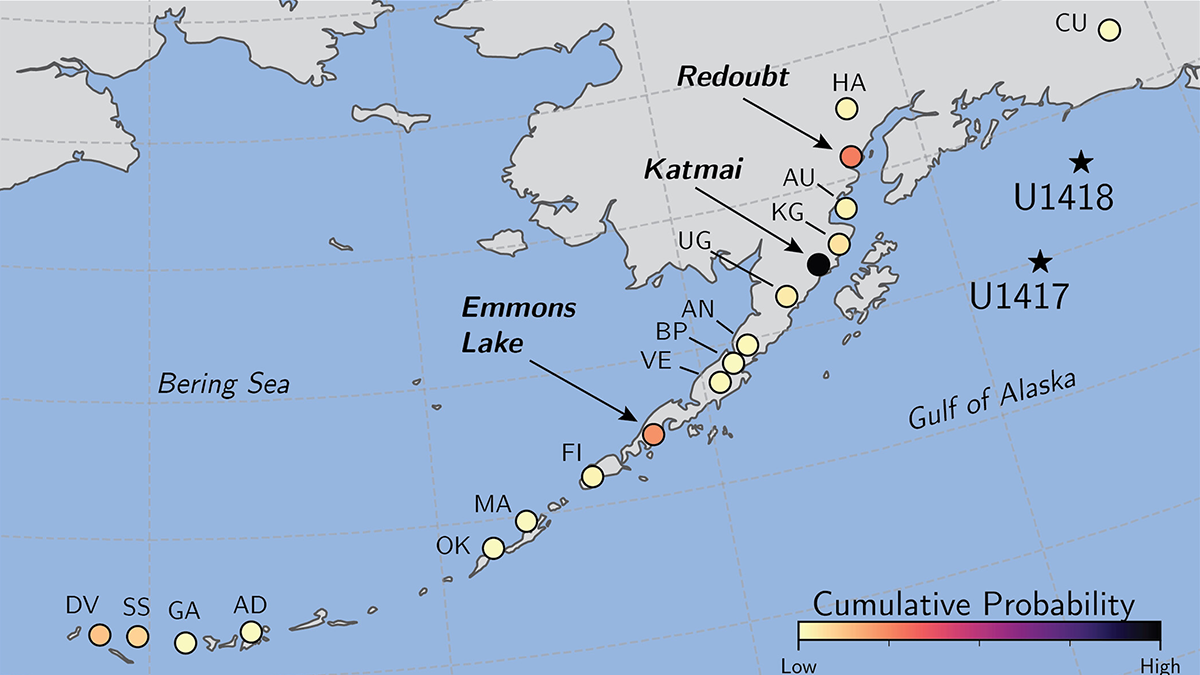
Tracing ash layers from explosive eruptions back to their source volcanoes is needed to evaluate hazards to population and aviation, a problem addressed by a new machine learning classification method.
Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems
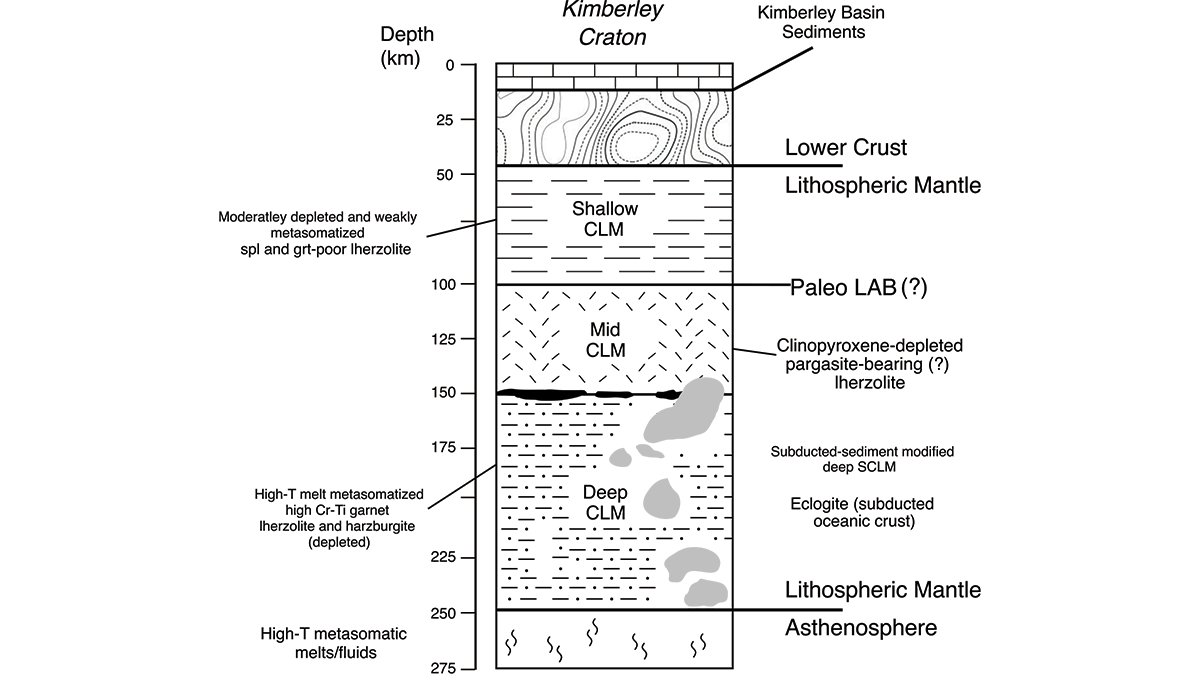
Piecing Together the Roots of the Ancient Australian Continent
Mineral compositions from numerous volcanic rocks that sample the mantle keel beneath Western Australia’s Kimberley Craton reveal the temperature and mineralogy that explain its long-lived stability.
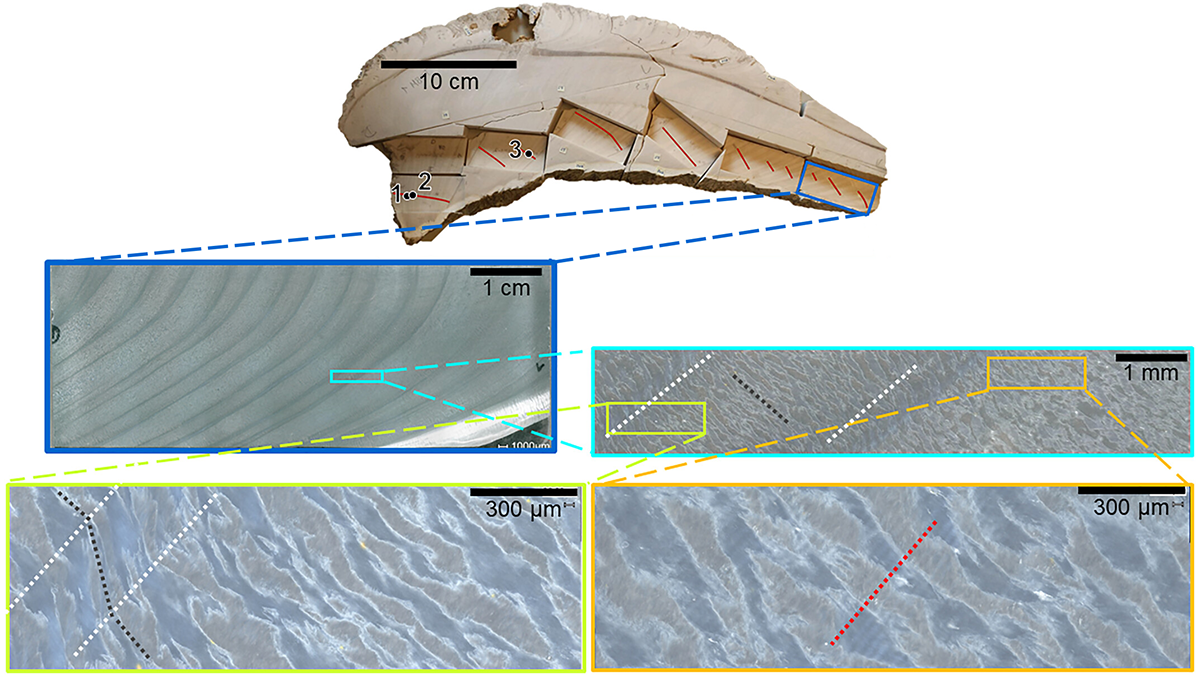
Ultra-High-Resolution Age Model in Clams Yields Daily Paleo-Data
Using geochemical techniques, scientists identify daily cycles in fossilized giant clams, which permits climate reconstructions at the weather timescale.
Talc May Make Mexico’s Subduction Zone More Slippery
Production of the weak, water-bearing mineral at the interface between the Cocos and North American Plates could contribute to the occurrence of poorly understood episodic tremor and slow slip.
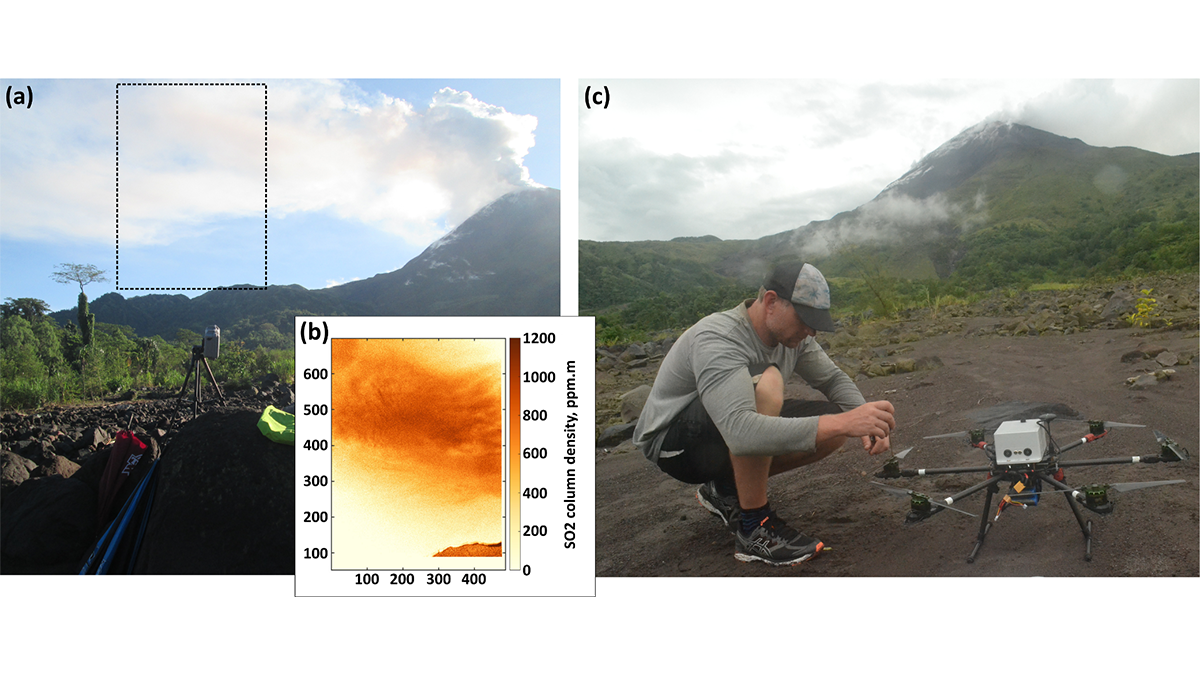
Send in the Drones: Safely Monitoring Volcanic Gas Emissions
New drone technology was combined with satellite and ground-based data to improve volcanic gas flux monitoring at the remote Bagana Volcano in Papua New Guinea.
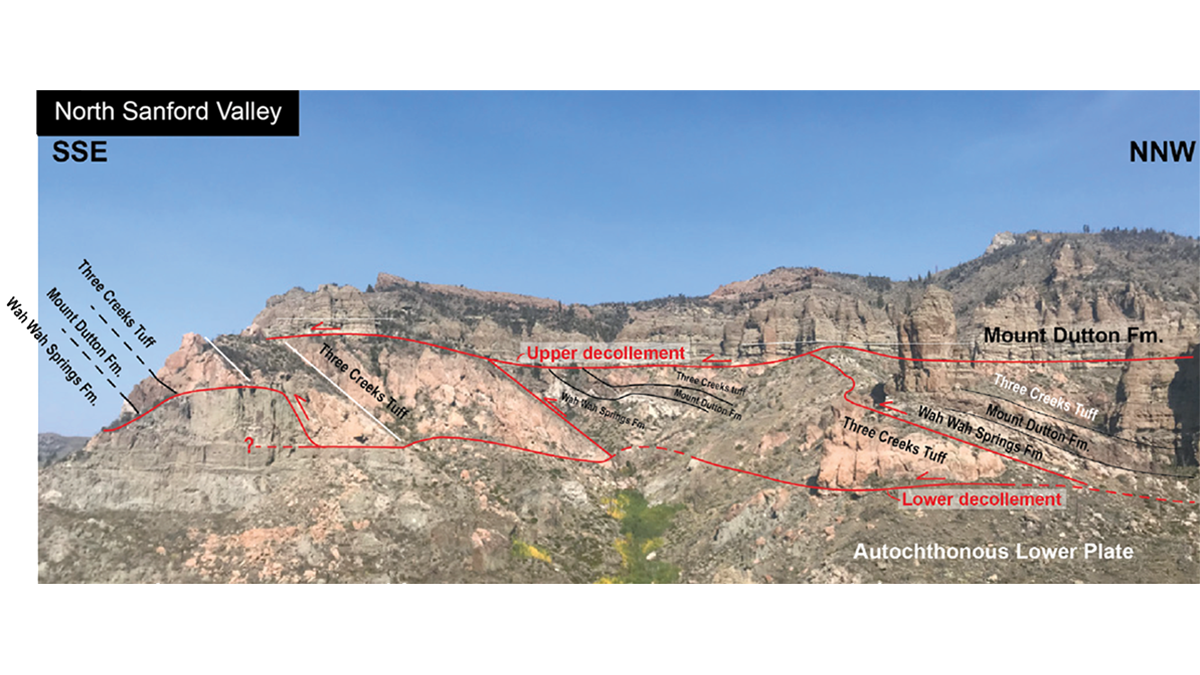
A Giant Rockslide on a Bed of Steam
Detailed observations of the giant Sevier gravity slide in Utah show that the exceedingly low basal friction required for its rapid emplacement was developed by trapped thermally pressurized fluids.
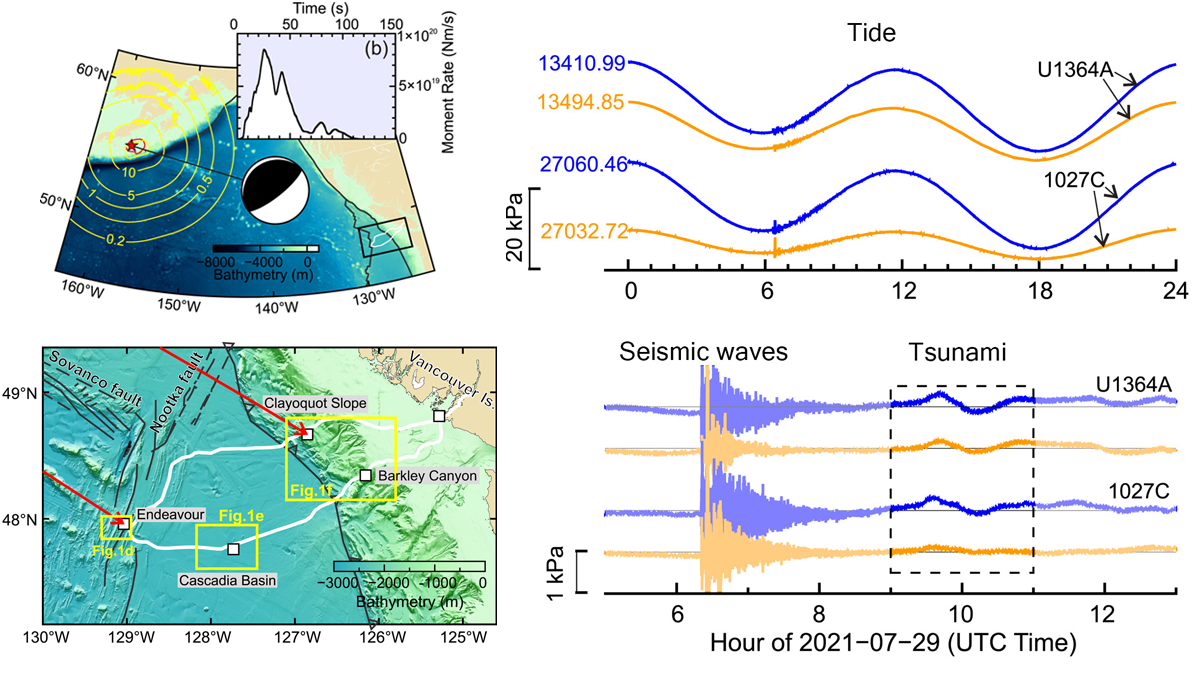
Under Pressure: Recording Earthquakes at and Below the Seafloor
Cabled ocean-floor observatories record ground shaking and pressure variations, which contribute to early warning systems and give us a unique view of the ocean–crust coupling.
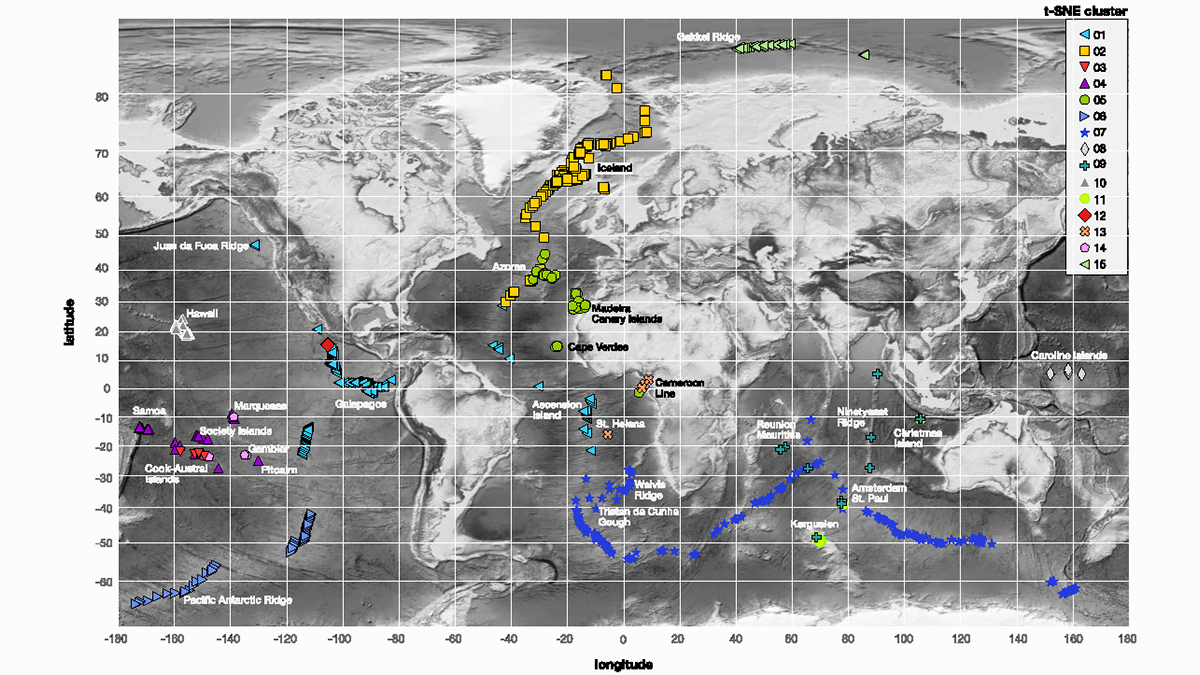
Machine Learning Looks Anew at Isotope Ratios in Oceanic Basalts
While past attempts to define isotopic endmembers and assign them a geodynamic significance ended in controversy, a machine-learning clustering algorithm offers a solution to this classical problem.
Probing the Sedimentology of a Continental Megathrust
Detailed analysis of sediments covering the Main Frontal Thrust in Nepal show how climate-driven baselevel changes affect sedimentation and should be considered when inferring thrust activity.
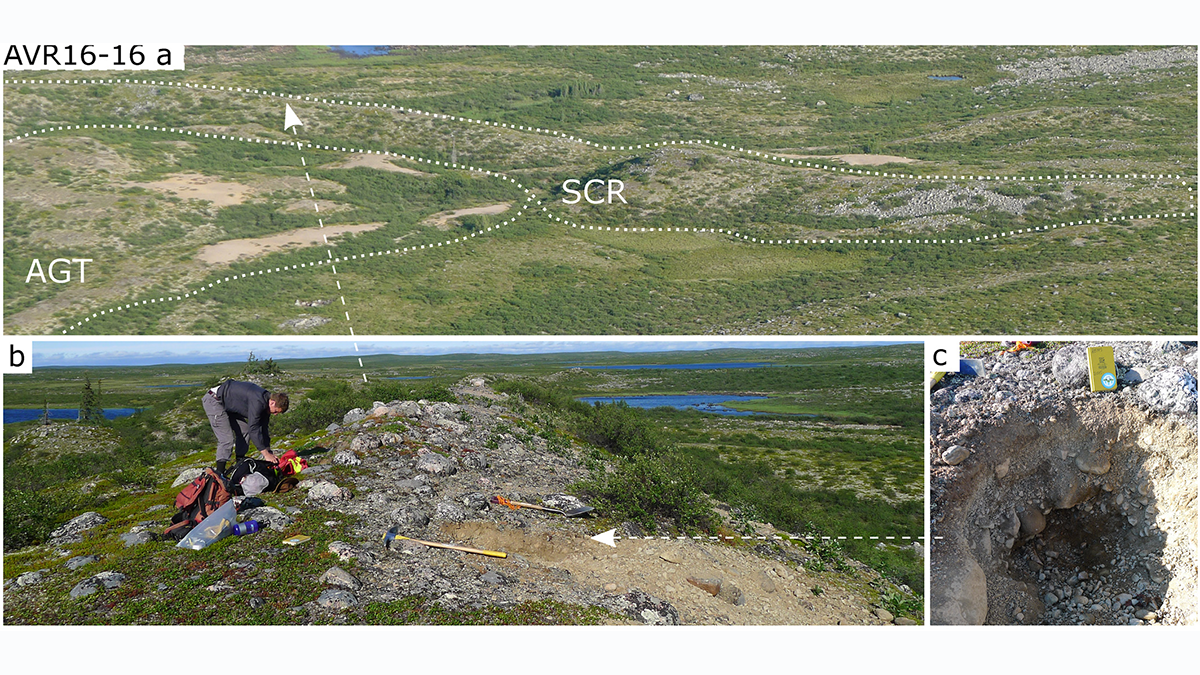
Searching for Earth’s Oldest Rocks in its Youngest Deposits
By sampling and analyzing zircons from glacial eskers dating from about 20,000 years ago, the extent of the oldest known rocks on Earth can be better mapped and constrained.