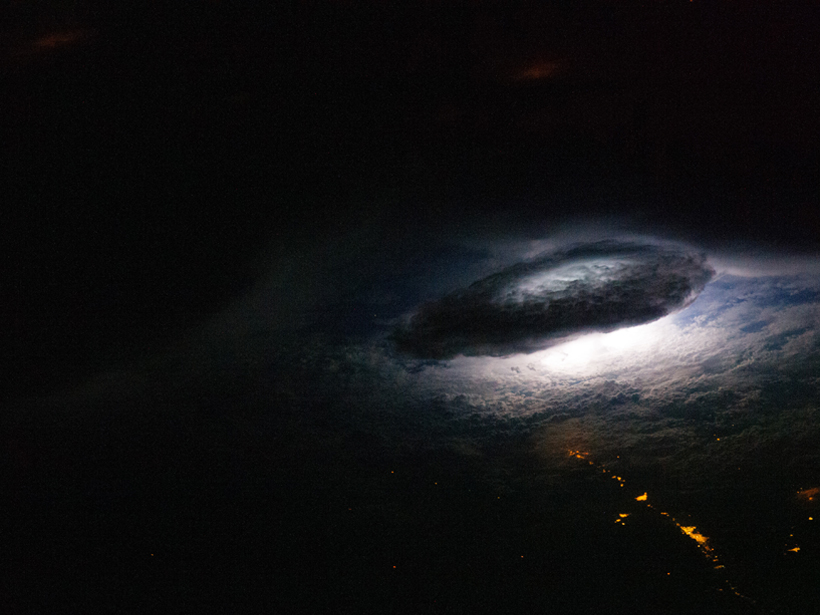
A thunderstorm made waves on a rare “bright night.”
clouds
More Clustered Clouds Amplify Tropical Rainfall Extremes
Both satellite observations and model simulations reveal that more aggregated convection amplifies the increase in extreme rainfall events on a year-to-year basis.
¿Podría la Vida Estar Flotando en las Nubes de Venus?
Si están presentes, los microbios podrían explicar patrones de evolución en la atmósfera planetaria de Venus, al observarse con luz ultravioleta.
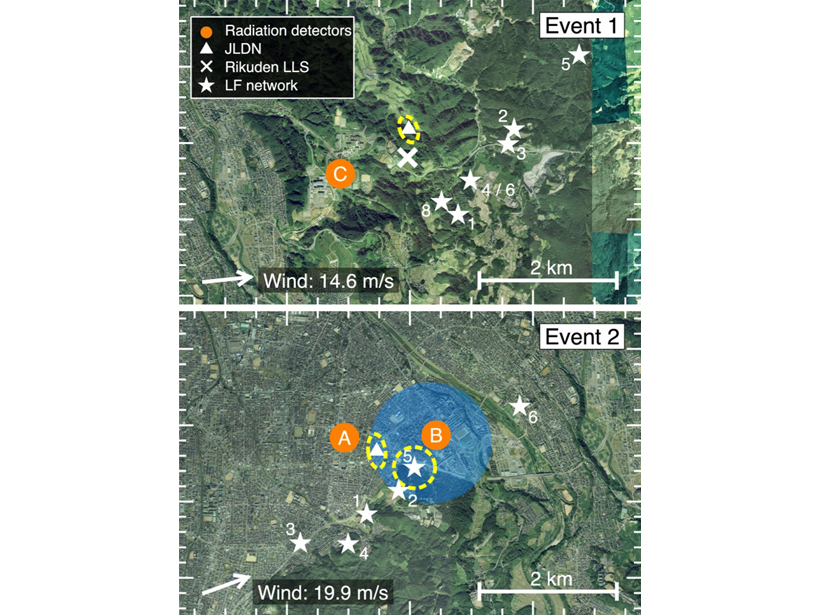
Lightning Discharge Type Linked to Terrestrial Gamma‐Ray Flashes
For the first time, the connection between energetic in cloud pulse and terrestrial gamma‐ray flashes is confirmed in the Gamma-Ray Observation of Winter Thunderclouds experiment in Japan.
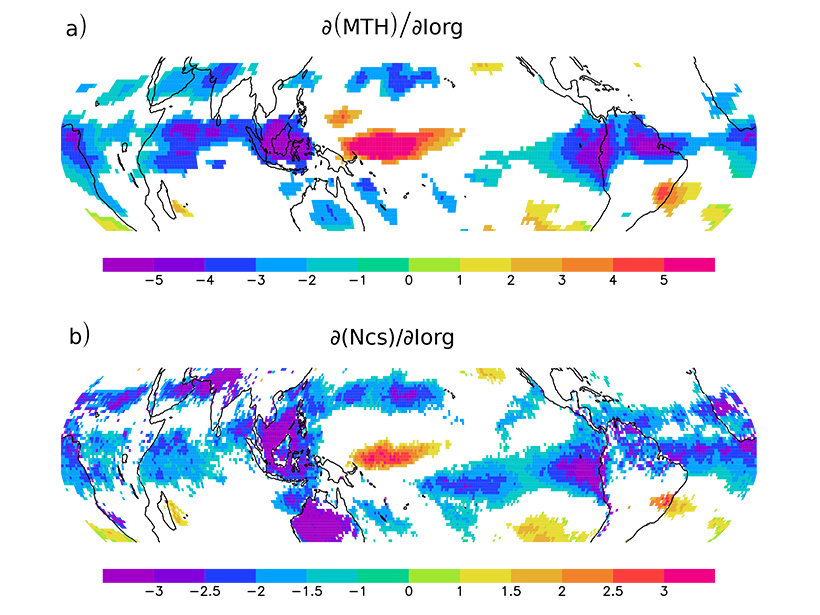
Can We Observe How Cloud Clustering Affects the Radiation Budget?
Satellite observational analysis confirms that lower-atmospheric stability and cloud clustering are major factors modulating the tropical radiation budget that had been suggested by modeling studies.
A Global View of Shapes and Sizes of Ice Crystals in Cloud Tops
Ice particles have systematic covariations and temperature dependences that are surprisingly consistent with a simple ice growth theory as revealed by satellites.
Studying Earth’s Double Electrical Heartbeat
Charged by thunderstorms and other weather phenomena, the global electrical circuit connects the entire planet.
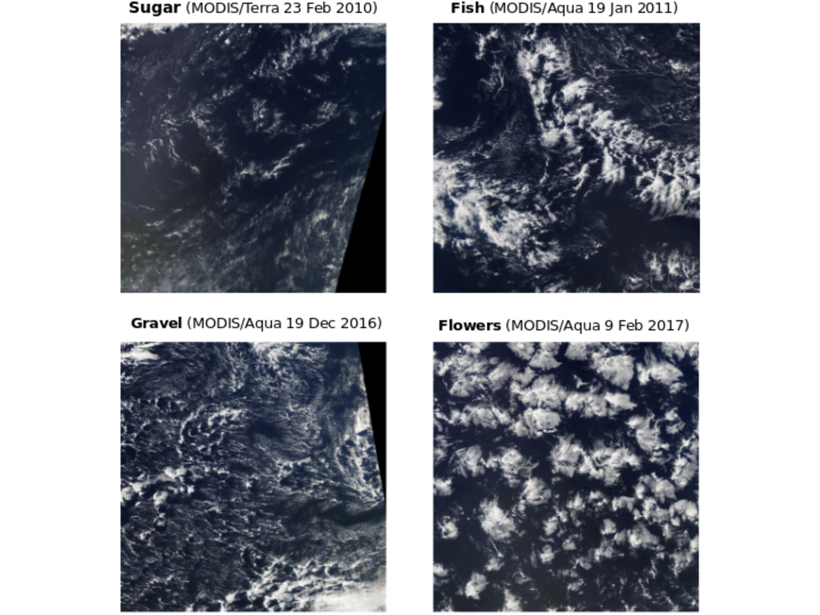
A New View of Old Clouds
Satellite images of marine shallow clouds are objectively classified into four distinct types, illuminating new ways to tackle a long-standing problem in climate predictions.
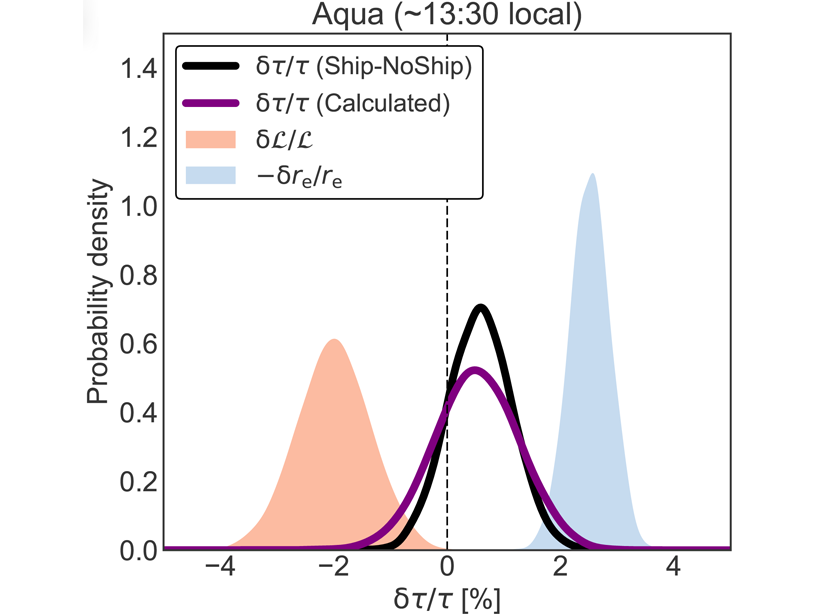
Quantifying Aerosol Effects on Climate Using Ship Track Clouds
A new methodology for measuring how human emissions influence cloud properties and radiative forcing developed by reconstructing cloud fields in maritime shipping lanes.
Evaluating Cloud Cover Predictions in Climate Models
A new analysis highlights progress in predictions of cloud cover from models that are part of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project.