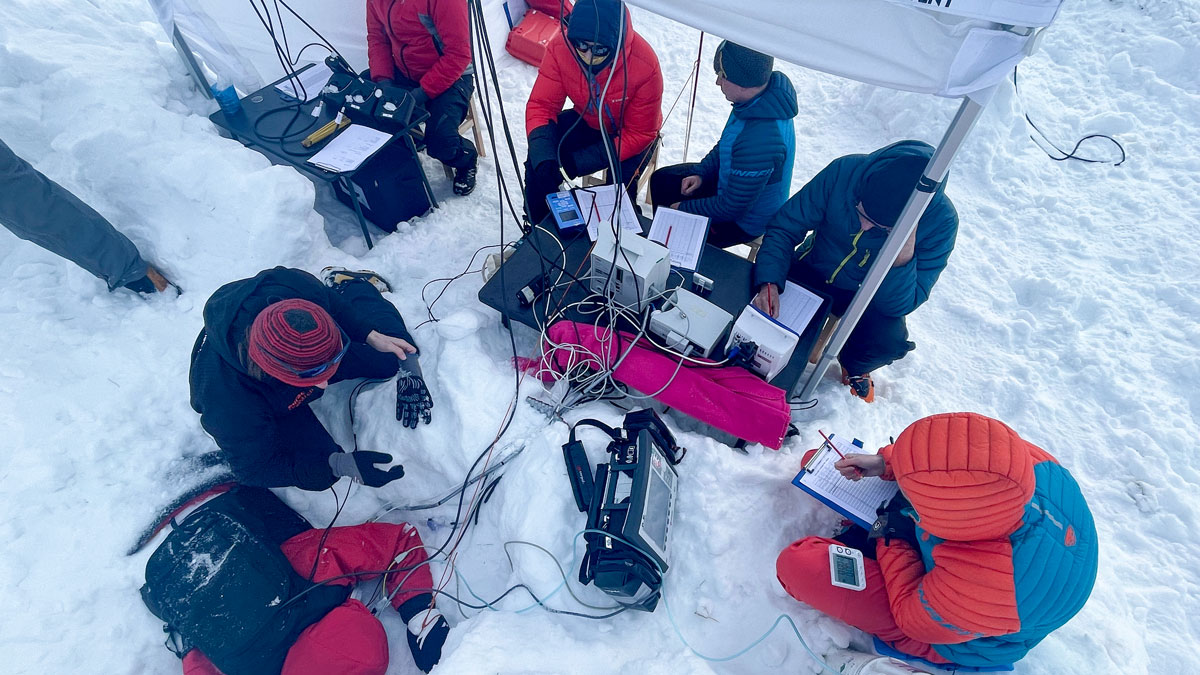
An Alpine medical team buried 24 volunteers in a mountain pass. Their study confirmed the efficacy of the Safeback SBX, which uses snow’s natural porosity to supply air to buried avalanche victims.
extreme events
Environmental Hazard Impact Metrics That Matter
Humans acutely experience climate change when they encounter extreme environmental conditions, but scientific definitions of “extreme” often don’t reflect communities’ complex lived experiences.
Europe Faces Increased Heat Mortality in Coming Decades
Extreme temperature caused by unchecked climate change could claim 2.3 million lives in Europe by 2100, a new study warns.
Dry Heat, Wet Heat, and Wetland Methane Emissions
Compound weather events—such as extreme cold or heat combined with severe dryness or precipitation—have a greater effect on wetland methane emissions than discrete weather extremes do.
Blasts from the Past: New Insights from Old Space Storms
Reassessment and comparison of past space weather events highlight the potential for Earth to experience destructive geomagnetic disturbances.
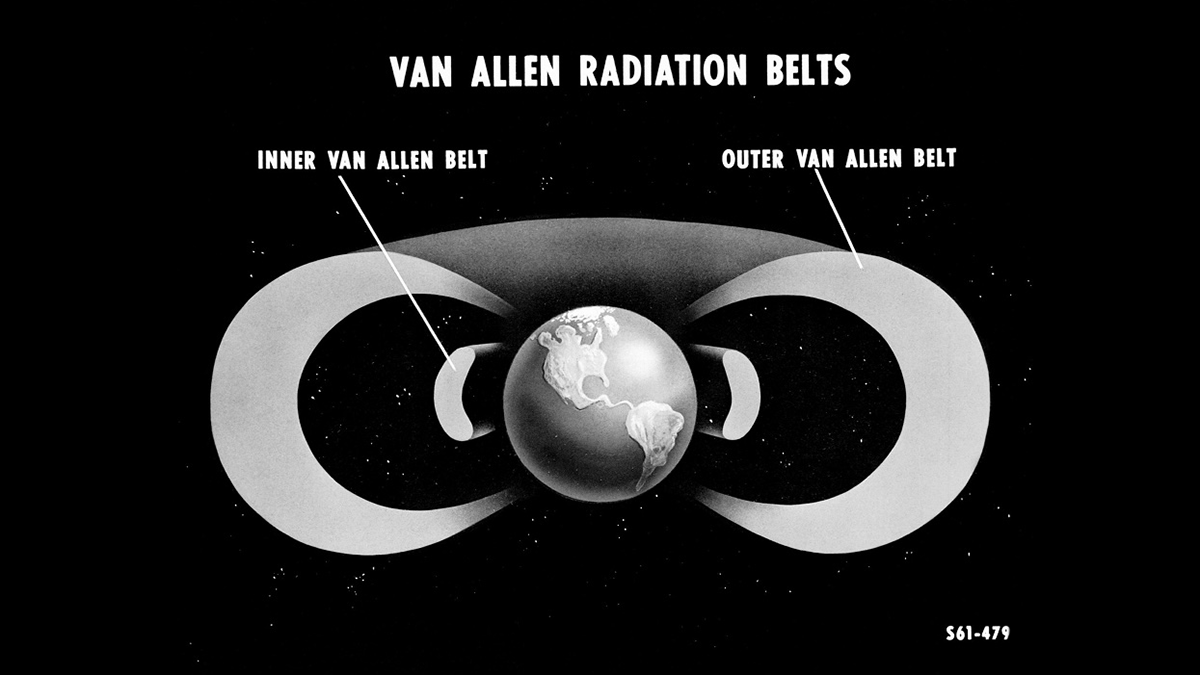
Audible Storm Waves Could Turbocharge Earth’s Radiation Belts
Electromagnetic chorus waves could generate more extreme radiation levels than previously thought, posing severe hazards for Earth-orbiting spacecraft.
Extreme Wildfires Make Their Own Weather
Extreme fires in the western United States and Southeast Asia influenced the local weather in ways that make fires and smoke pollution worse.
Tracking from Space how Extreme Drought Impacts Carbon Emissions
Carbon dioxide emissions from wildfires combined with reduced carbon uptake by intact ecosystems during the 2019-202
0 fire season to approximately double Australia’s annual carbon emissions.
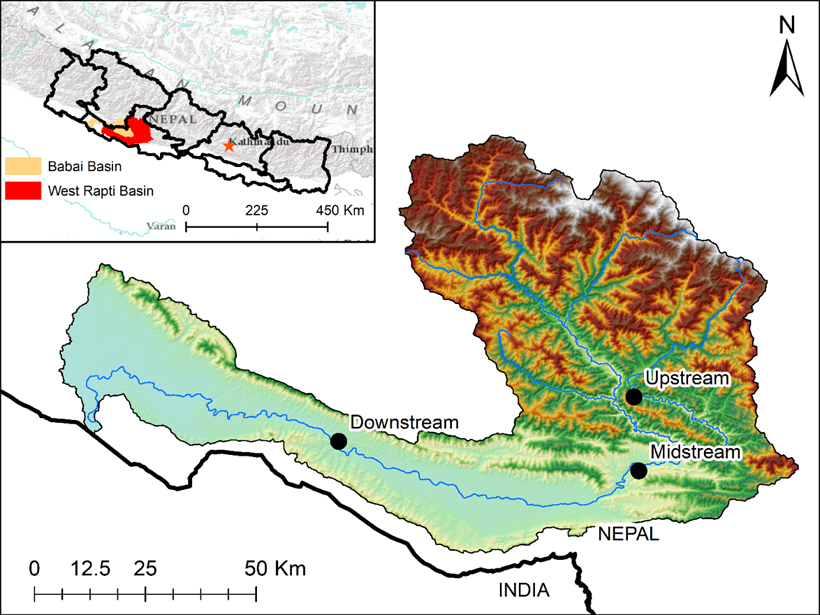
Satellite Estimates for Hydroclimatic Extremes
A new study corrects poor-performing satellite-based rainfall estimates with gauge data and also fills gauge data gaps using well-performing satellite-based rainfall estimates.
Siberian Heat Wave Nearly Impossible Without Human Influence
A new study finds that the exceptional temperatures seen in Siberia in the first half of 2020 would have been extremely unlikely without anthropogenic climate change.