For the first time, scientists have observed a deviation from the typical alternating pattern of easterly and westerly winds in the equatorial stratosphere.
Geophysical Research Letters
The Role of Seafloor Methane in Ancient Global Warming
New research suggests that release of methane from seafloor hydrates was much slower than hypothesized during a period of rapid global warming about 56 million years ago.
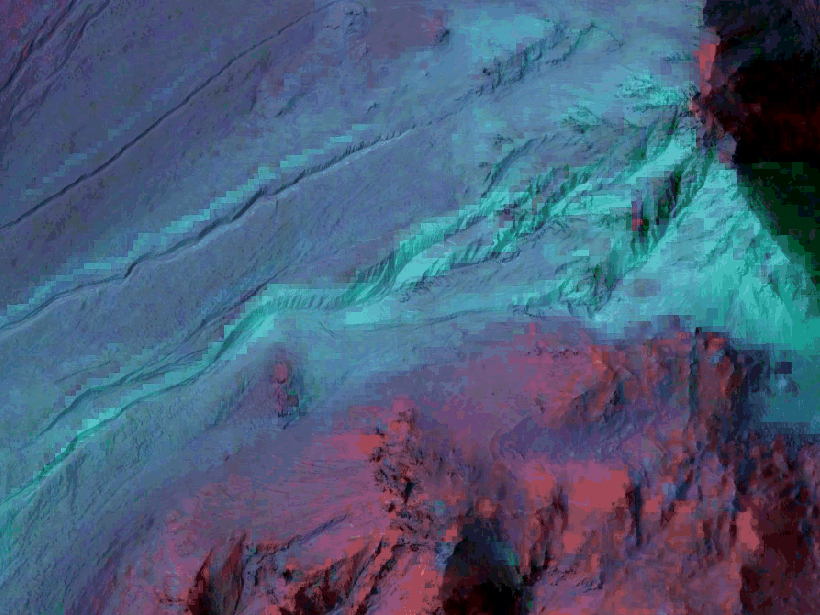
How Do Gullies Form on Mars?
New orbiter data support an important role for seasonal frost—not liquid water—in the formation of Martian gullies.
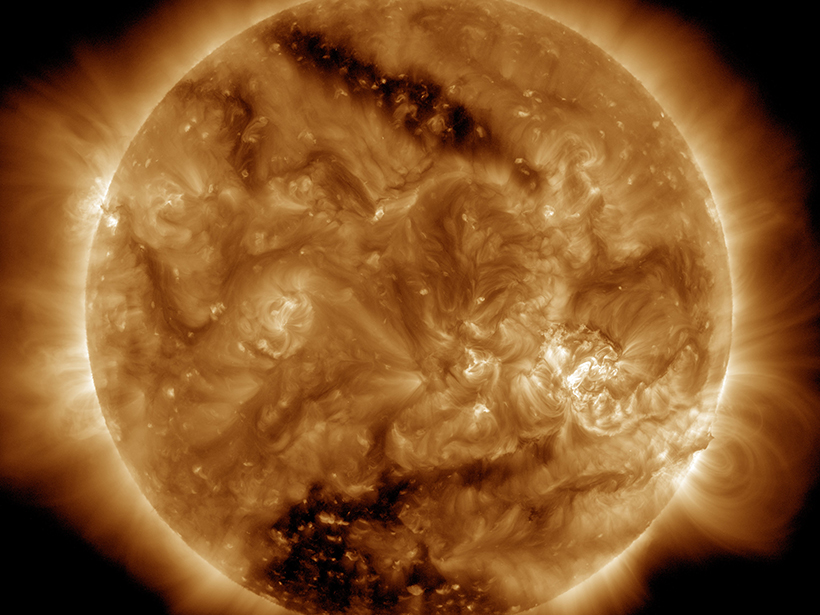
Spotting the Source of Slow Solar Wind
A new study suggests that magnetic reconnection may fuel slow solar winds, which top out at speeds below 500 kilometers per second.
Does Water Vapor from Volcanic Eruptions Cause Climate Warming?
By studying past volcanic eruptions, scientists find that the amount of water vapor reaching the stratosphere during moderately explosive eruptions may not be contributing to the greenhouse effect.
Cold Temperatures Set Off Slow-Moving Landslides
Falling ground temperatures in the cold season are found to trigger shallow, slow-moving landslides on slopes with clayey soil.
Minerals Hint at Liquid Groundwater, More Oxygen in Mars's Past
Manganese deposits in Gale Crater fractures are similar to Earth features that usually require flowing water and highly oxidizing conditions.
Going Against the Flow: Documenting Seasonal Current Reversal
Scientists discover the source of a coastal Korean current that reverses its flow in the summer.
Tackling the Paris Temperature Targets
The global temperature targets established in Paris in 2015 are ambitious; new research examines what it would take to achieve those targets.
How Irrigation in Asia Affects Rainfall in Africa
Up to 40% of the total rainfall in arid parts of East Africa may be caused by water vapor from farming practices in South Asia.