Extreme heat in 2023, 2024, and 2025 indicates a warming spike, a new analysis finds.
ENSO
Globe-Trotting Weather Pattern Influences Rainfall in Hawaii
Isolated islands that depend on rainfall could benefit from improved forecasting of near-future events, and understanding the Madden-Julian Oscillation could hold an important key.
Panama’s Coastal Waters Missed Their Annual Cooldown This Year
The unprecedented failure of tropical upwelling will likely affect the country’s fisheries. Scientists aren’t certain whether it will happen again next year.
Droughts Sync Up as the Climate Changes
A new study reconstructs roughly 800 years of streamflow history in India’s major rivers, showing an increase in synchronous drought linked to anthropogenic climate change.
El Niño May Be Driving Insect Decline in the Tropics
Stronger and more frequent El Niño events are contributing to a decline in arthropod diversity and population, as well as to a reduction in the ecological services the animals provide.
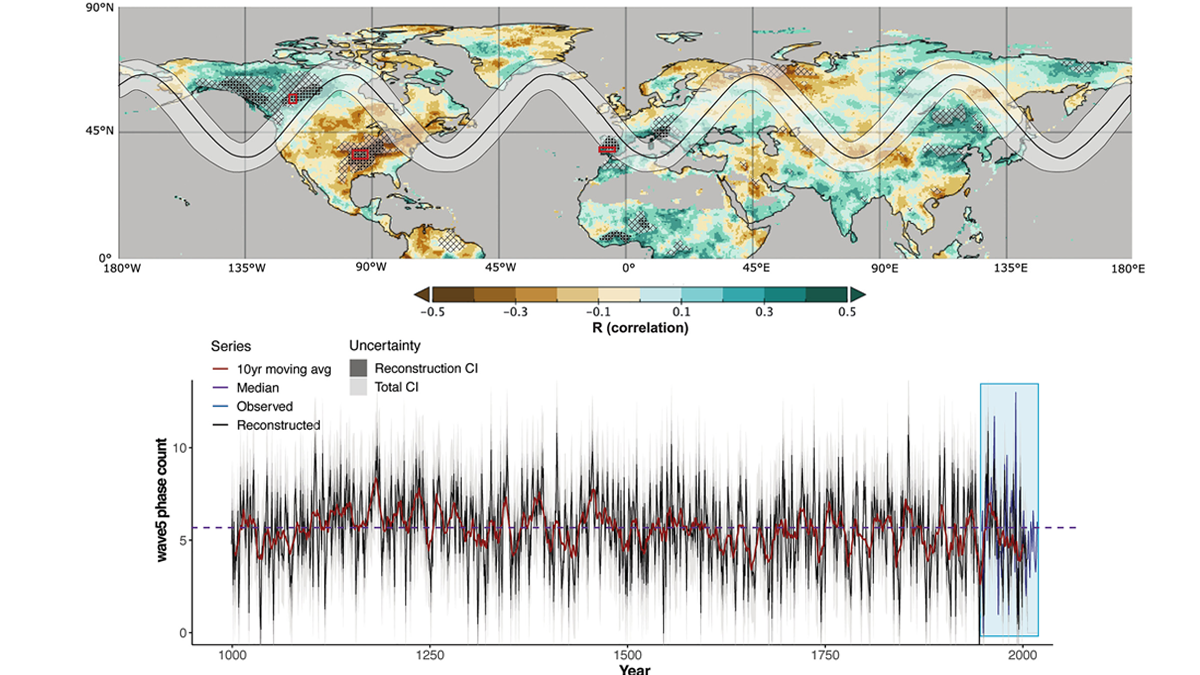
Tree Rings Record History of Jet Stream-Related Climate Extremes
Persistent spatial patterns of summer weather extremes in the northern hemisphere recorded in tree ring growth records provide a thousand-year history of jet stream ‘wave5’ dynamics.
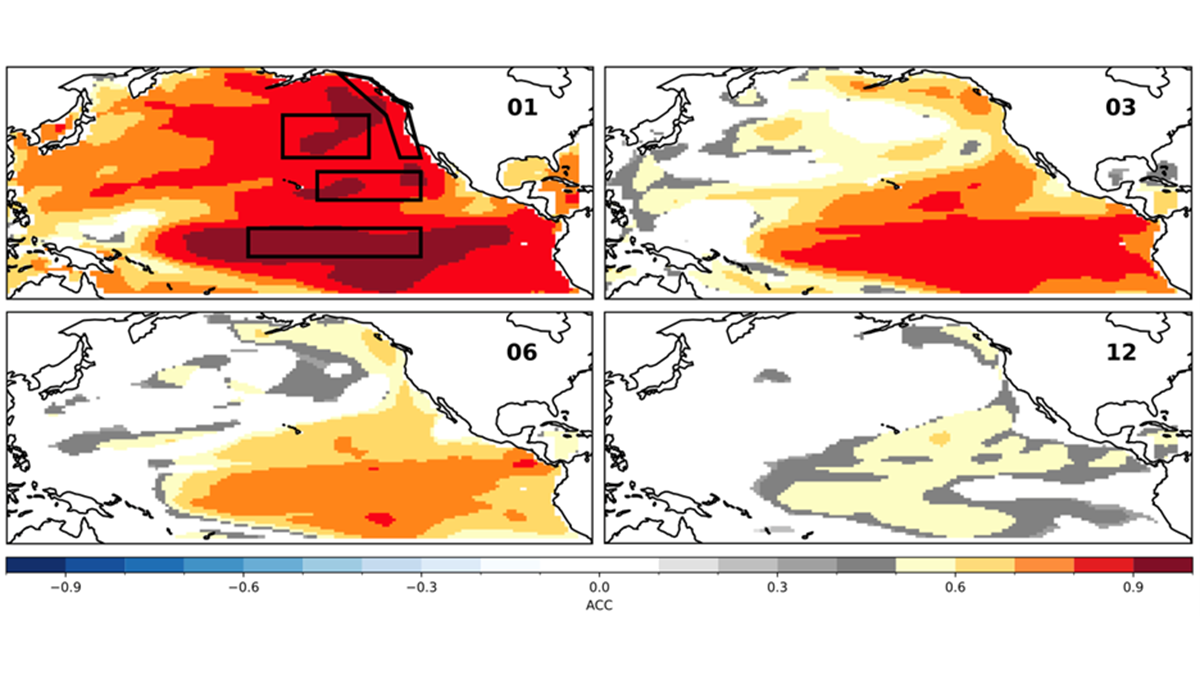
Decadal Forecasts with a SMYLE
Scientists use a large suite of simulations with an established climate model to predict the Pacific Decadal Oscillation up to one year in advance, but El Niño can still get in the way.
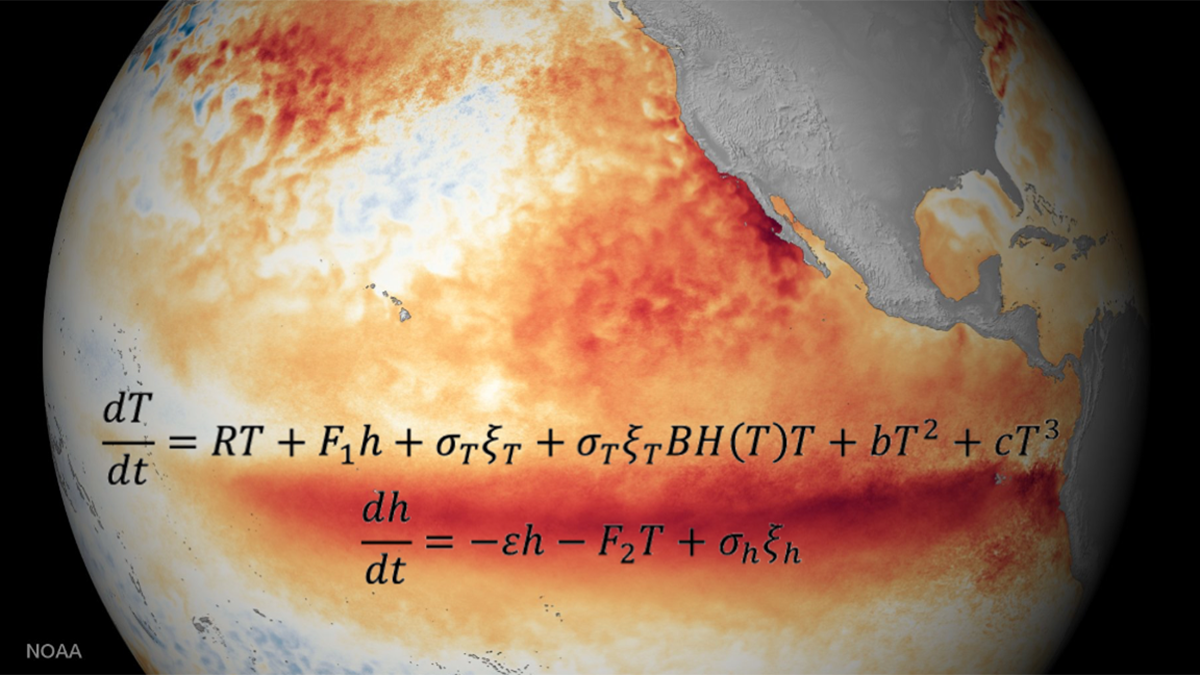
Two Equations that Unlock El Niño
Despite the El Niño–Southern Oscillation’s global reach and complex ocean–atmosphere interactions across timescales, two simple, elegant equations capture its key dynamics and defining properties.
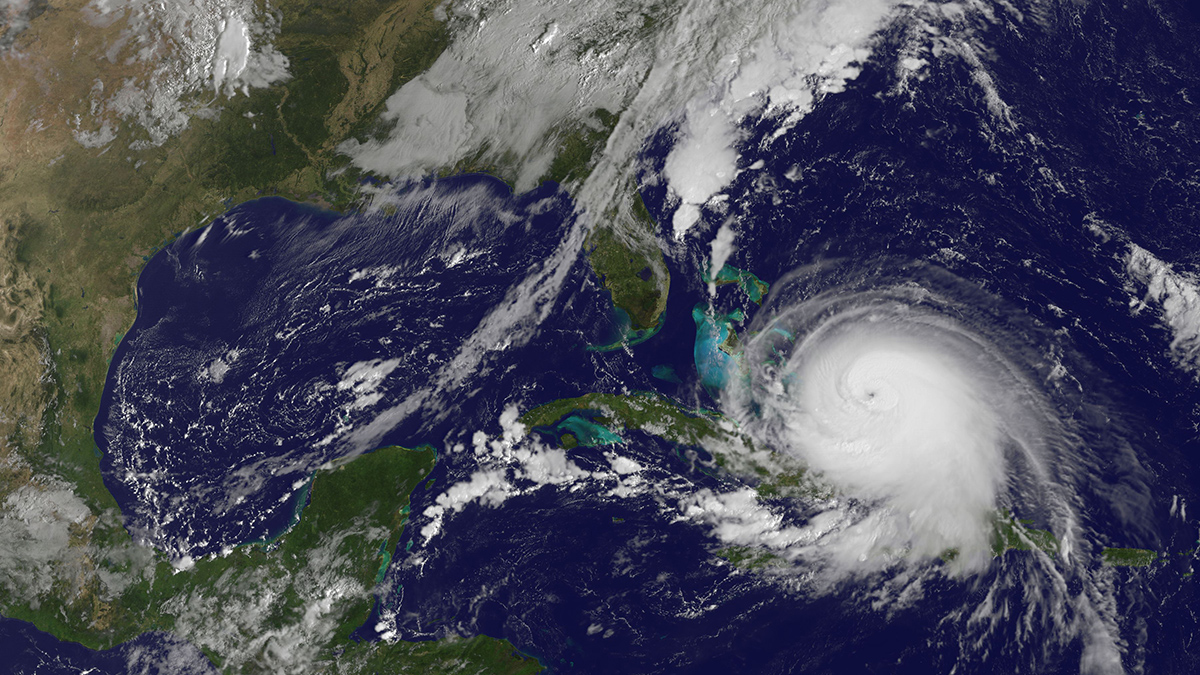
Busy Hurricane Season Expected in 2025
A new NOAA report predicts an active Atlantic hurricane season, though global weather patterns could still shift predictions.
The Interplay of ENSO and Immunity in Infectious Disease Outbreaks
El Niño and La Niña events can affect the spread of infectious diseases including cholera and dengue fever. The effects of some diseases may persist over several years.