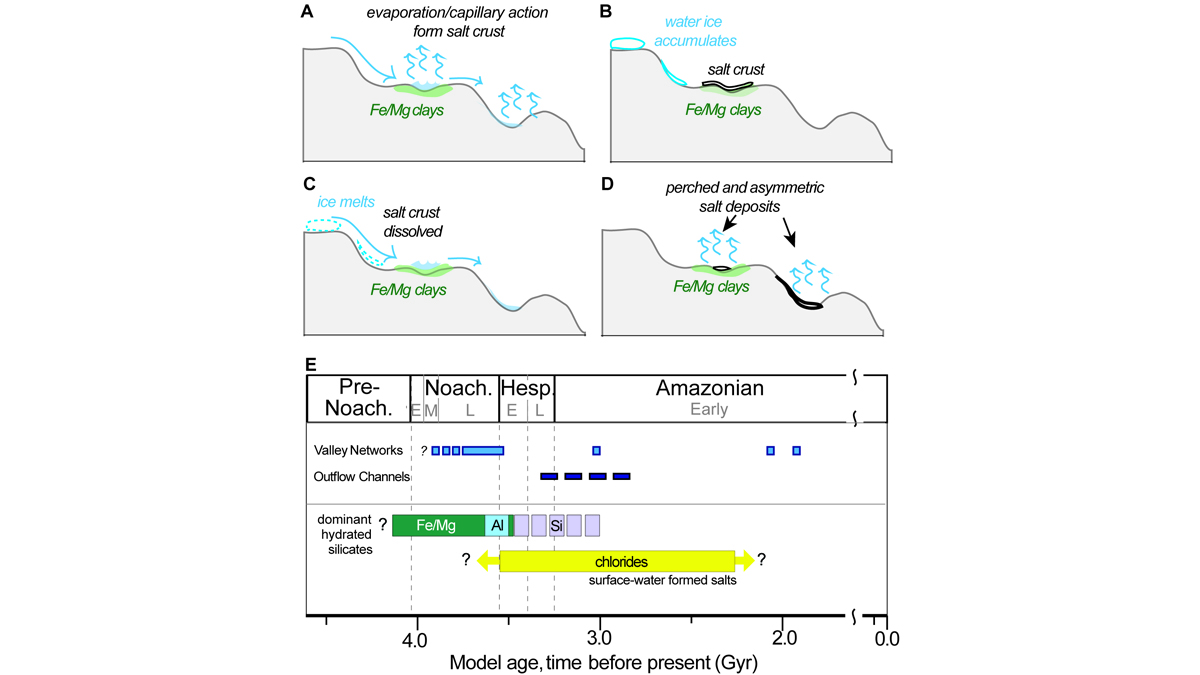
Young Ponds on Mars
A detailed study of evaporite (chloride) deposits on Mars shows that small bodies of surface water persisted until about 2.5 Ga, more recently than previously thought.