Scientists are stunned by the changes in multiple Arctic lakes, all transforming in the same way.
color
Coastlines Around the World Are Losing Sediment
A new tool maps coastal sediments on the basis of water color. It shows that 75% of the world’s coastlines may be losing suspended sediment.
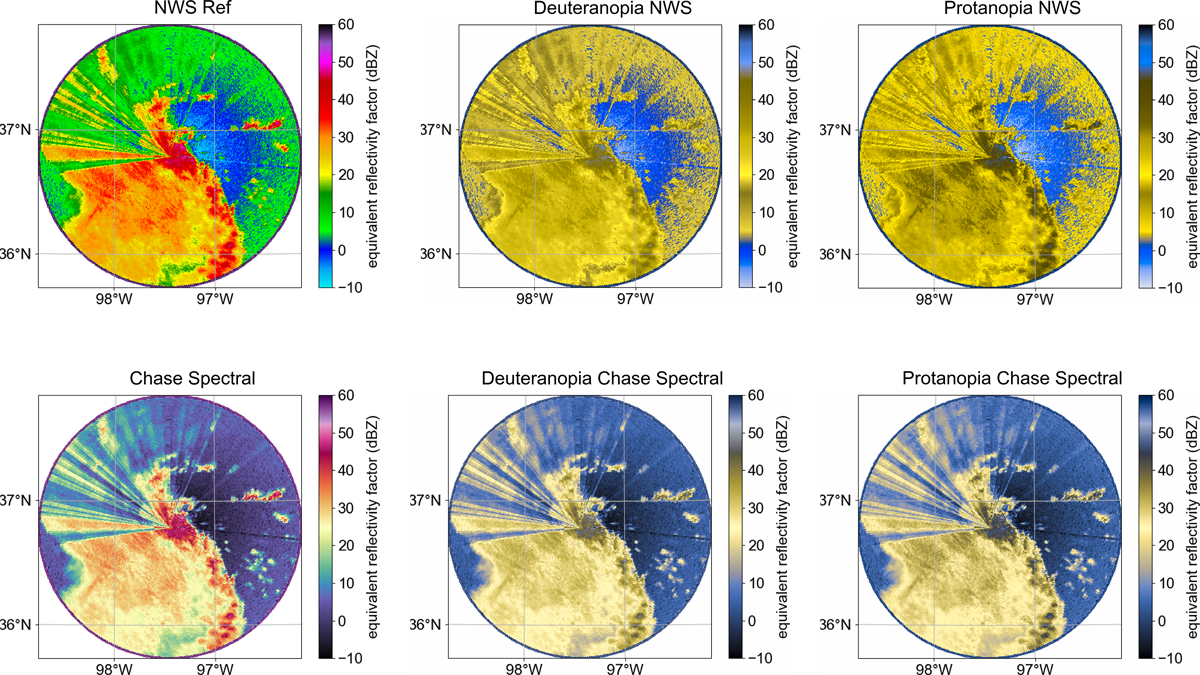
Putting Accessibility on the Map
New research demonstrates how to make radar maps more easily interpretable for people with color vision deficiency.
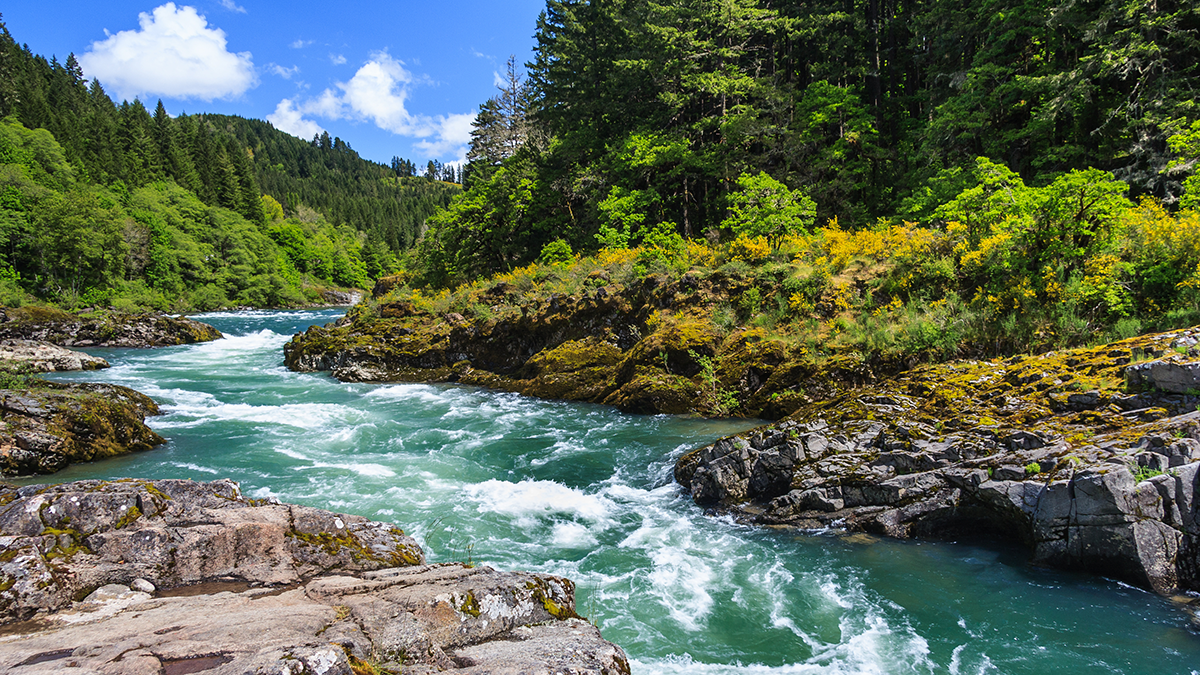
As the River Flows the Colors Sparkle
Diving into the science behind river color and its relationship with flow.
A Sugar Coating for Arrokoth
A Kuiper Belt object might contain ribose and glucose on its surface—the same elements that could have seeded life on Earth.
New Satellite Will Help NASA Keep PACE with Earth Systems
Color and light measurements will help scientists better assess how our oceans and atmosphere interact.
More Than Half the World’s Ocean Surface Is Getting Greener
Advances in data analysis help researchers spot shifting ocean colors, which could be associated with climate change.
Carbon In, Carbon Out: Balancing the Ocean’s Books
Scientists have developed a consensus guide of standard protocols for how best to measure oceanic primary productivity, a key component in Earth’s carbon cycle.
Las hojas están brotando más temprano en el Sendero de los Apalaches
Imágenes satelitales de nuevas y brillantes hojas revelan cambios que producirán un efecto de cascada en diversos ecosistemas al este de los Estados Unidos.
Leaves Are Springing Up Earlier Along the Appalachian Trail
Satellite images of lustrous new leaves reveal changes that will have cascading effects on diverse ecosystems in the eastern United States.