By using novel aircraft measurements over the eastern North Atlantic Ocean, researchers shed light on the relationship between common marine biogenic gases and the microphysical properties of clouds.
clouds
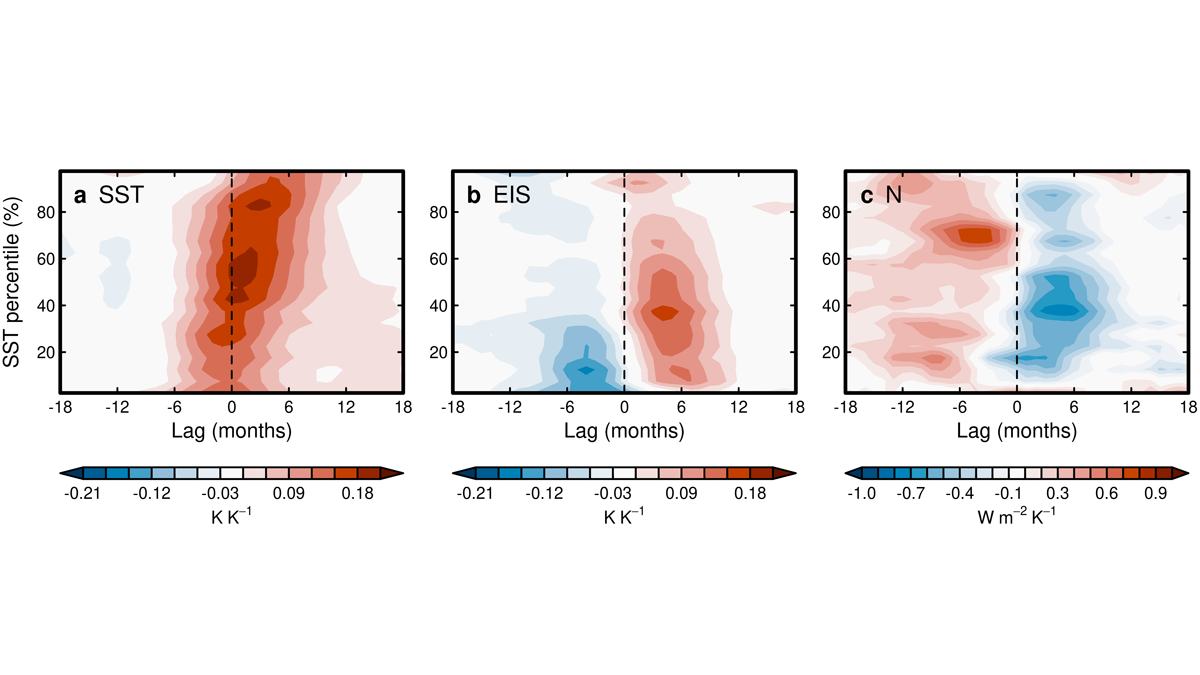
El Niño-Southern Oscillation and Radiation Two-Way Coupling
Changes in sea surface temperature during ENSO events and radiation are related, suggesting a two-way coupling between sea surface temperature and radiation in coupled climate variability.
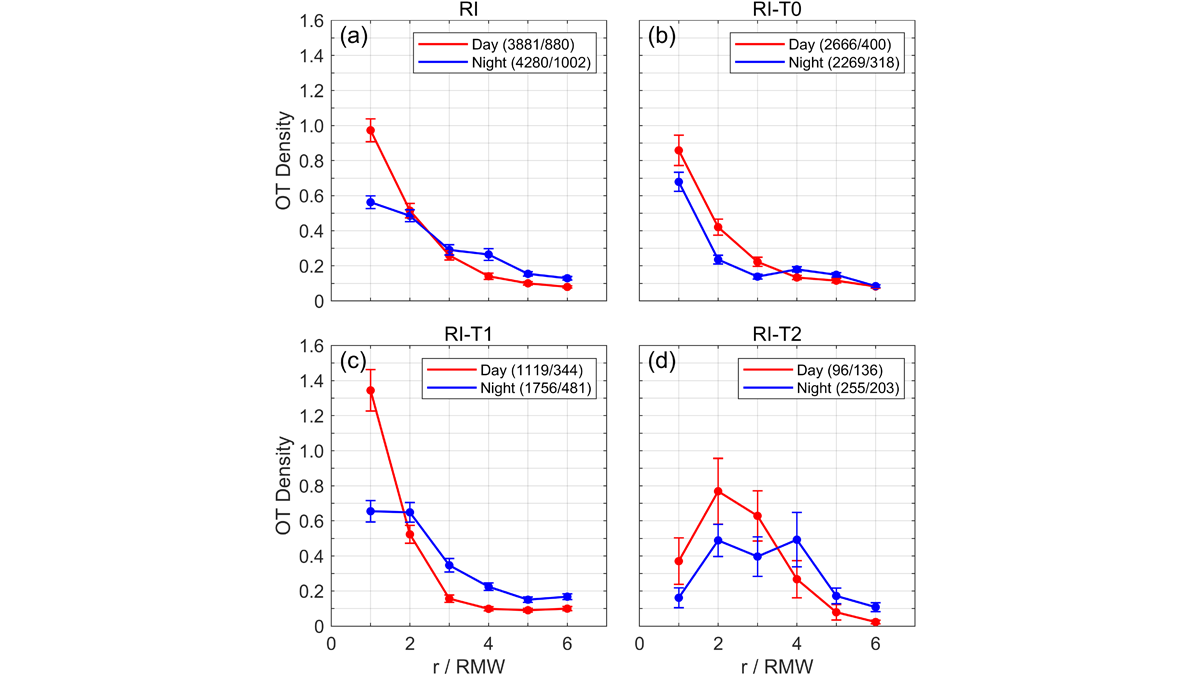
Clouds Overshooting Tops and Typhoon Intensity
An examination of the relationship between the diurnal variation of cloud overshooting tops density and typhoon intensity in 45 typhoons, using the Himawari-8 Satellite.
A Transition Zone Below Jupiter’s Clouds
The microwave radiometer aboard NASA’s Juno spacecraft reveals the hidden atmospheric circulations at work deep below Jupiter’s colorful clouds.
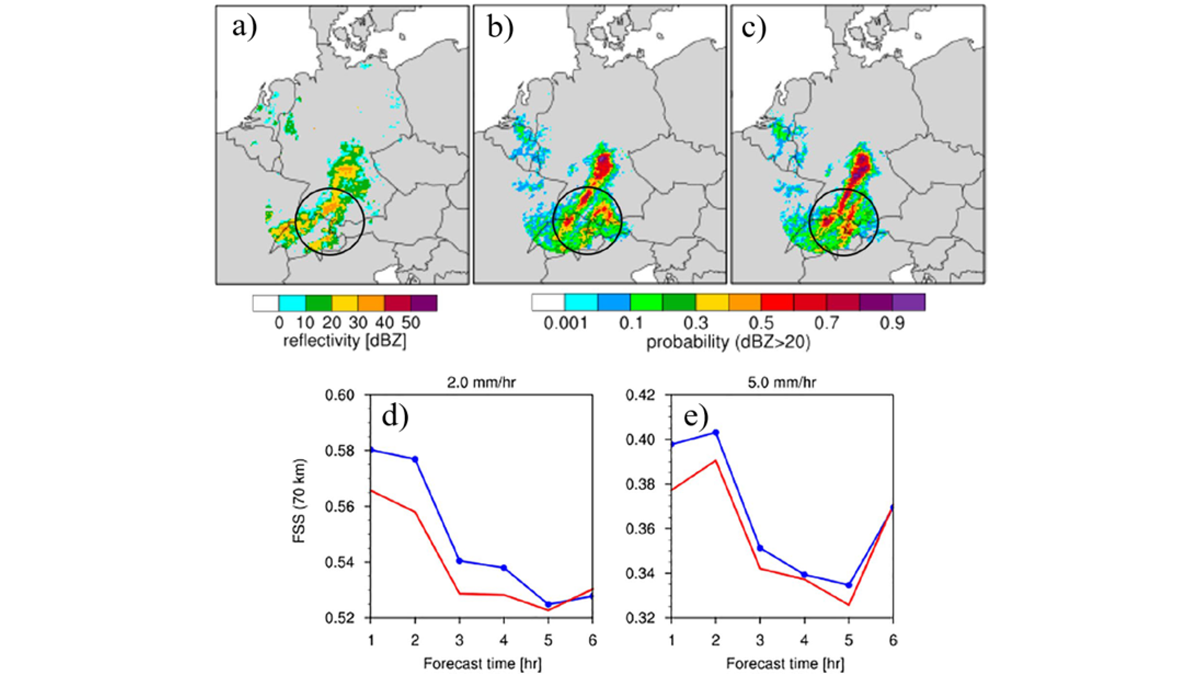
A New Way to Represent Microphysical Uncertainty
A new way of representing microphysical uncertainty in convective-scale data assimilation reduces biases in model states and improves the accuracy of short-term precipitation forecasts.
Importance of High Clouds and Moisture in Rainstorm Aggregation
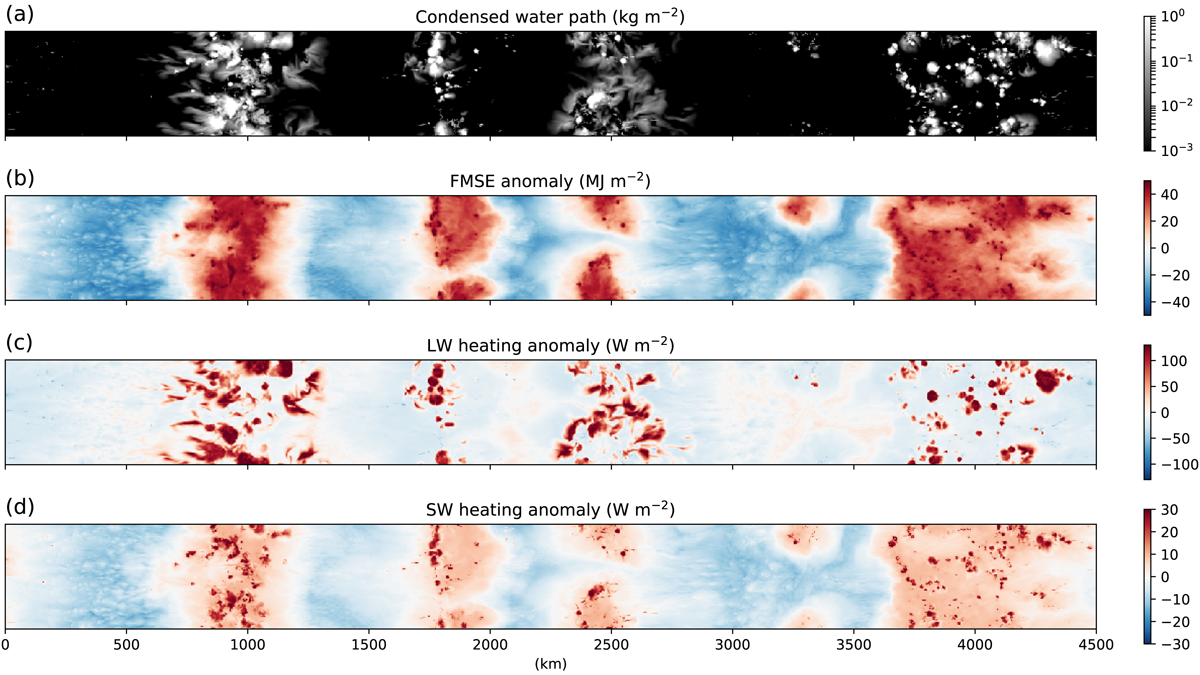
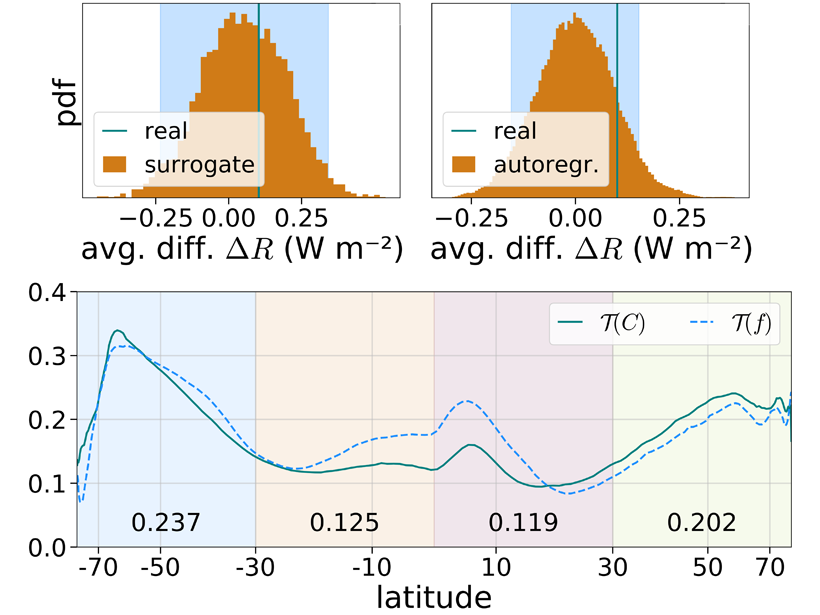
A study of the impacts of radiative interactions with different cloud types on aggregation of rainstorms finds that interactions with high-clouds and water vapor are key.
New Insights into Polar Stratospheric Clouds
New satellite observations of polar stratospheric clouds have advanced our understanding of how, when, and where they form, their composition, and their role in ozone depletion.
How Long Do Black Carbon Particles Linger in the Atmosphere?
Researchers uncover how black carbon evolves from hydrophobic particles to cloud nucleation sites, eventually removing the heat-absorbing particles from the sky.
Is Earth’s Albedo Symmetric Between the Hemispheres?
The two hemispheres feature the same planetary albedo despite a larger land fraction in the north, because storms over the southern ocean are cloudier than their northern counterparts.
The Forecast for Exoplanets is Cloudy but Bright
Clouds make climate modeling on Earth difficult. Identifying—and even defining—atmospheric phenomena on other planets is the next big exoplanet challenge.