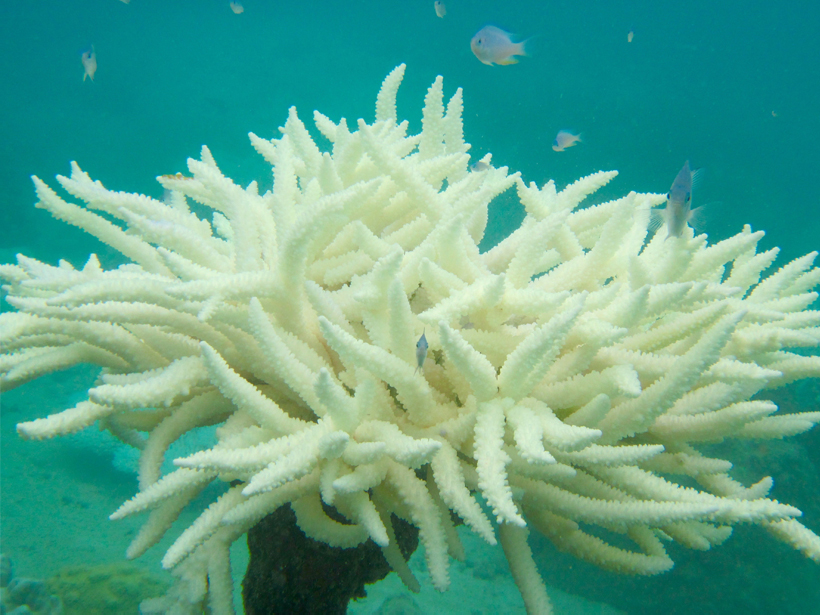
New research indicates that longitude, as well as warming waters, may be a key predictor of coral bleaching events.
biogeosciences
Integrating Landscape Terrestrial and Aquatic Carbon Fluxes
Workshop on the Integration of Aquatic and Terrestrial Carbon Fluxes across landscapes; Montreal, Quebec, Canada, 9–10 May 2019
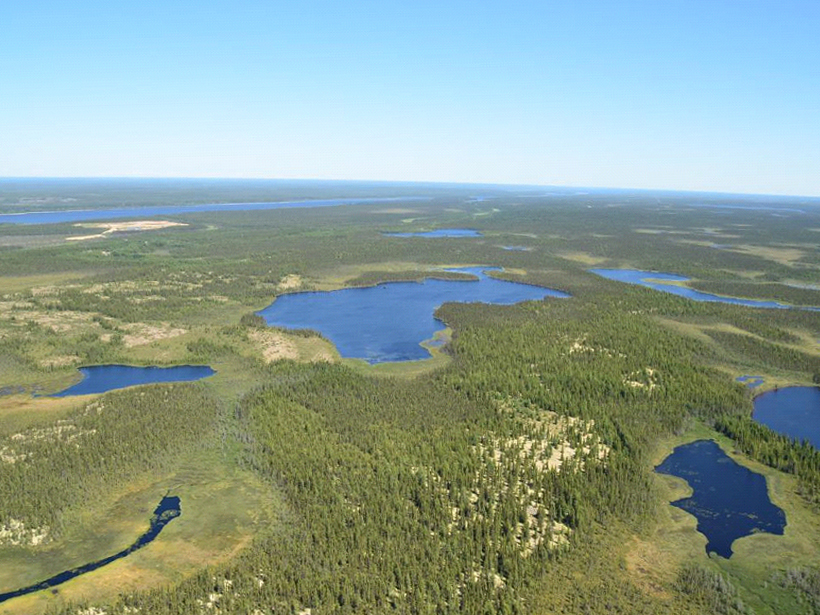
Is the Northern Permafrost Zone a Source or a Sink for Carbon?
Thawing permafrost could release large amounts of carbon into the atmosphere, but finding out how much requires better collection and curation of data.
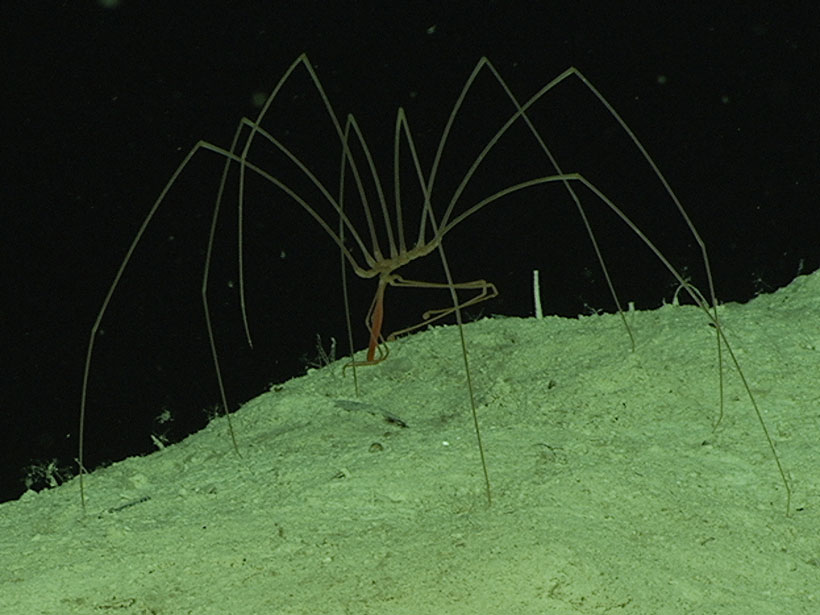
Extreme Life and Where to Find It
Life finds a way in the most extreme environments on Earth and sparks the imagination about far-off places where we may yet find it.
Satellite Data Reveal Growth and Decline of Sargassum
High nutrient levels in 2018 resulted in a nearly 9,000-kilometer belt of Sargassum, a seaweed critical to many marine animals but also a nuisance when it washes up on shorelines, new results reveal.
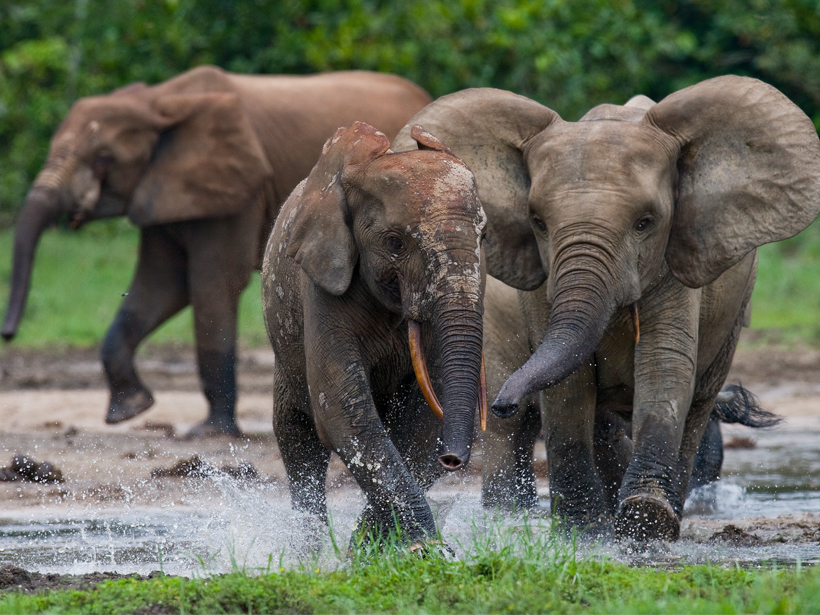
Elephants Boost Carbon Storage in Rain Forests
Forest elephants are the “gardeners of the Congo.” How might their dwindling population affect carbon storage in the world’s second-largest tropical forest?
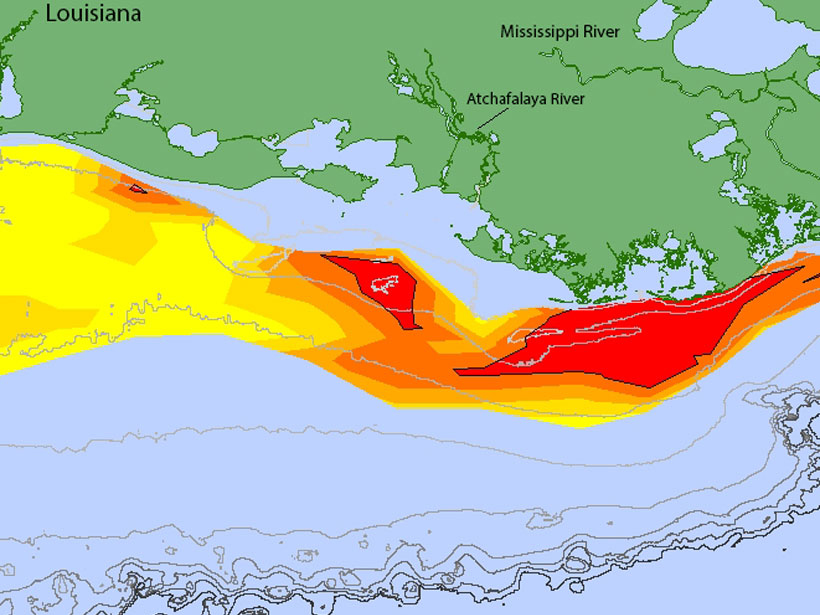
Gulf Dead Zone Looms Large in 2019
A new forecast predicts widespread hypoxia after a wet Midwest spring.
Designing the Global Observing System for Marine Life
Identifying the Backbone of a Global Observing System for Marine Life and Planning Its Implementation for the Next Decade; Santa Barbara, California, 5–7 March 2019
Ecohydrology: What’s in a Name?
Scientists were studying ecohydrology for decades before it became an official ‘ology’. Find out how this field has evolved over the past century.
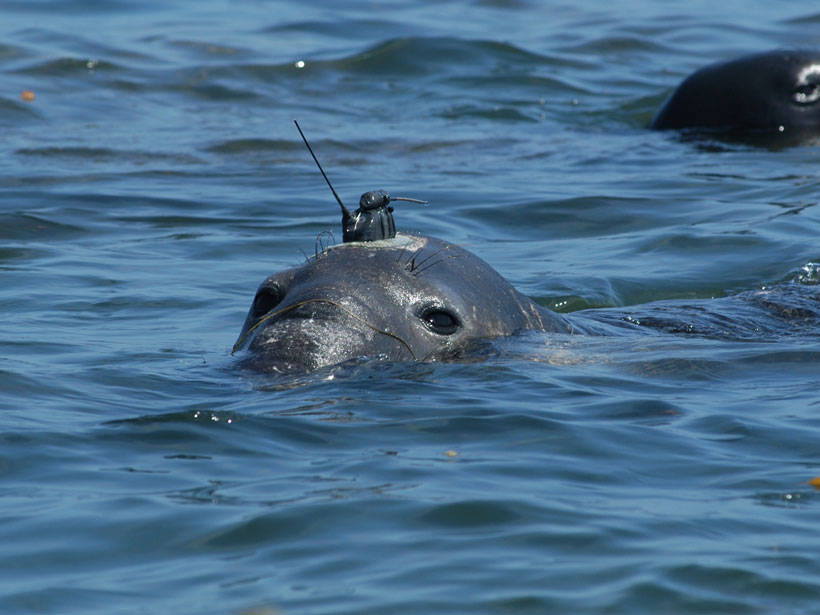
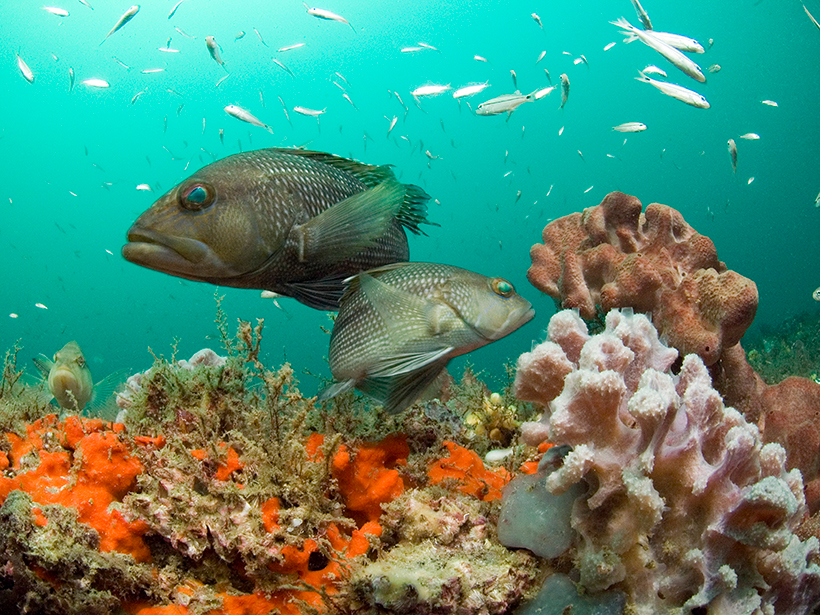
Global Warming Hits Marine Life Hardest
The lack of thermal refugia in the ocean means marine life has nowhere to escape from rising sea temperatures.