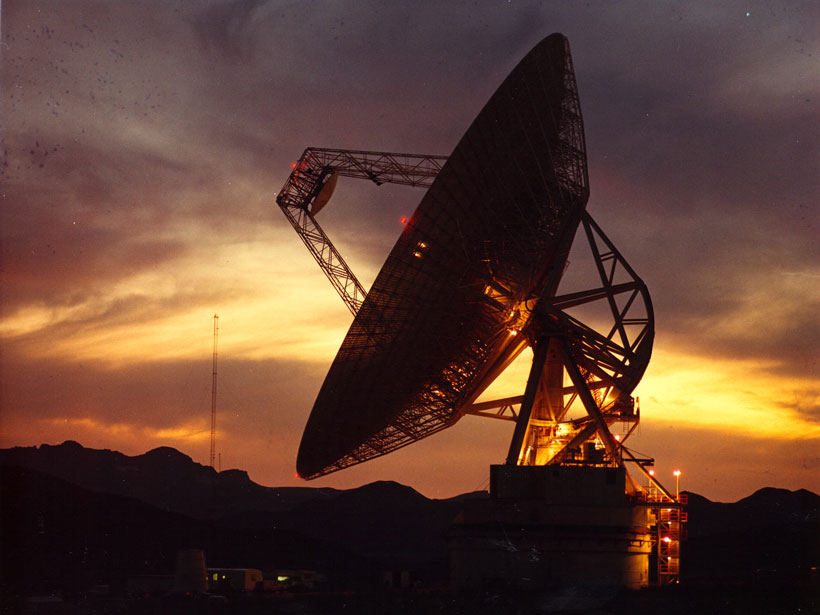
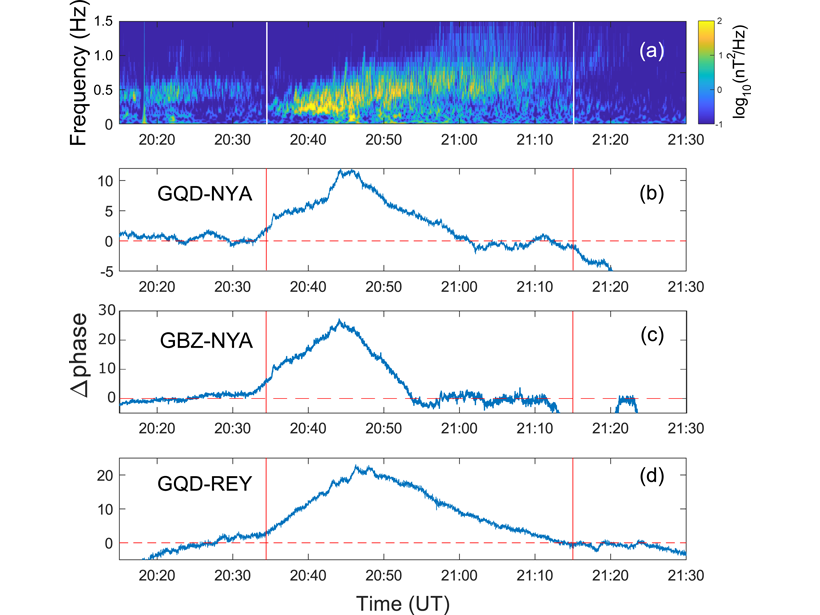
An international armada of orbiting satellites and ground VLF network join forces to form a “magnetosphere-ionosphere observatory” to size up electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves in the magnetosphere.
astrophysics
Ghostly Particles from the Sun Confirm Nuclear Fusion
Using the Borexino particle detector—located deep underground in Italy—researchers spot elusive neutrinos from the Sun’s CNO cycle.
“Electron Wings” Can Interfere with Spacecraft Measurements
Spacecraft sometimes produce a form of electrical self-interference as they zip through plasmas in space—a previously unreported effect that may be lurking in old data sets.
More Than Just Astronomy: Radio Telescopes for Geophysics
Linking an existing network of radio telescopes with satellite radar would make it possible to measure ground displacements in a globally consistent way, scientists propose.
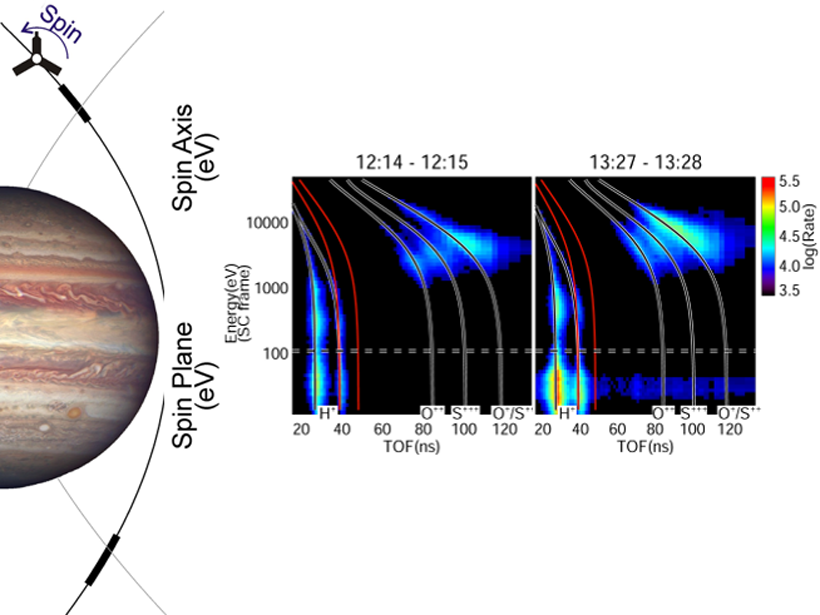
First Inside Look at Hot and Cold Ions in Jupiter’s Ionosphere
The first in-situ ion observations from NASA’s Juno spacecraft reveal the surprising, simultaneous presence of cold protons and hot oxygen and sulfur ions in the high-latitude ionosphere of Jupiter.
New Proof That Accretion Disks Align with Their Black Holes
In the most detailed and highest-resolution black hole simulation to date, an international team of researchers showed the Bardeen-Petterson effect for the first time.
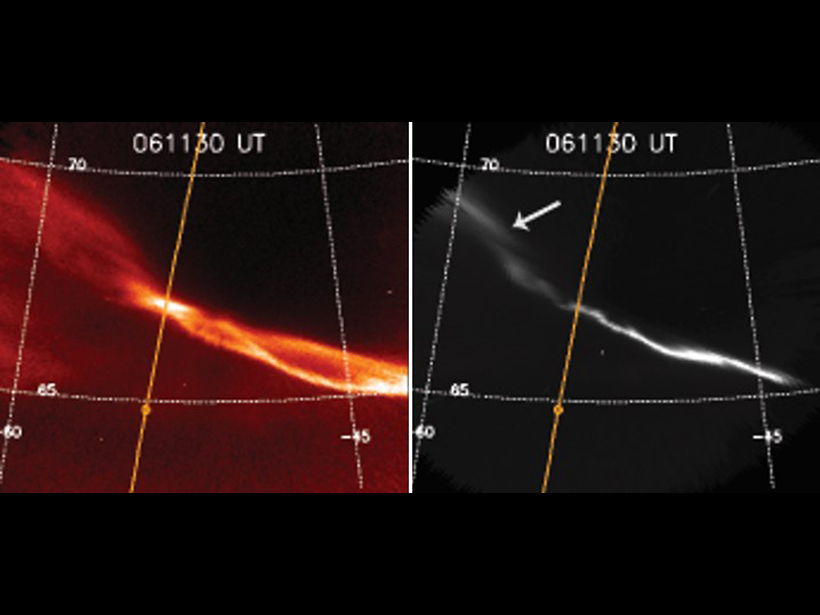
Red and Green Aurora Stop and Go for Different Reasons
Green-line arc is found to be embedded within large-scale upward field aligned currents while red-line-only arc is found to be associated with low-energy precipitation bursts.
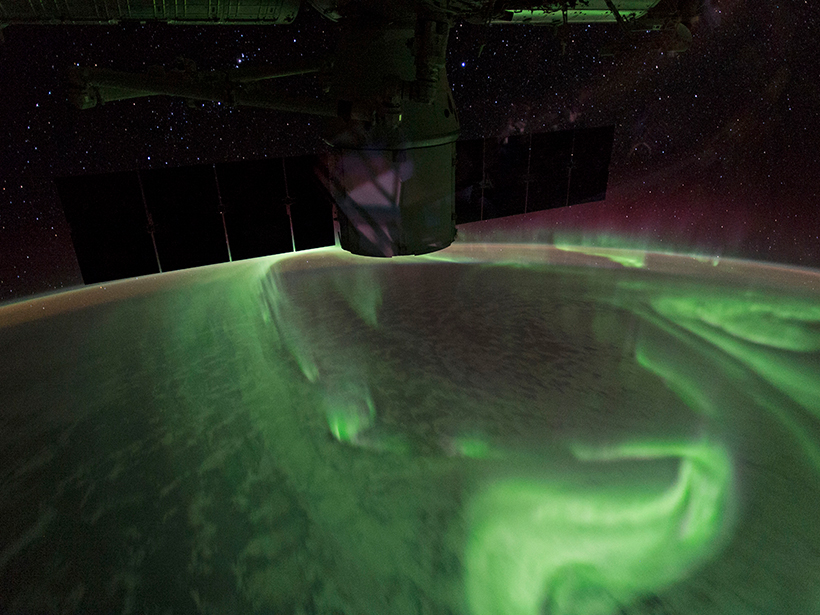
Bringing Clarity to What Drives Auroras
A new classification scheme helps researchers distinguish what accelerates the electrons that create auroras.
Doherty Receives 2018 Space Physics and Aeronomy Richard Carrington Education and Public Outreach (SPARC) Award
Patricia Doherty will receive the 2018 Space Physics and Aeronomy Richard Carrington Education and Public Outreach (SPARC) Award at AGU’s Fall Meeting 2018, to be held 10–14 December in Washington, D. C. The award is given “for significant and outstanding impact on students’ and the public’s understanding of our science through their education and/or outreach activities.”
Energetic Electrons Can Penetrate the Stratosphere
Precipitations of electrons with energies greater than 30 kiloelectron volts from the slot region penetrate at low altitude and can contribute to destroy ozone.