El fechamiento por radiocarbono es un pilar de la climatología y la arqueología. Sin embargo, esta metodología se encuentra amenazada por las emisiones de combustibles fósiles, que invalidan una señal útil proveniente de pruebas nucleares.
carbon emissions
Tracing Anthropogenically Emitted Carbon Dioxide into the Ocean
Researchers labeled anthropogenically emitted carbon and tracked it with an ocean circulation model to determine whether it winds up in the sky or sea.
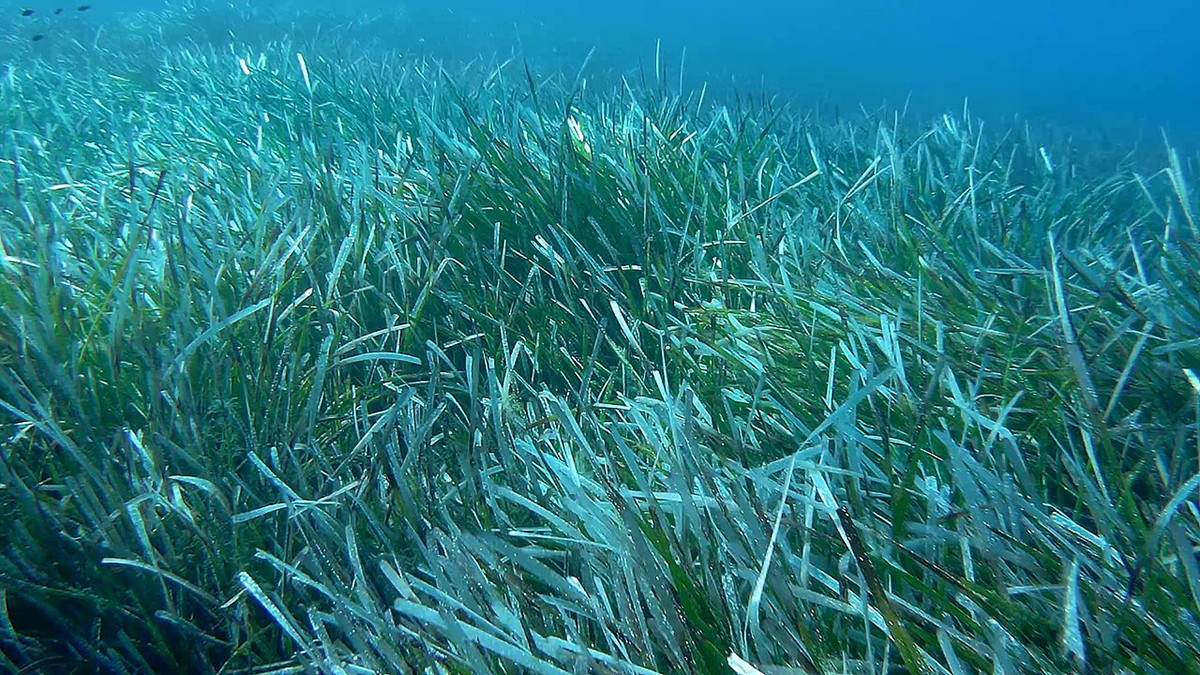
Warming and Agitation Intensify Seagrass Meadow Carbon Fluxes
Carbon dioxide emissions surge in sediments when temperature and agitation increase, both of which are likely to continue rising in degraded Mediterranean seagrass meadows.
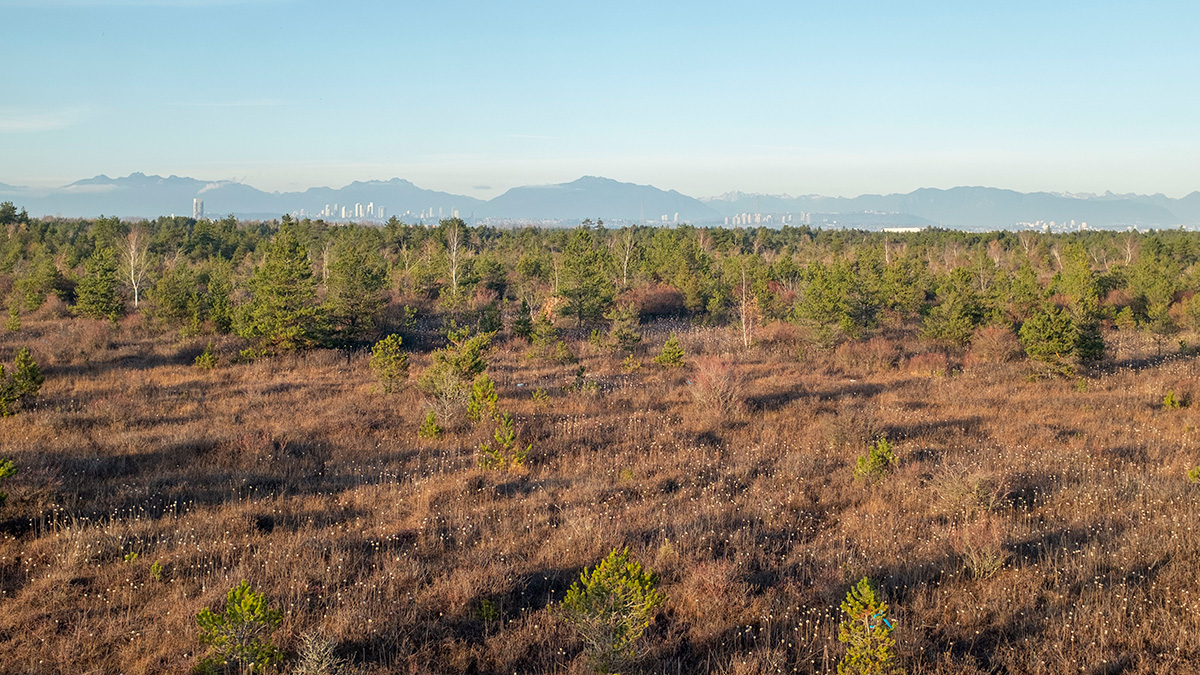
Exploring Carbon Emissions in Peatland Restoration
Rewetting bogs can increase methane emissions in the short term, but ultimately the approach helps restore peatlands and create larger carbon sinks.
Un nuevo enfoque para un misterio sin resolver en la economía climática
¿Tienen los cambios de temperatura impactos económicos duraderos? Un truco “ingenioso” que identifica tendencias climáticas nos lleva un paso más cerca a abordar esta vieja pregunta en la economía climática.
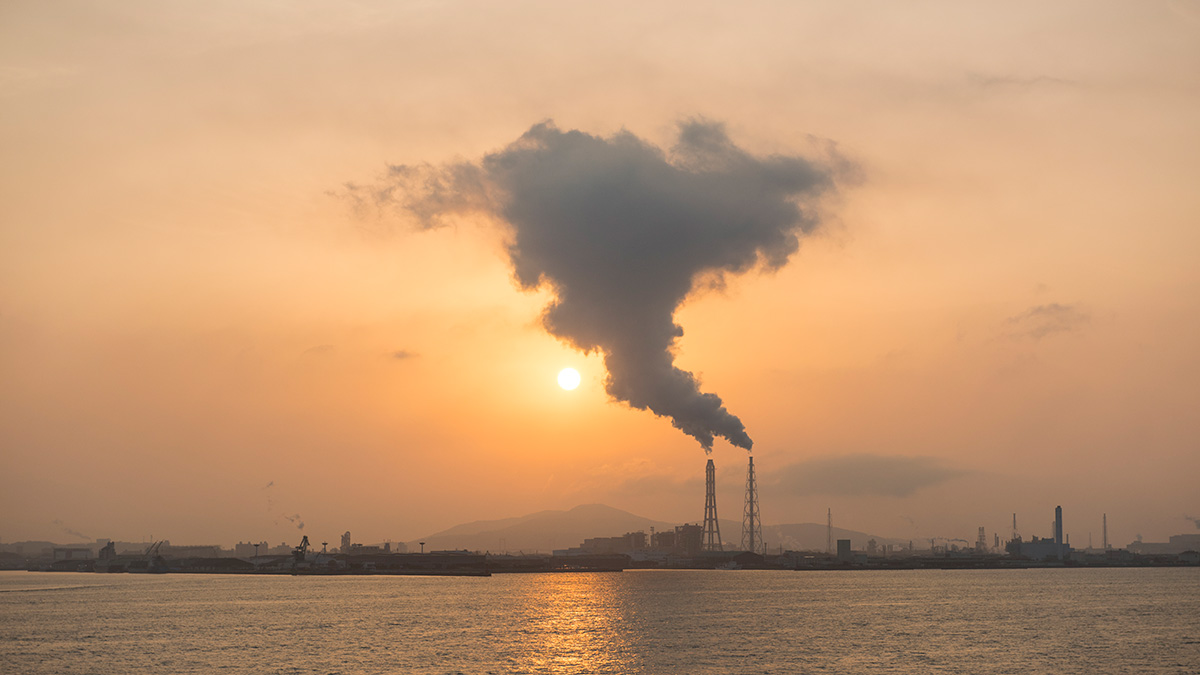
Radiocarbon’s Blast from the Past
Radiocarbon dating is a cornerstone of climate and archaeological sciences. But the method is under threat as fossil fuel emissions negate a useful signal from atomic tests.
Simpler Presentations of Climate Change
The basics of climate change science have been known for a long time, and the predicted impact of a doubling of atmospheric carbon dioxide on global temperature hasn’t changed much in 100 years.
Major Investment in Air-Conditioning Needed to Address Future Heat Waves
More than 80% of urban residents will need AC by the 2050s, but many of the world’s poorer countries may struggle to meet that demand.
A New Approach to an Unresolved Mystery in Climate Economics
Do shifts in temperature have enduring economic impacts? A “clever” trick identifying climate trends gets us one step closer to addressing this long-standing question in climate economics.
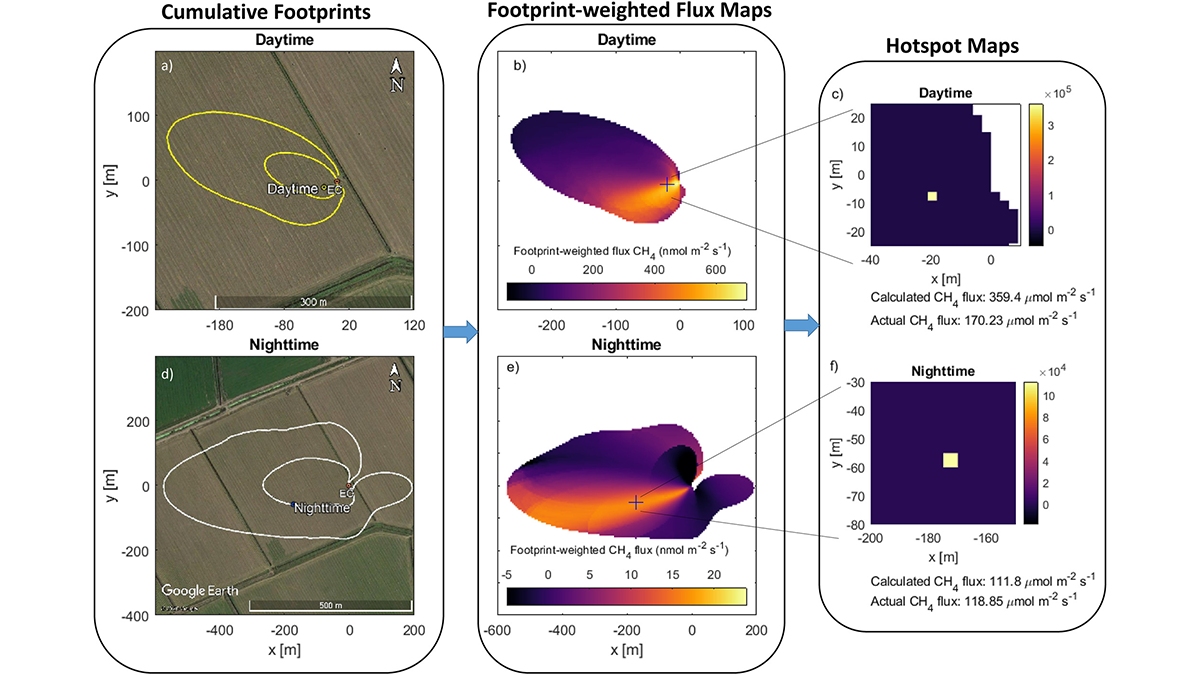
Sleuthing for Culprits of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
A new approach to detect hot spots of methane emissions with eddy covariance flux towers proves to be a worthy contender.