Cosmogenic geochronology of Scotland’s vanished glaciers indicates that the paradigm of weakened North Atlantic currents causing a rapid regional cooling is no longer valid.
geochronology
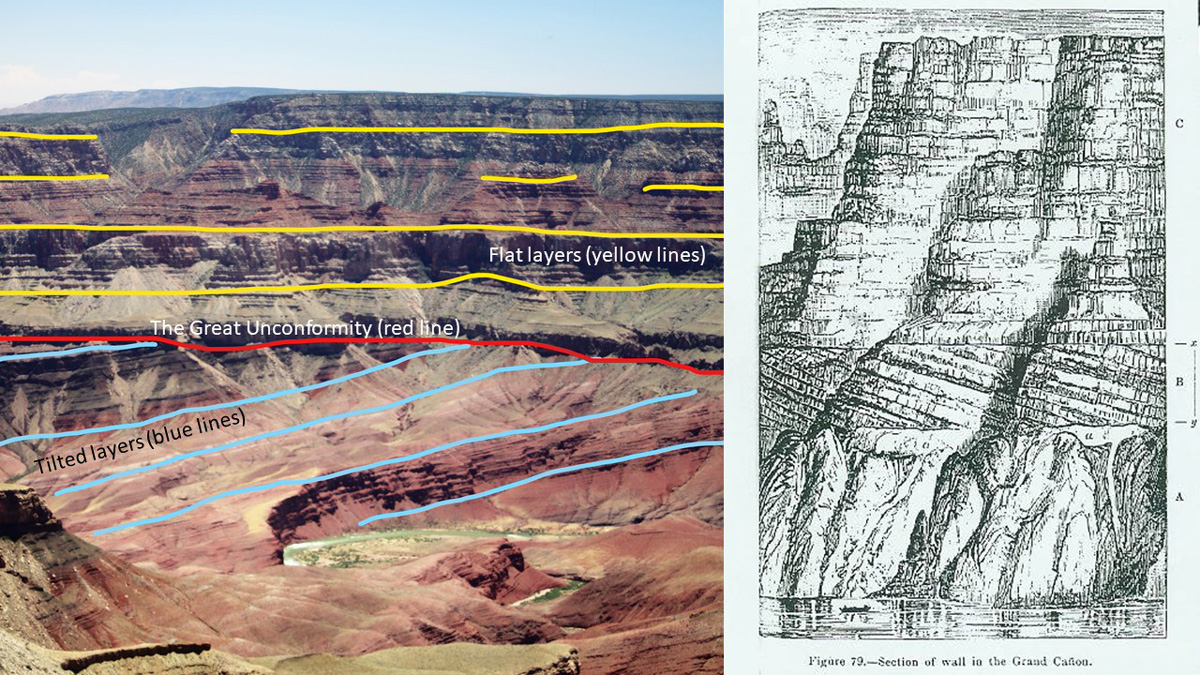
The Great Unconformity or Great Unconformities?
Some scientists think the Great Unconformity was caused by Snowball Earth’s glaciations. Recent work suggests these phenomena might not be related.
A Day in the Life Used to Be 17 Hours
The Moon was a lot closer to Earth 2.46 billion years ago, and the shorter distance contributed to shorter days.
研究揭示尼泊尔西部喜马拉雅港湾状地形的形成
研究人员通过热运动学研究发现,沿着板块汇聚界面大型逆冲断层在中下部地壳深处的地壳物质堆叠塑造了高原的生长和区域水系的发育。
What Can Zircons Tell Us About the Evolution of Plants?
The versatile mineral could contain evidence of the evolution of land plants and their effect on the sedimentary system.
Supervolcanoes Linger a While, Then Rush to Erupt
Geologists examined crystals in rock from four massive eruptions in the Chilean Andes.
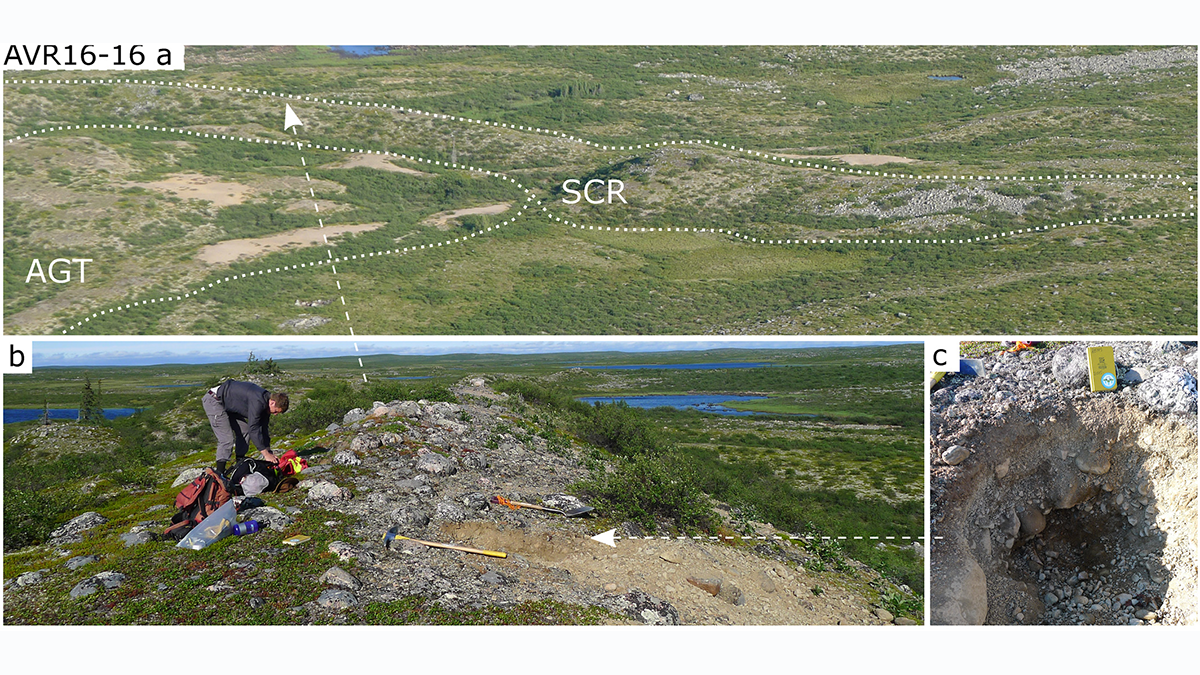
Uncovering the Formation of the Western Nepal Embayment
Using thermokinematics, researchers have found that crustal accretion along the megathrust at mid-lower crustal depths shapes plateau growth and regional drainage development.
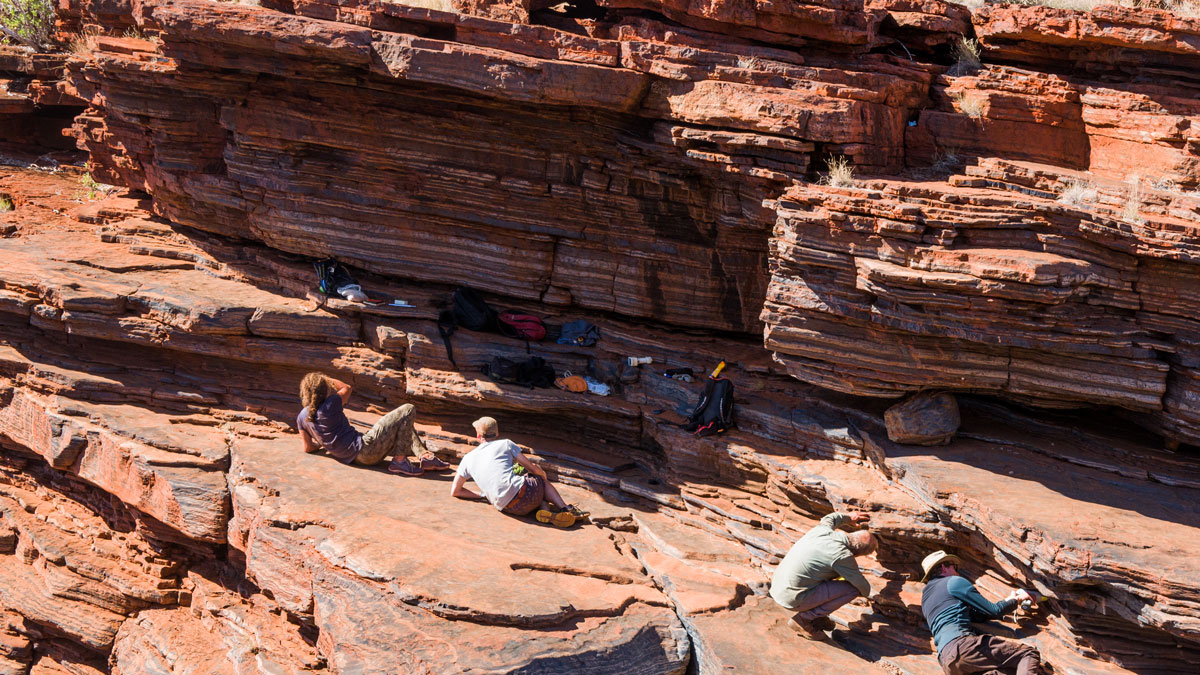
Searching for Earth’s Oldest Rocks in its Youngest Deposits
By sampling and analyzing zircons from glacial eskers dating from about 20,000 years ago, the extent of the oldest known rocks on Earth can be better mapped and constrained.
Sorting Minerals Differently Could Usher a New Era for Mineralogy
Grouping minerals by how they were formed yields insights into our planet’s evolution across billions of years.
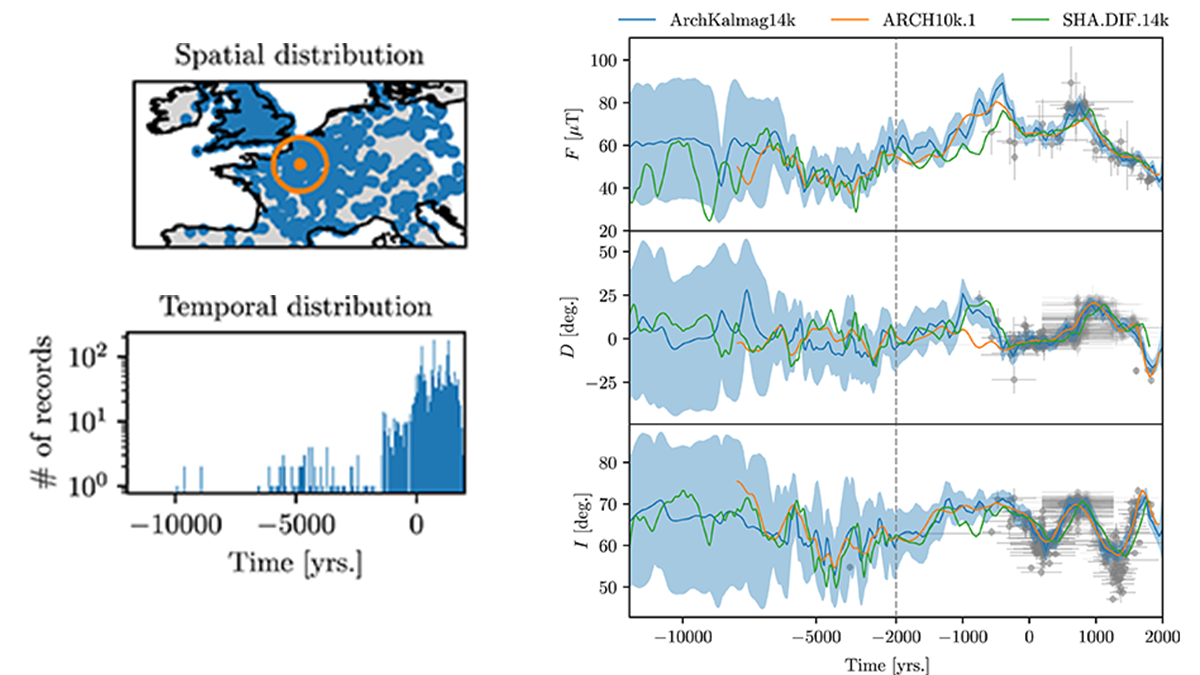
Time-Step Filtering in Holocene Global Magnetic Field Models
Through a local fixed time-step filter, global Holocene magnetic field models remain mathematically tractable refining our insight into field variability and improving archeological dating.