Mathematical models describe how water moves through rocks in deep Earth.
Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems
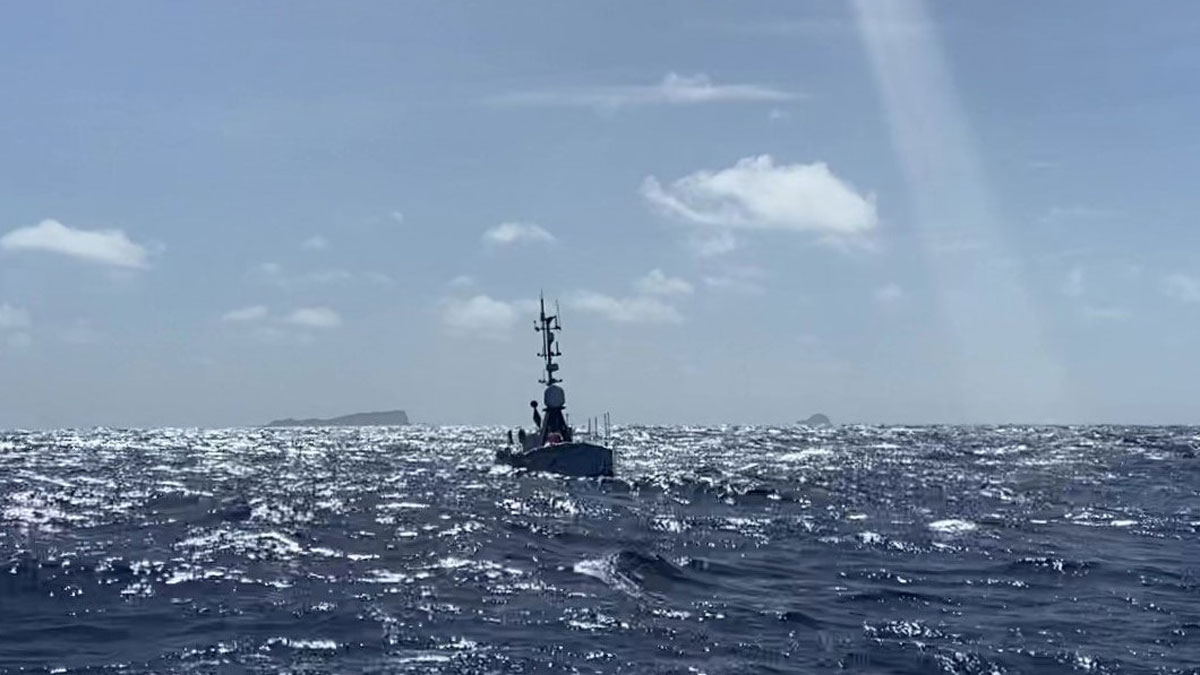
Exploring an Underwater Volcano from 16,000 Kilometers Away
Measurements of Hunga volcano’s crater continued for months after its 2022 eruption.
Unlocking Earth’s Terrestrial Sedimentary Record with Paleosols
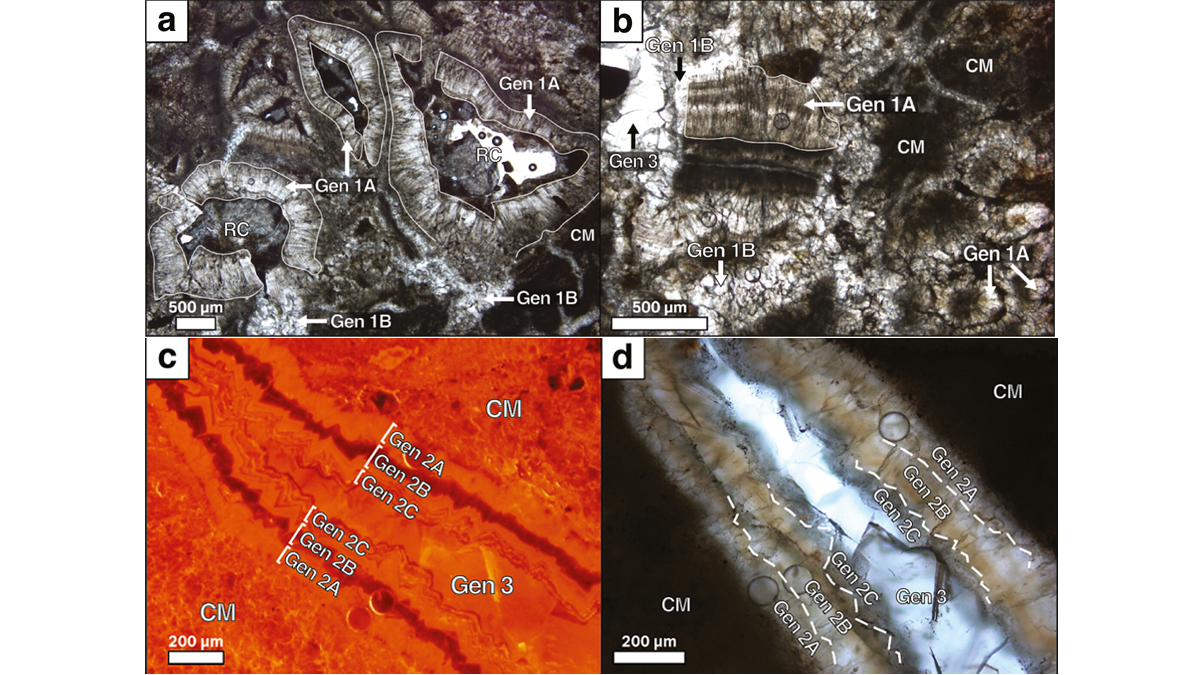
Harnessing the micro-stratigraphy of pedogenic carbonates, scientists have demonstrated that age determination of fossil soils is possible via uranium-lead dating.
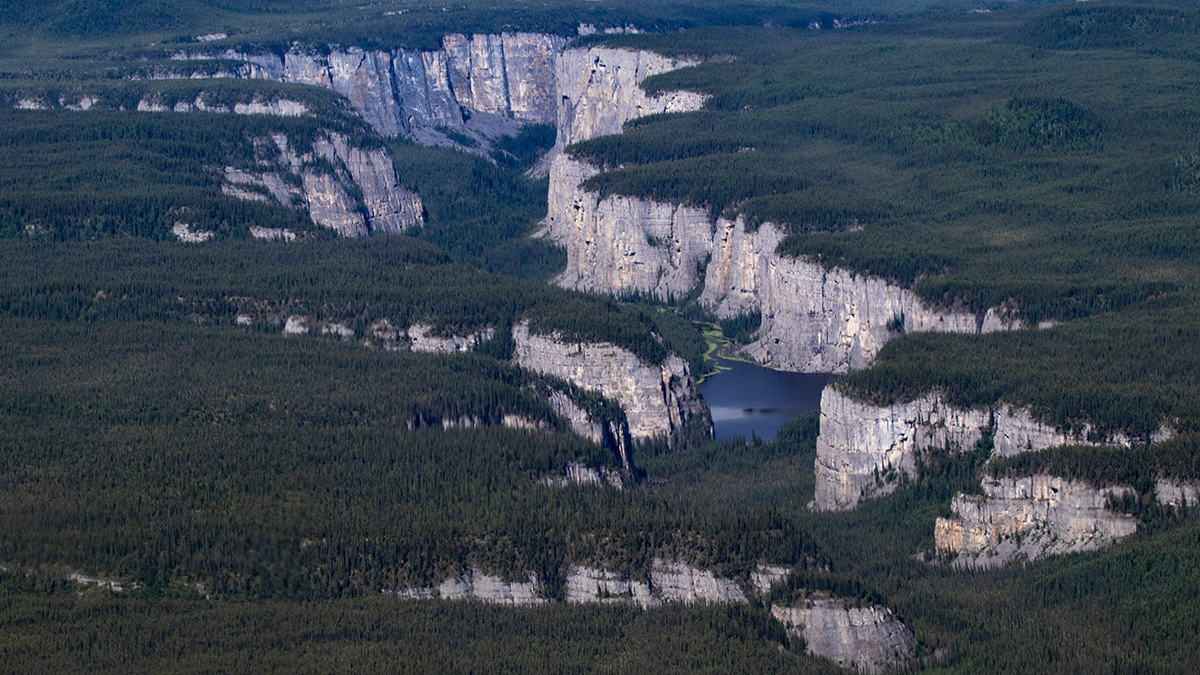
A Seismogenic Shear Zone Diagonal to the Main Himalayan Thrusts
Scientists document active seismic shear along a major lineament of Sikkim Himalaya diagonal to the Main Himalayan Thrusts.
How Tiny Cracks Lead to Large-Scale Faults
Researchers could soon gain new insights into fault development in Earth’s brittle crust, thanks to a computational approach that harnesses experimental observations of microscale rock damage.
The Nature of Mantle Flow May Depend on the Type of Slab Subducting
Researchers tease apart the links between slabs and mantle flow near subduction zones, upending some traditional views of subduction-induced mantle flow.
Plate Boundaries May Experience Higher Temperature and Stress Than We Thought
Surface heat flux data shed light on conditions deep below Earth’s surface, at a tectonic plate interface where major earthquakes initiate.
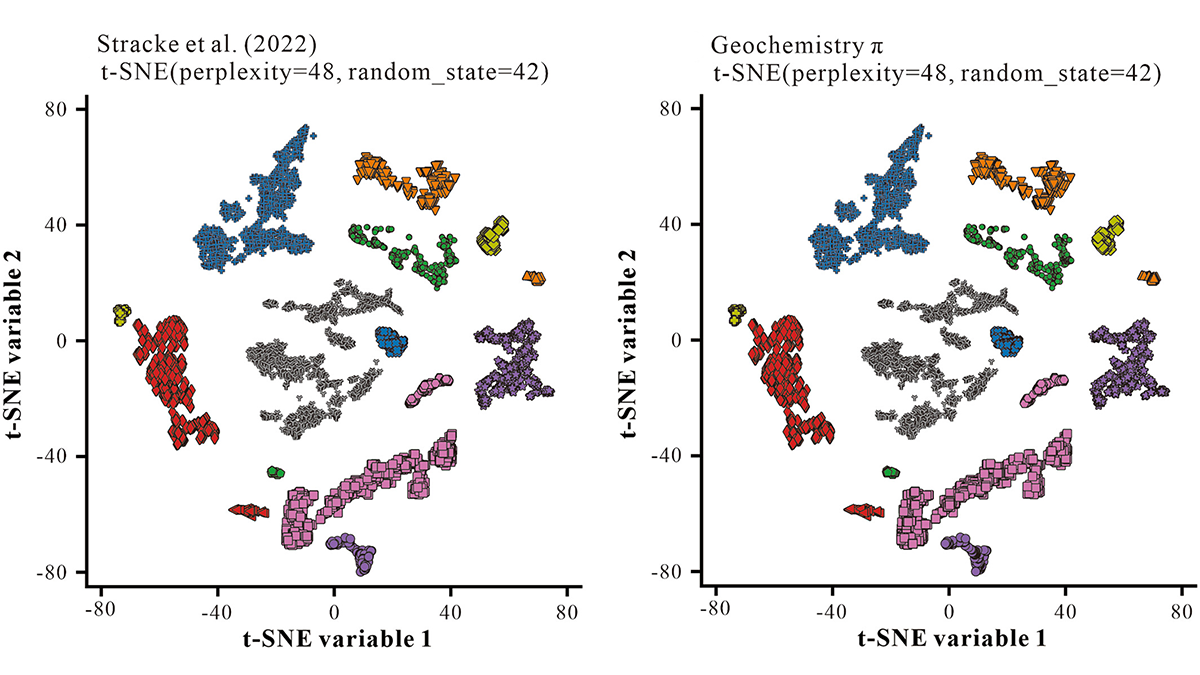
Machine Learning for Geochemists Who Don’t Want to Code
Geochemistry π is an easy-to-use step-by-step interface to carry out common machine learning tasks on geochemical data, including regression, clustering, classification, and dimension-reduction.
Some High-Threat Volcanoes Are Severely Understudied
Scientists have little understanding of where magma is stored along the Cascade Volcanic Arc or how its volcanoes could affect population centers.
Announcing New AGU Journal Editors-in-Chief Starting in 2024
AGU is excited to welcome new Editors-in-Chief for seven of our journals in 2024, including the founding Editor of JGR: Machine Learning and Computation.