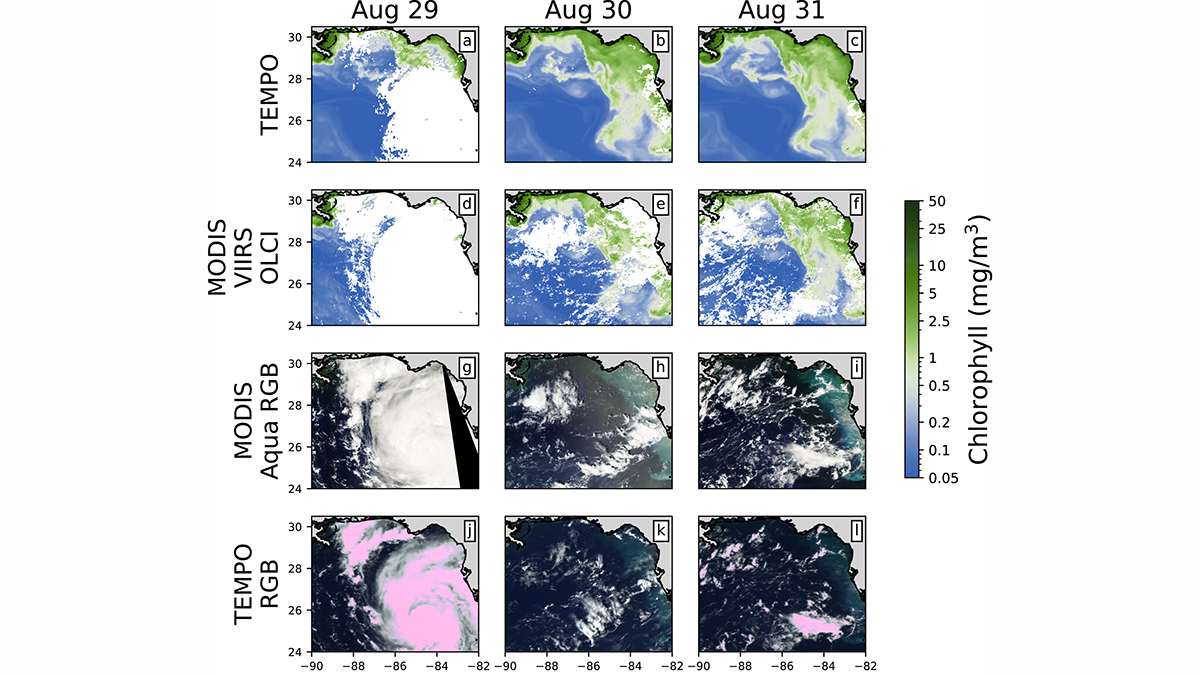
Scientists apply machine learning to demonstrate that geosynchronous satellites can be used to assess the health of oceans from deep space.
carbon dioxide
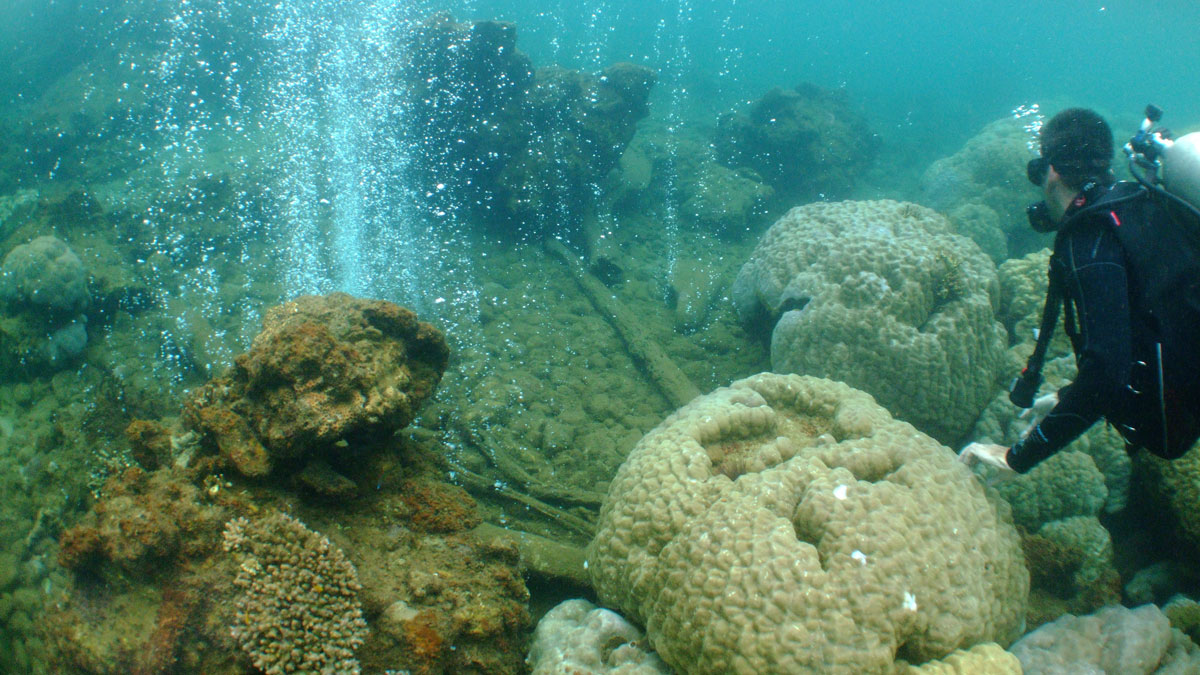
Coral Diversity Drops as Ocean Acidifies
As seawater becomes steadily more acidic, complex branching corals die off and are replaced with hard boulder corals and algae.
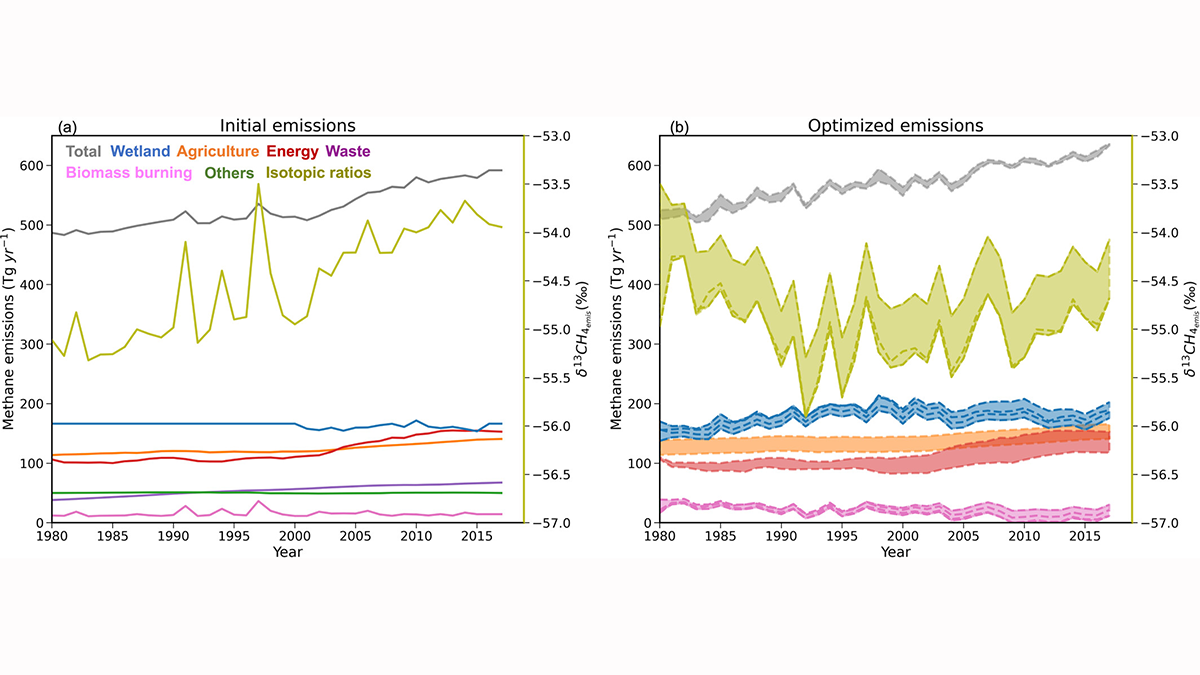
Cows, Coal, and Chemistry: The Role of Photochemistry in Methane Budget
Recent increases in atmospheric methane are a result of changing natural and manmade sources, climate, and other less-understood factors linked to its role in the atmosphere’s self-cleaning mechanisms.
What Could Happen to the Ocean’s Carbon If AMOC Collapses
Mass glacier melting may have led this influential ocean current system to collapse at the end of the last ice age. A pair of modeling studies examines how such a collapse could affect dissolved inorganic carbon and carbon isotopes in Earth’s oceans.
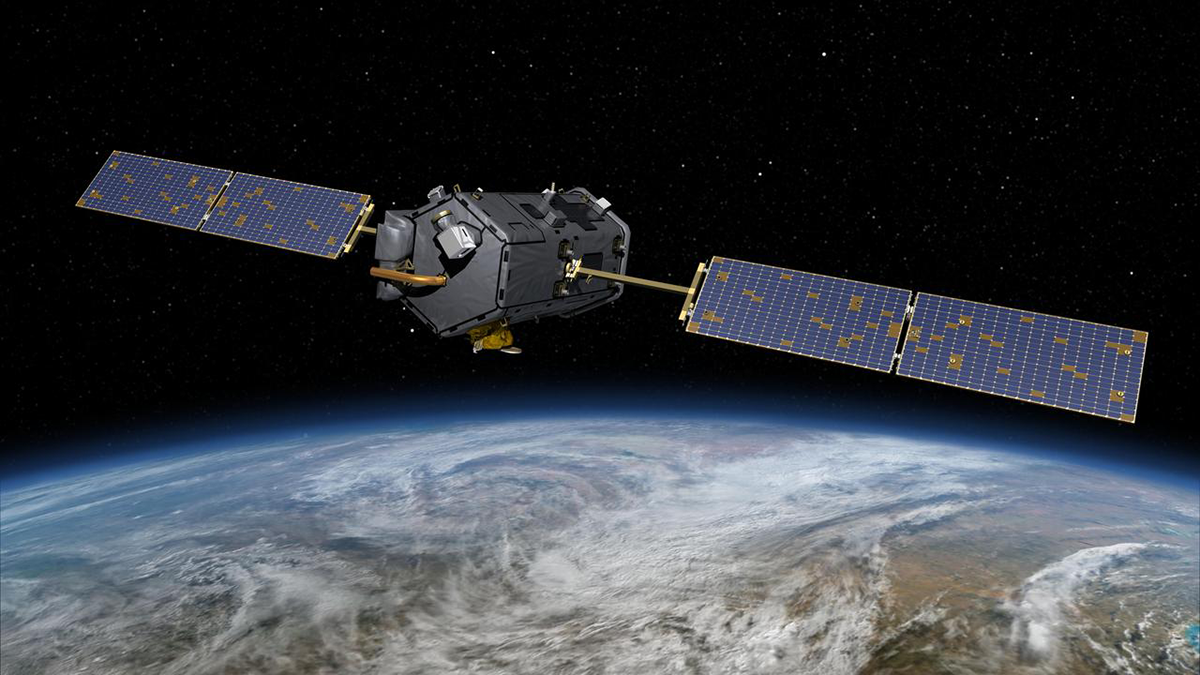
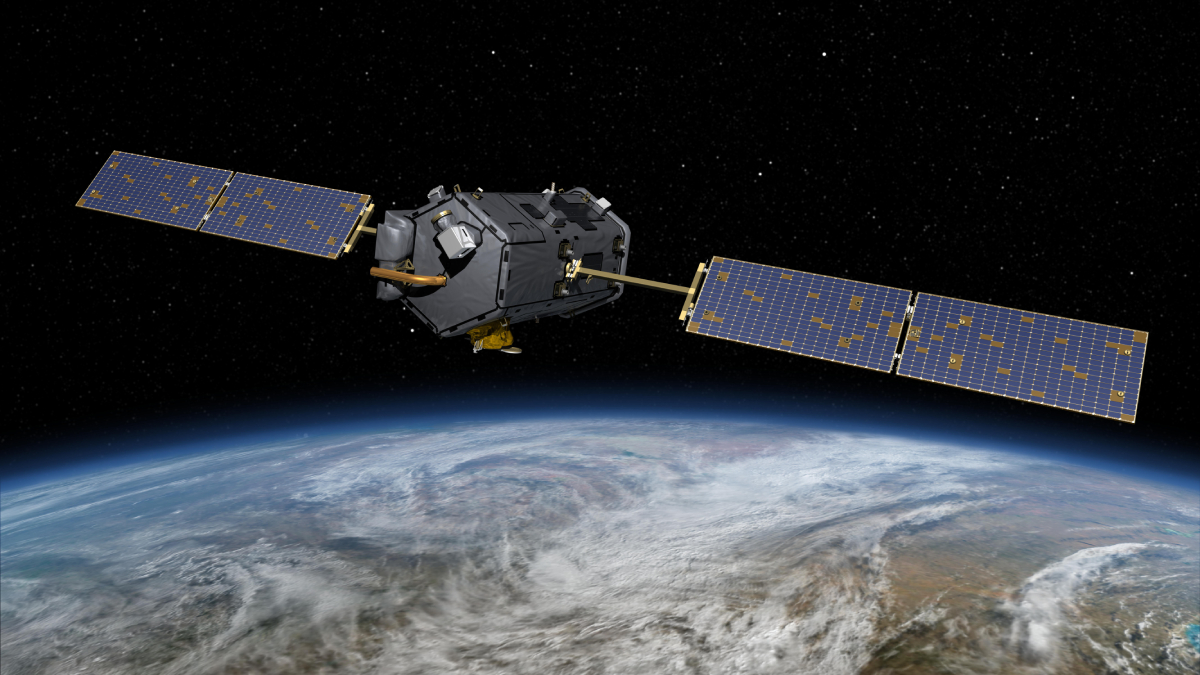
Taking Carbon Science Out of Orbit
NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 satellite reveals an impressively dynamic picture of the Earth’s carbon cycle, yet it may be prematurely decommissioned and destroyed due to budget cuts.
Serendipity in Space: NASA’s Eye in the Sky
The Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) mission, proposed for early termination, has turned out to be a boon to forest and agricultural management.
Rising CO2 and Climate Change Reorganize Global Terrestrial Carbon Cycling
Rising CO2 and climate change are redistributing terrestrial carbon fluxes and reservoirs across latitudes and reducing carbon residence times globally.
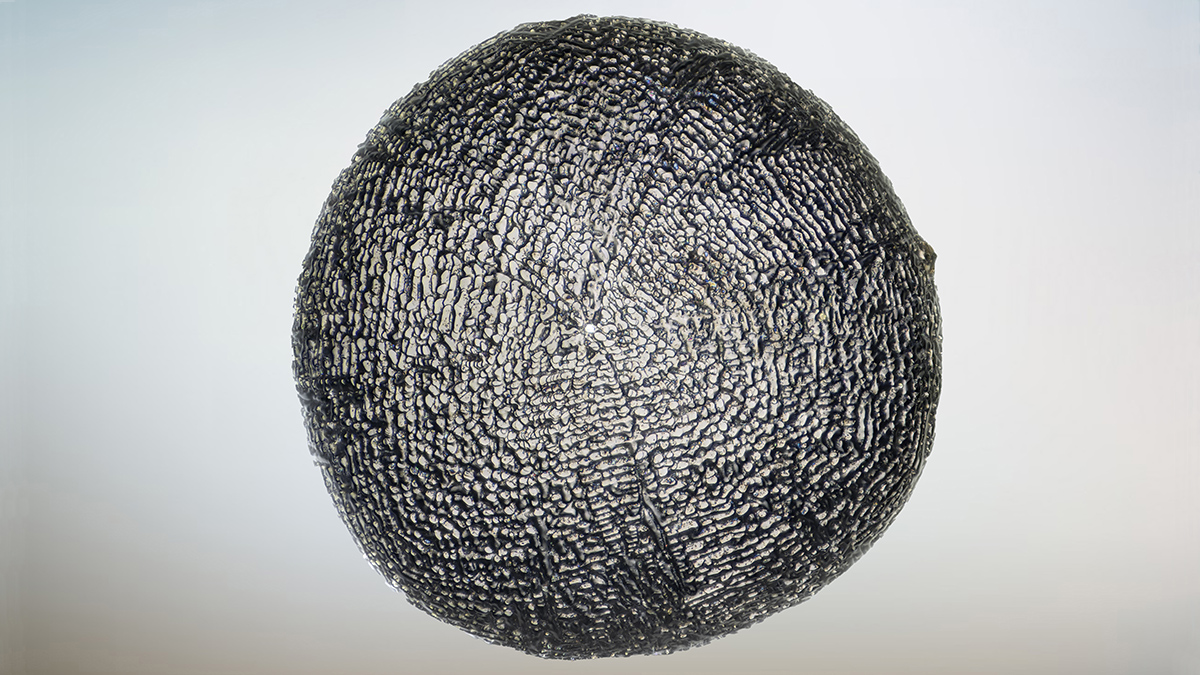
Fossilized Micrometeorites Record Ancient CO2 Levels
A cadre of iron-rich extraterrestrial particles picked up faint whiffs of our planet’s atmosphere when they fell to Earth millions of years ago.
NASA Planning for Unauthorized Shutdown of Carbon Monitoring Satellites
Despite warnings that their actions are illegal, Duffy and other senior NASA officials have continued to secretly direct NASA employees to draw up plans to end at least two major satellites missions specifically designed to monitor global carbon dioxide.
Verdaderas soluciones climáticas están debajo de nosotros
Es momento de aceptar que el almacenamiento duradero de carbono en el subsuelo, junto con la reducción de emisiones, debe ser parte del plan para mitigar los efectos del cambio climático, y las geociencias deben desempeñar un papel central.