Although all the exoplanets orbit closer than Mercury does to our Sun, liquid water may persist on some of them because their star radiates so little heat.
exoplanets
Closest Ever Terrestrial Exoplanet Found, Habitability Debated
Researchers are excited about a new, potentially habitable exoplanet orbiting our closest stellar neighbor, Proxima Centauri.
Venus's Unexpected, Electrifying Water Loss
New research shows that an electric field surrounding Venus is stripping its atmosphere of water—and the same phenomenon may plague exoplanets scientists hope might be habitable.
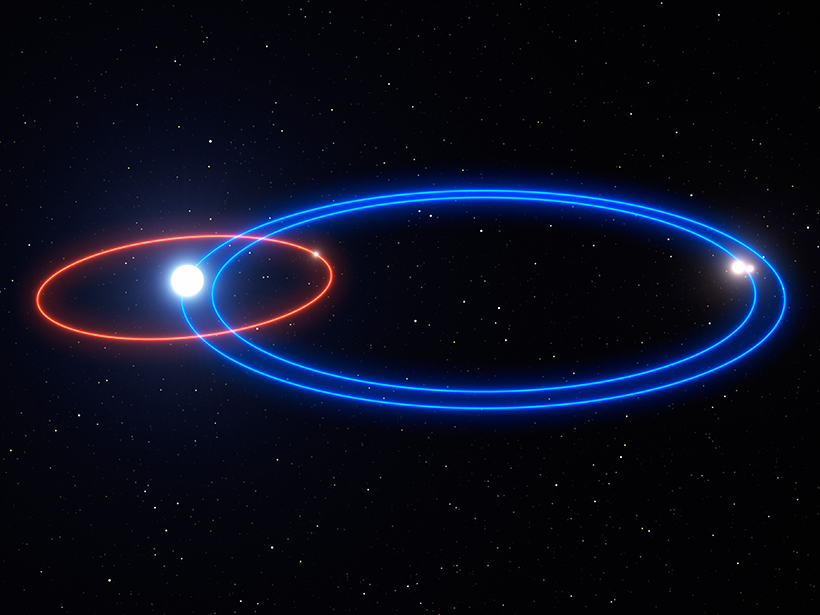
Exoplanet Found in Curious Triple-Star System
The newly discovered planet balances precariously in orbit within the star system, puzzling scientists.
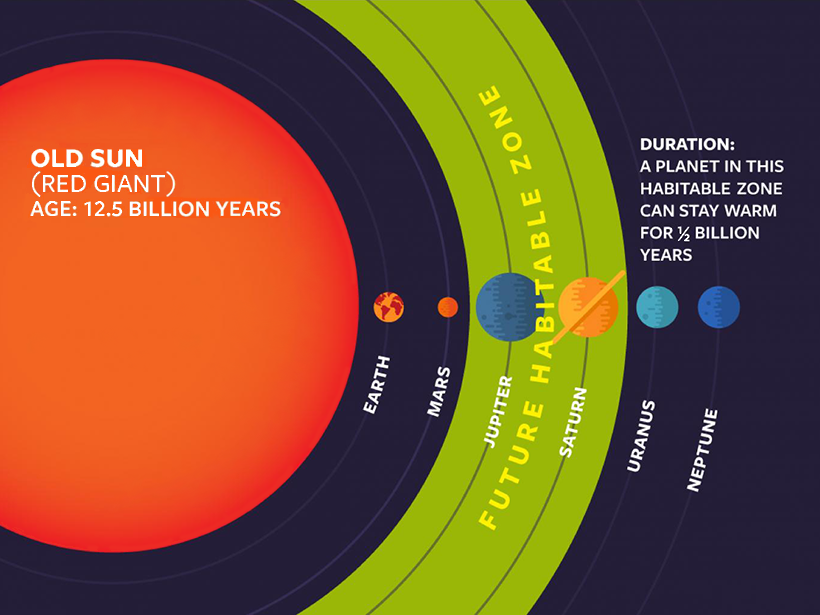
Aging Stars Make New Habitable Zones
Scientists searching for life in the universe now have a new target: the once-icy worlds orbiting red giants.
Largest Haul of Newly Verified Exoplanets Announced
About 550 of the planets could be rocky like the Earth, and nine of the planets orbit within their star's habitable zone.
Space Telescope Findings Suggest Molten Planetary Surface
Researchers studying the super-Earth 55 Cancri e spotted some puzzling features that provide a new vision of the orb's surface.
Comparing Planetary Climates to Investigate Climate Systems
Comparative Climates of Terrestrial Planets II (CCTP2 ): Understanding How Climate Systems Work; Moffett Field, California, 8–11 September 2015
New Step Toward Finding Earth 2.0
Researchers unveil a way to tease out the wobble of a star caused by unseen planets despite the confounding effects of star spots, which are the sunspots of distant stars.
Atmospheres Can Collapse on the Dark Sides of Planets
Planets that orbit close to their stars might lose their atmospheres along with any chance of life, but new models show a way in which these planets may retain their atmospheres and habitability.