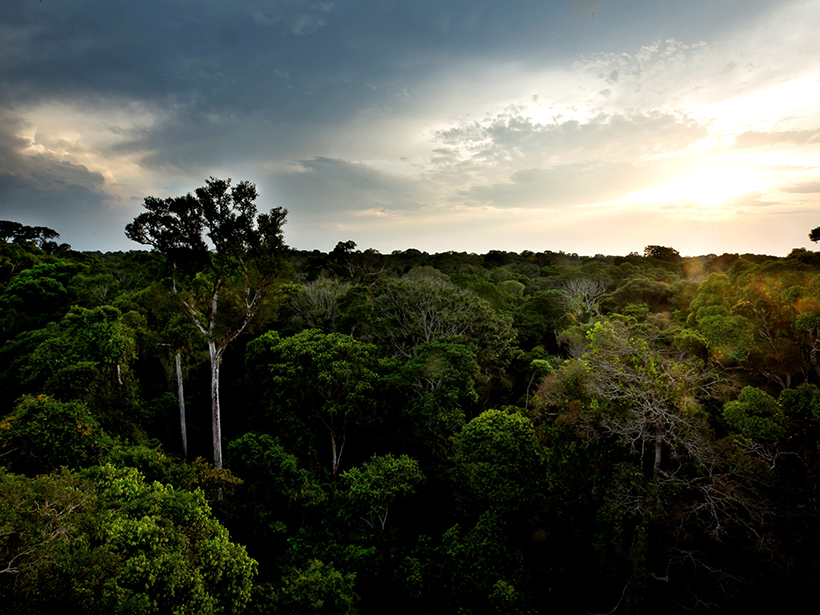
Evapotranspiration is the exchange of water vapor between land and the atmosphere, and it is hard to measure and model. A new study shows promise for its estimation over large, vegetated landscapes.
Geophysical Research Letters
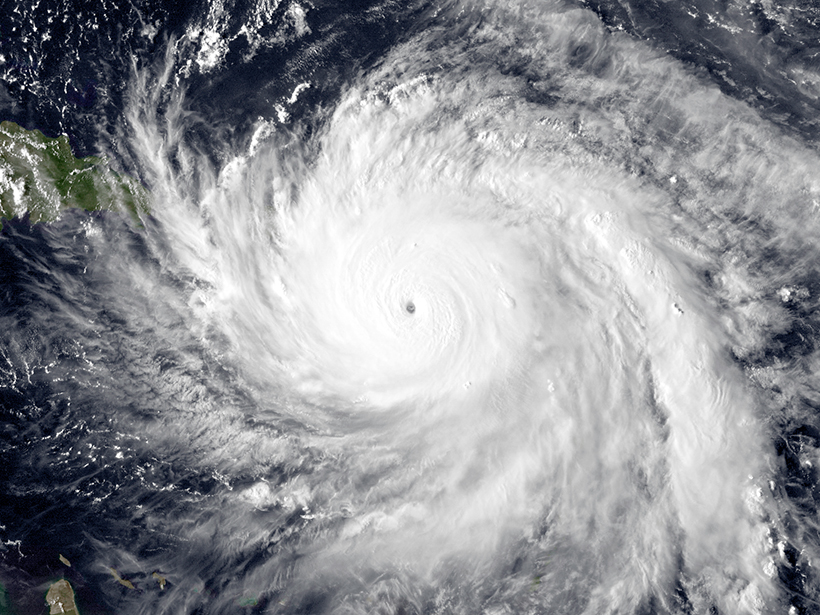
A Better Understanding of Tropical Cyclones
A new model of how anvil clouds form could improve short-term hurricane forecasts.
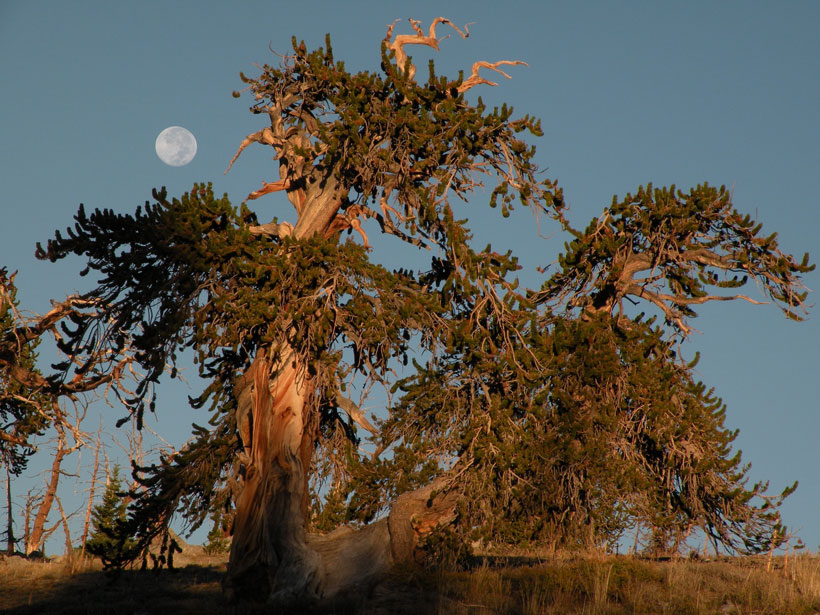
Topography and Microclimate Shape Tree Ring Growth
Wizened bristlecone pines in California reveal past climate trends, and new research shows how slight variations in landscape position drive different growth patterns in trees’ annual rings.
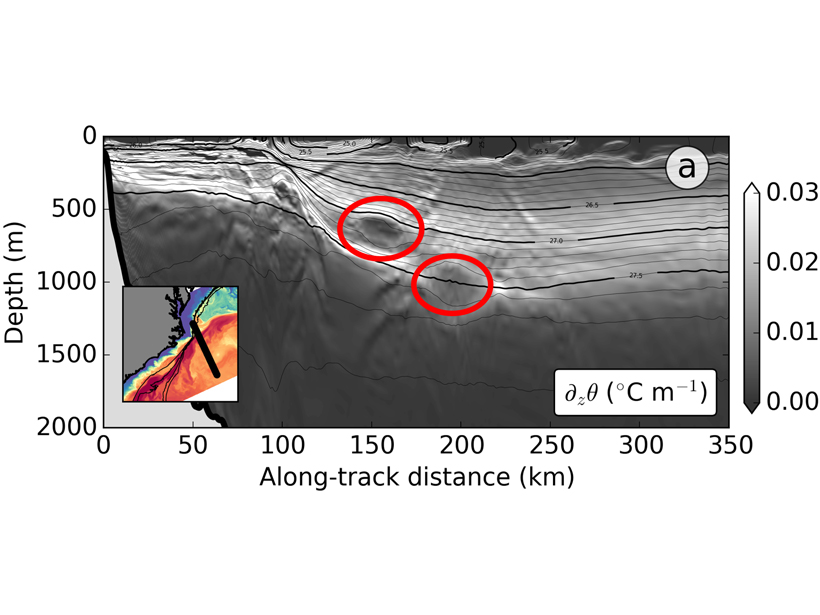
Wrinkles and Bumps in the Gulf Stream
Observations of tiny vortices in the ocean interior provide hints of a dynamic richness of the deep ocean that we are yet to fully appreciate.
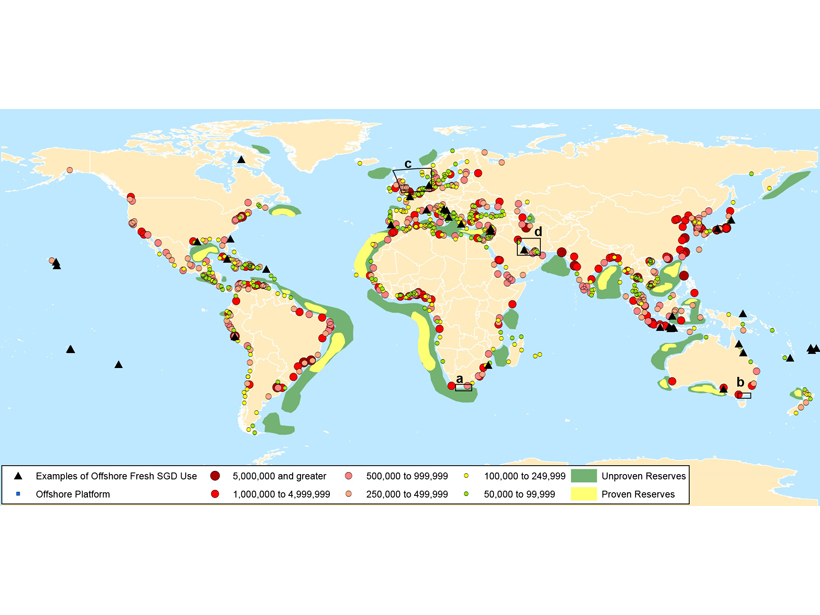
Pumping Offshore Groundwater Resources Has Consequences on Land
While vast volumes of fresh groundwater are located offshore, pumping these reserves can also deplete on-shore aquifers and cause land subsidence.
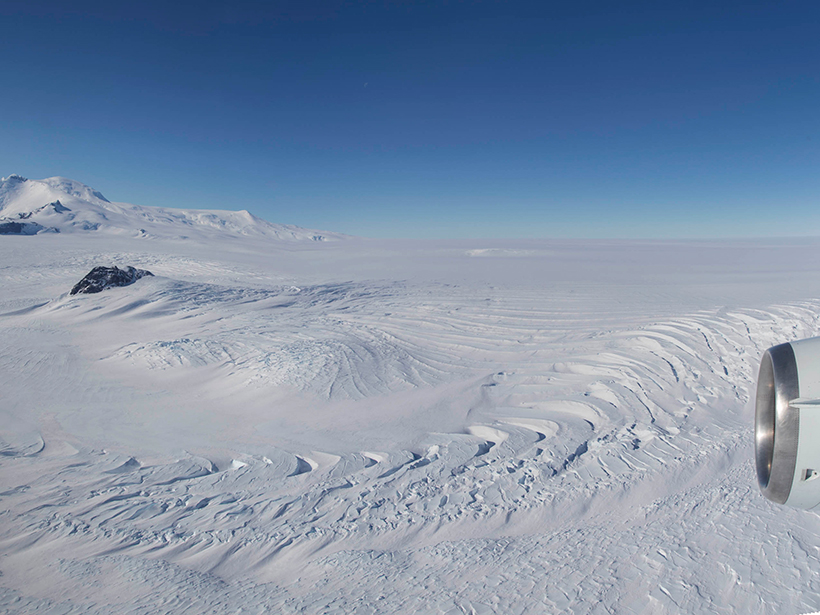
What’s Missing from Antarctic Ice Sheet Loss Predictions?
Accurately modeling melt rates in specific ice shelf locations is critical for forecasting how Antarctica’s ice sheet will respond to climate change.
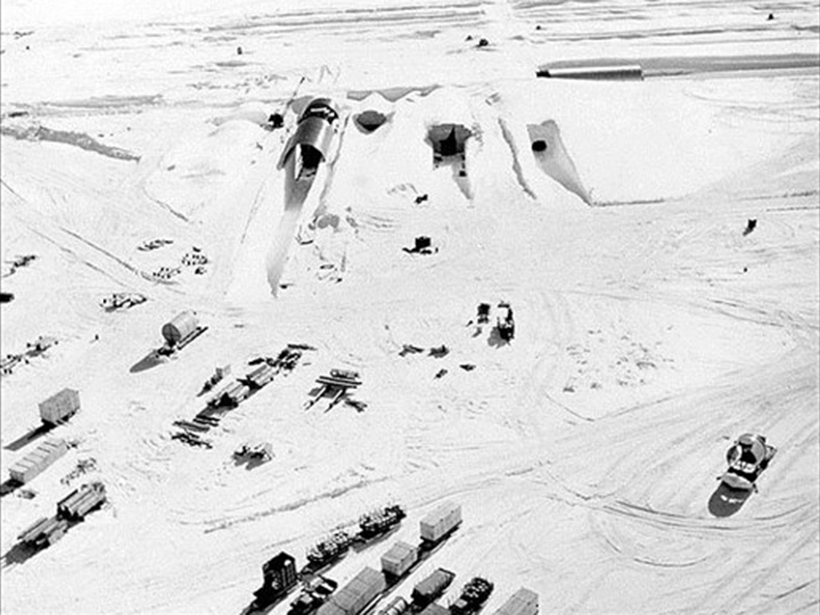
Podcast: Toxic City Under the Ice
In the latest episode of its Centennial series, AGU’s Third Pod from the Sun recounts the history of a top-secret military project with unintended environmental consequences.
A Step Closer to Quantifying Global Photosynthesis in Real Time
High spatial and temporal resolutions of a data set on a proxy for plant photosynthesis, as well as contiguous global coverage, have great utility for a variety of applications.
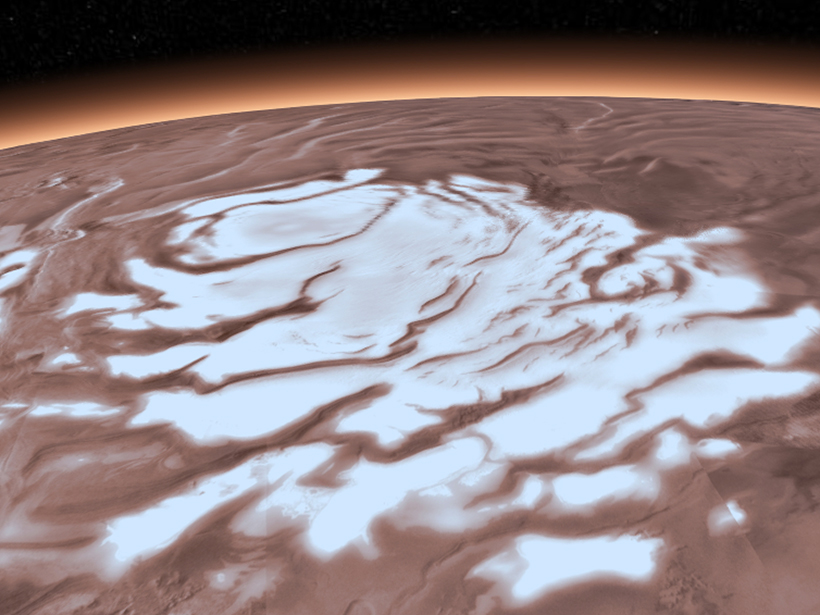
Local Heat Source Needed to Form Liquid Water Lake on Mars
Thermal modeling suggests that active magmatism in the past few hundred thousand years could account for the presence of a large lake previously hypothesized beneath the Red Planet’s southern ice cap.
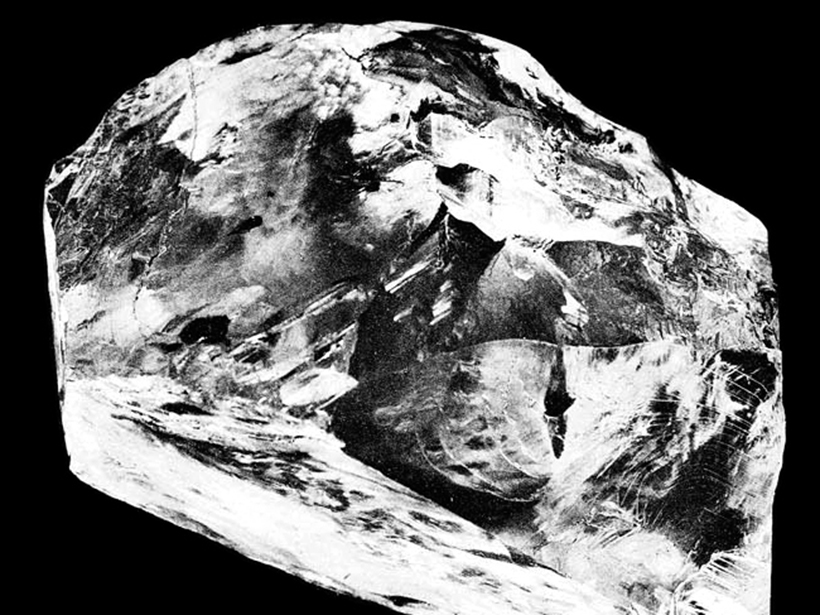
Explaining the Genesis of Superdeep Diamonds
Real-time tracking during diamond anvil cell experiments indicates reaction rates may control the unusual depth distribution of the extremely rare diamonds that form deep within Earth’s mantle.