Tens of thousands of ship tracks—cloud structures created when ships’ exhaust plumes interact with the atmosphere—are pinpointed automatically, furthering study of these climate-altering features.
clouds
Contrails’ Climate Impact Could Triple by 2050
Contrail cirrus clouds have warmed the atmosphere more than all the carbon dioxide from planes since the dawn of aviation and will do so even more in the future.
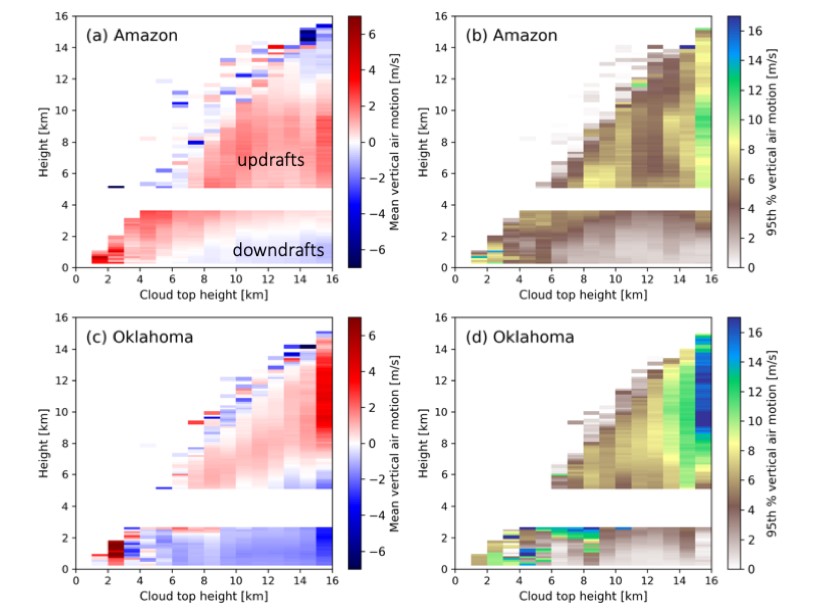
New Observations of Thunderstorm Updrafts and Downdrafts
Unique measurements of air motion within deep convective clouds offer new insights in our understanding of these storms and provide constraints for weather and climate prediction.
Precipitation in the Tropics: A New View
The first study to simultaneously investigate precipitation and cloud structures in tropical weather systems concludes observation systems significantly overestimate the height of raining clouds.
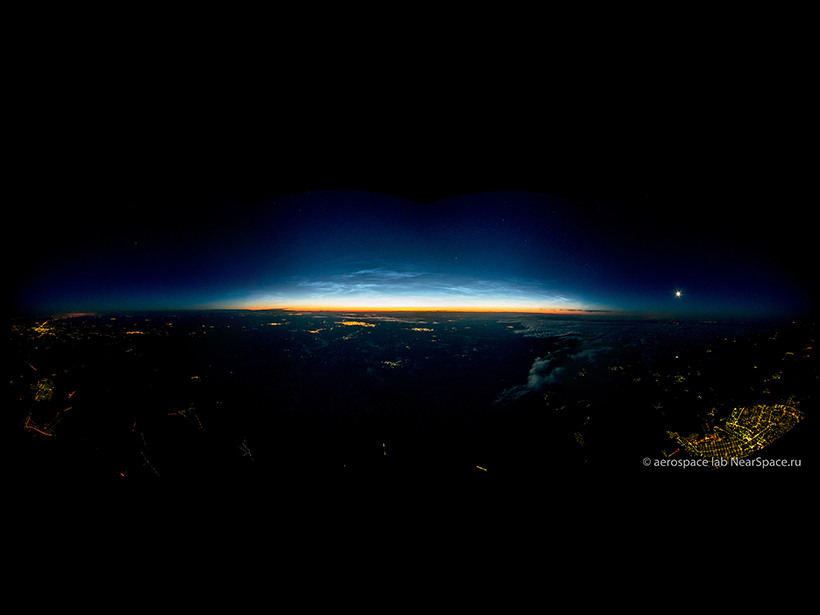
Looking at “Night-Shining” Clouds from the Stratosphere
One research group studied noctilucent clouds at large distances from a different point of view, using cameras aboard a meteorological balloon that sailed into the stratosphere.
Connecting the Southern Ocean with Clouds
ACE-DATA/Antarctic Sea-Atmosphere Interactions Data (ASAID) Workshop; 5–6 November 2018, Lausanne, Switzerland
Improving Retrievals for Vertically Inhomogeneous Warm Clouds
Cloud droplet size changes with height, but passive sensors are virtually blind to see it; however, combining passive with active sensors helps profile it in vertically inhomogeneous warm clouds.
Improving Estimates of Long-Term Climate Sensitivity
New modeling casts doubt on the suitability of running experiments with fixed sea surface temperatures to understand the effects of cloud aggregation on Earth’s climate.
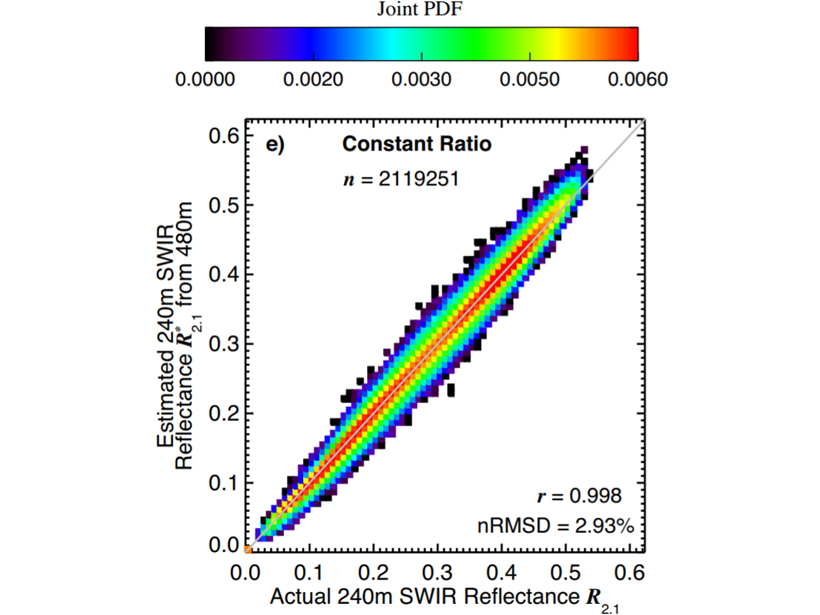
Improving Retrievals for Partially Cloudy Pixels
Cloud retrievals for partly cloudy pixels might be able to be improved by using high-resolution samples in a visible to near-infrared band, which many satellite sensors offer.
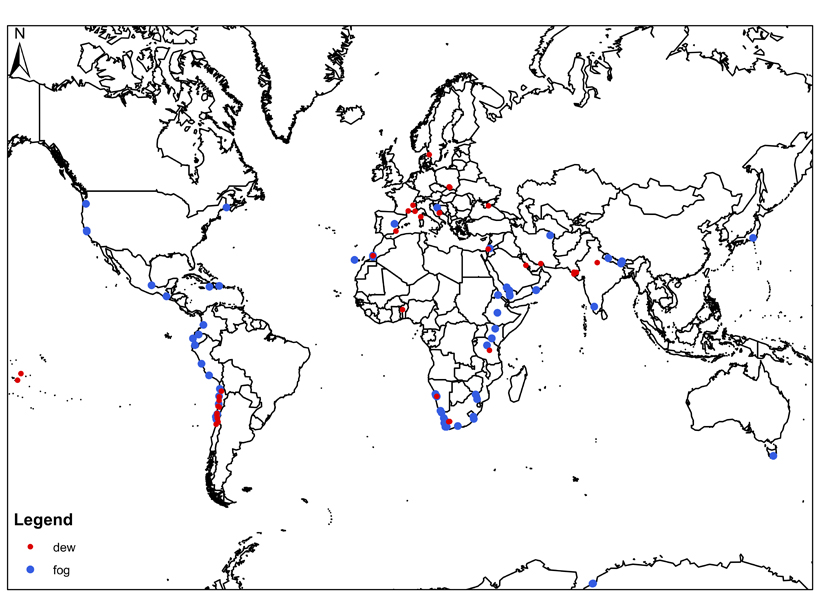
Fog Catching for Thirsty Locales
Many arid and semi-arid regions experience very little rainfall, but quite a bit of fog, which might be a viable source of drinking water.