The Red Planet’s Grasberg and Burns formations have different compositions today, but they may have started out the same way.
geochemistry
Wildfire Smoke Destroys Ozone
Smoke aerosols from large wildfires are the perfect reaction surface for chlorine chemicals, speeding their transformation from ozone-friendly forms to reactive ones.
Hydrogen May Push Some Exoplanets off a Cliff
High-pressure reactions of hydrogen and iron could explain gaps in the distribution of exoplanets.
A New Approach to Spinning-Up Passive Tracers in Ocean Models
A new computational method enables finding steady-state distributions of tracers in ocean circulation models, opening opportunities for physical and biogeochemical insight.
Silicate Weathering Throttles the Global Thermostat
The natural breakdown of some rocks sucks carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere. Knowing how quickly it happens could help scientists engineer solutions to the climate crisis.
A Tiny New Device Could Help Find Extraterrestrial Life
Researchers developed a mini analyzer that could be a giant step forward in the search for life and habitable environments beyond Earth.
What Electrons Can Tell Us About the Speed of Sand
A new sediment tracer uses the interactions between radiation, charge, and the Sun to uncover the hidden transport histories of sand grains.
UV Radiation Contributed to Earth’s Biggest Mass Extinction
To find the first direct evidence of heightened UV radiation during the end-Permian mass extinction, researchers turned to chemical evidence preserved in pollen grains.
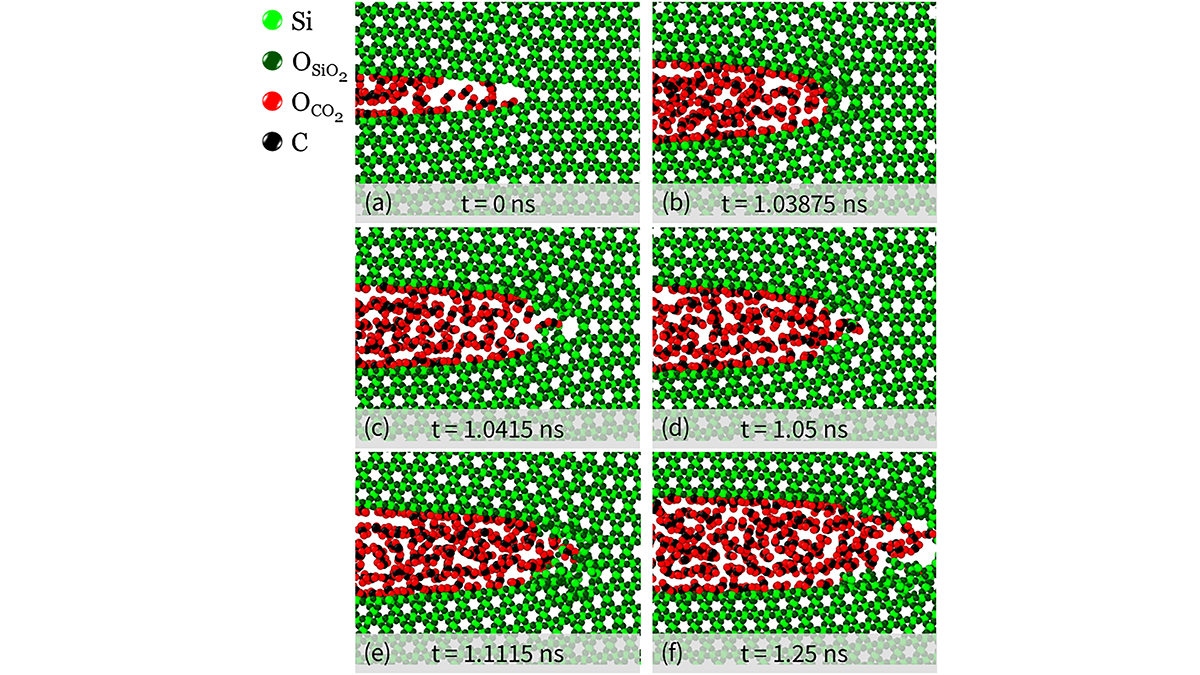
CO2 Reduces the Onset of Fracturing at the Nanoscale in Quartz
Large scale molecular dynamics simulations unravel the coupled processes at work during fracturing and flow of carbon dioxide and water in quartz grains at the nanoscale.
Does This Mineral Indicate Oxygen on Mars?
Manganese oxides are thought to be a signature of atmospheric oxygen. But on the Red Planet, recent results suggest they might be more of a red herring.