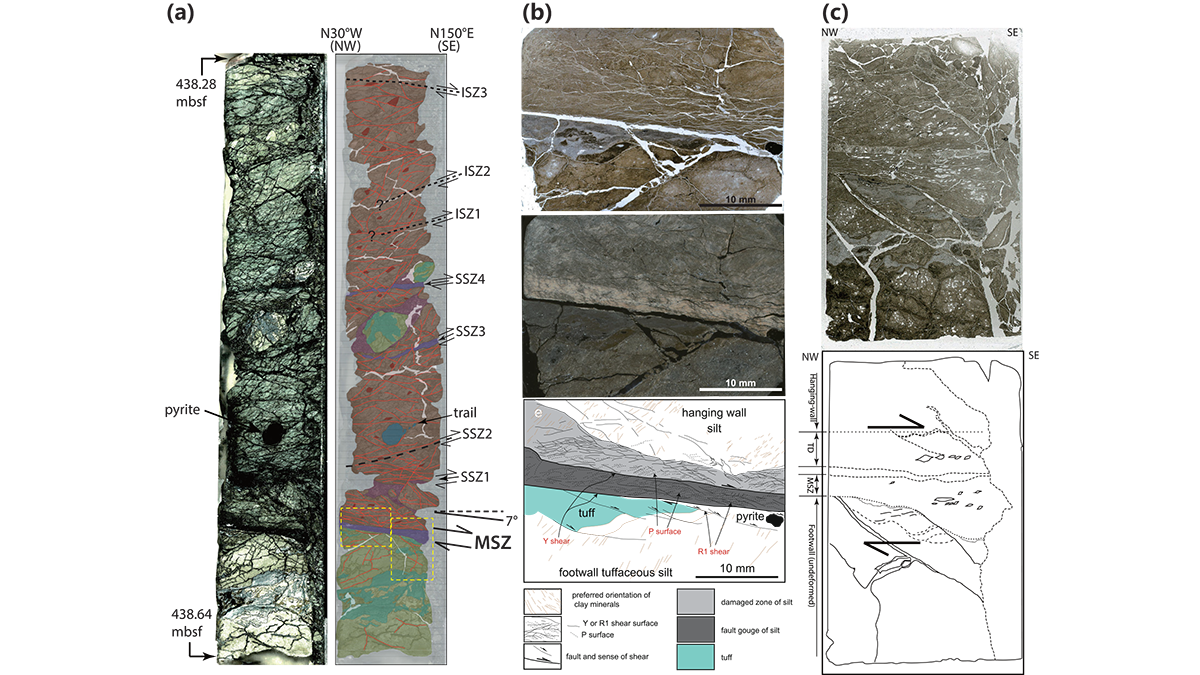
A database of frictional properties from IODP drilling materials explores the range of slip spectrum and the generation of slow to fast earthquakes in the Nankai subduction zone in light of mineralogy.
earthquakes
The Ridgecrest Earthquake Left Enduring Damage in Earth’s Deep Crust
The shallow crust has recovered since California’s 2019 quake, but damage persists at depths greater than 10 kilometers.
When Cascadia Gives Way, the San Andreas Sometimes Follows
Roughly half of the earthquakes that occurred along the southern Cascadia subduction zone over the past 3,000 years were temporally associated with earthquakes along the northern San Andreas fault.
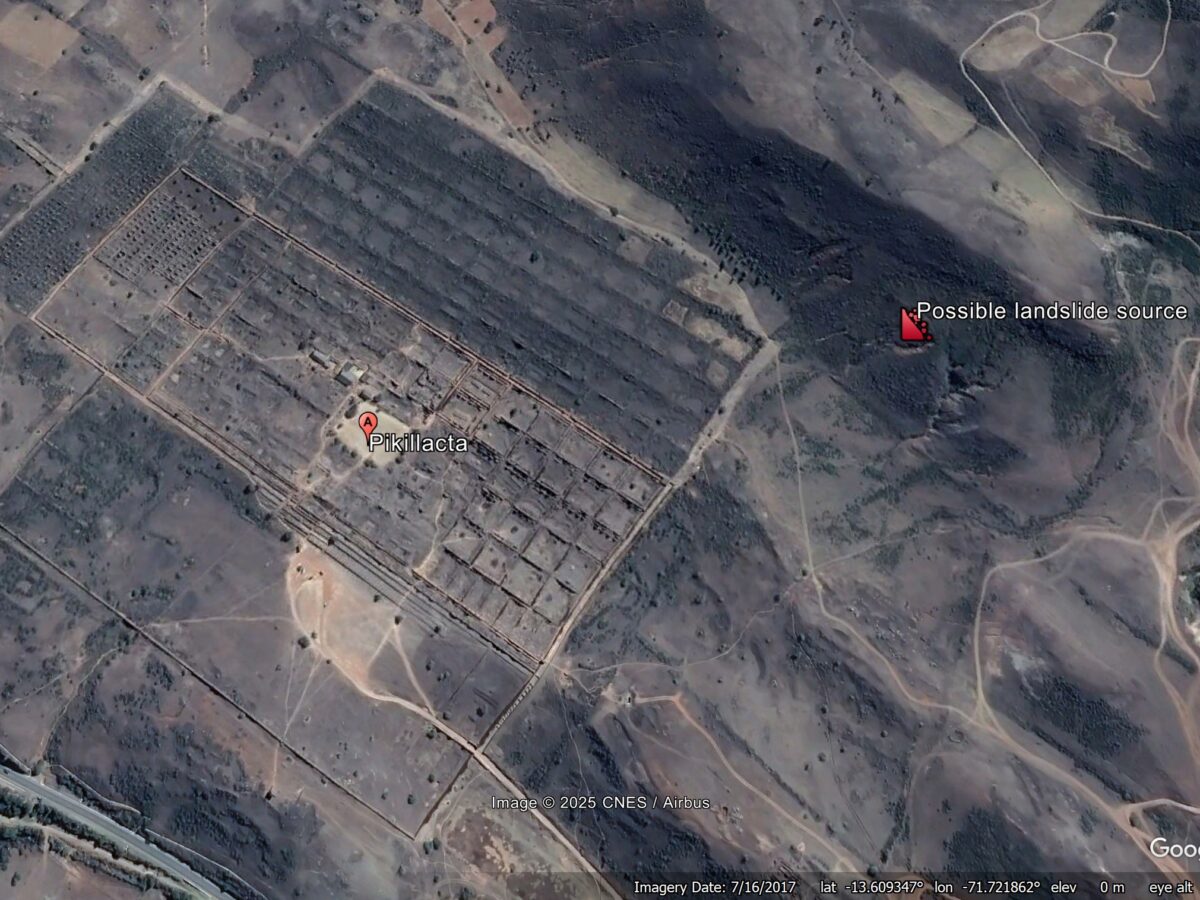
Pikillaqta in Cusco: the role of an earthquake-induced debris flow in about 900 AD
The Landslide Blog is written by Dave Petley, who is widely recognized as a world leader in the study and management of landslides. According to Wikipedia, Pikillaqta is a large archaeological site located 20 km to the east of Cusco in Peru. Inhabited by the Wari people, it was abandoned at about 900 AD for […]
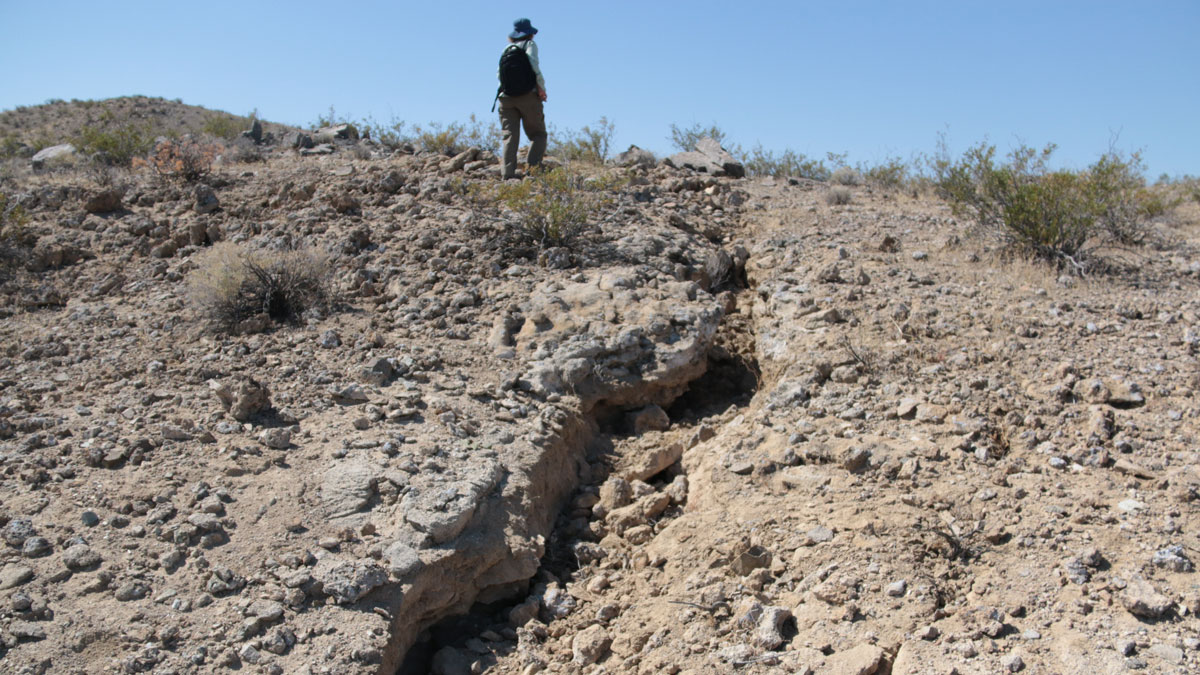
Landslides from the 3 November 2025 Afghanistan earthquake
Some videos have emerged from Afghanistan this morning, reportedly showing landslides and rockfalls triggered by the M=6.3 earthquake. At 12:59 am on 3 November 2025 (local time, which is 20:29 UT on 2 November 2025), an M=6.3 earthquake struck near to Mazar-E Sharif in Afghanistan. Initial reports suggest at least 20 fatalities have occurred, but […]
AI is Changing our Understanding of Earthquakes
Machine learning is expanding scientists’ catalogs of quakes and refining maps of underground faults. It also promises to improve quake forecasts.
New Earthquake Model Goes Against the Grain
Subducting plates are stronger in certain directions than others, which may be a factor in how earthquakes occur and how seismic waves propagate.
When the Earth Moves: 25 Years of Probabilistic Fault Displacement Hazards
Surface ruptures causing earthquakes pose risks to infrastructure and human lives, but advances in models and data in the last few decades have improved our ability to mitigate their effects.
The 22 May 1960 earthquake-induced landslides and tsunami at Lake Rupanco in Chile
Reconstruction of landslides on the banks of Lake Rupanco in Chile, triggered by the 22 May 1960 Mw-9.5 earthquake, suggests that a slope failure with a volume of 161 million cubic metres triggered a tsunami with a maximum amplitude of 33.3 metres. About 120 people were killed. A very interesting paper (Quiroga et al. 2025) […]
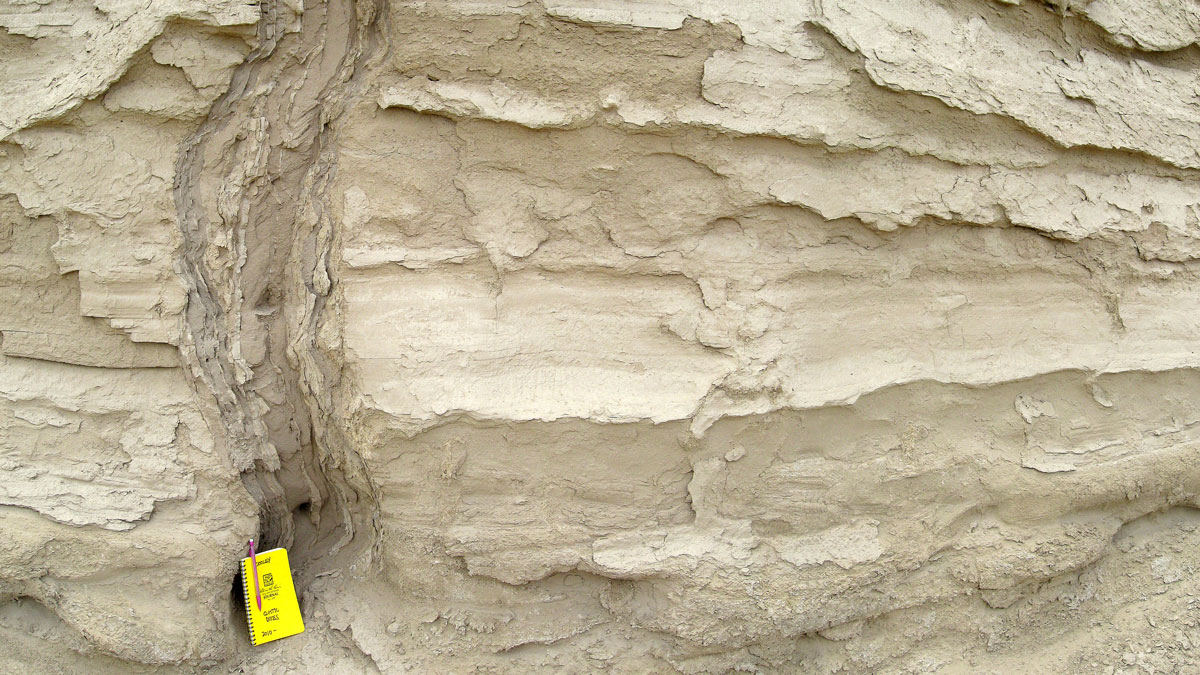
Spiky Sand Features Can Reveal the Timing of Ancient Earthquakes
Icicle-shaped features known as sand dikes form during ground shaking. New work reveals how these features can be used to date long-ago earthquakes.