A mineral common throughout the solar system nudges a reaction that produces sugar molecules from formaldehyde.
geochemistry
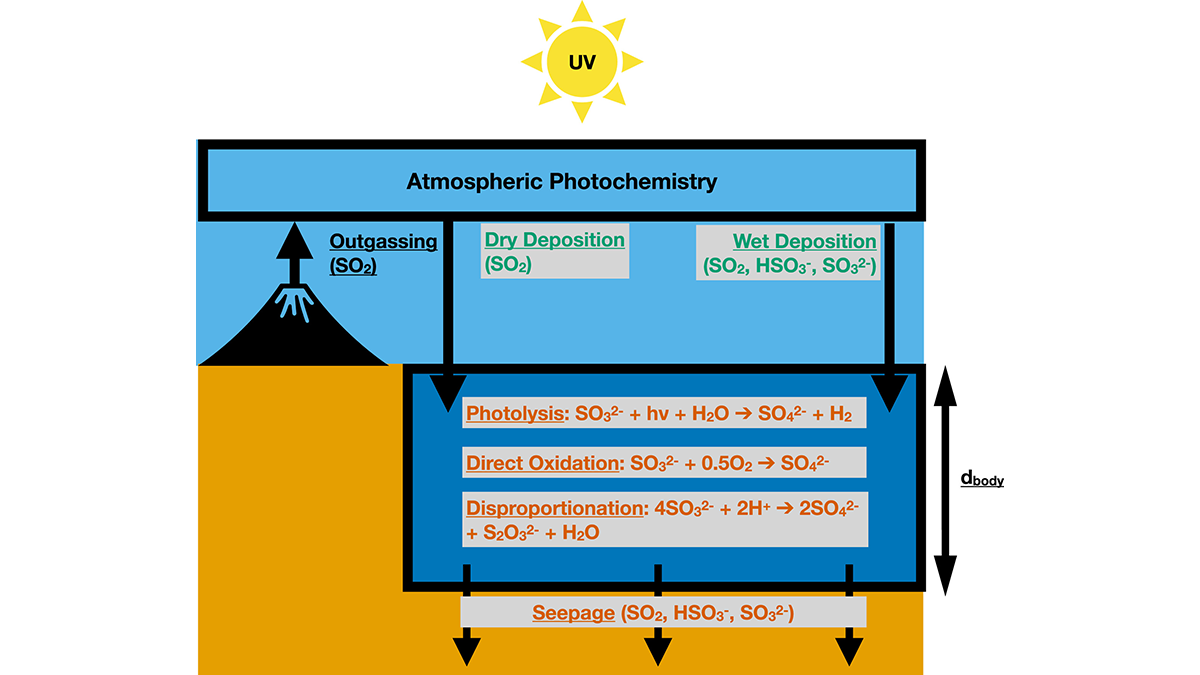
New Constraints on Sulfur Cycling in the Prebiotic Earth
Experiments constraining rates of aqueous reactions and photolysis coupled with a global model constrain the abundance and chemical speciation of sulfur in early Earth’s atmosphere and oceans.
Mammal Droppings Preserve Human and Climate History on the Tibetan Plateau
Geochemical signatures in sediment, which includes organic molecules from human and animal poop, help scientists track the rise and fall of the Tibetan Empire.
These Four Exoplanets Have Wild, Rocky Weather
On many exoplanets, conditions are so exotic that minerals form clouds and fall as rain. Recent studies revealed the rocky weather on these four exoplanets in more detail than ever before.
An Electrifying Approach to Carbon Capture
A new sodium-ion “battery” promises an environmentally friendly method of sequestering carbon in the ocean, but experts remain cautious.
Humans Have Boosted Atmospheric Mercury Concentrations Sevenfold
A new baseline of volcanic contributions to the global mercury cycle reveals how drastically human activities have increased the element’s concentration in the atmosphere.
Meteor Impact Site Holds 200-Million-Year-Old Atmospheric Snapshot
Minerals formed in short-lived hydrothermal systems set off by a meteor impact in France preserved information about noble gases in the ancient atmosphere.
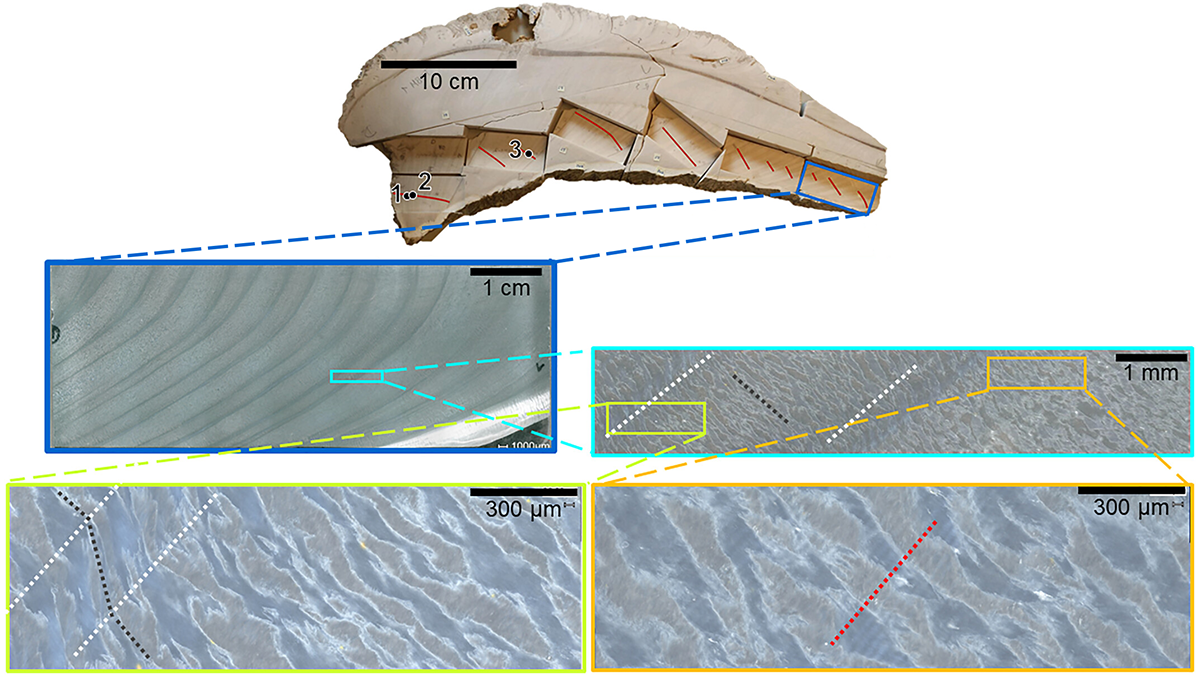
Ultra-High-Resolution Age Model in Clams Yields Daily Paleo-Data
Using geochemical techniques, scientists identify daily cycles in fossilized giant clams, which permits climate reconstructions at the weather timescale.
Natural Nitrogen Emissions Are Rising in California
Wildfires and soil microbes are releasing more nitrogen oxides in California as the climate gets warmer and drier.
Ancient Mars May Have Had a Cyclical Climate
Hexagonal structures in sediments are evidence of repeated wet and dry conditions on the Red Planet.