In Los Angeles, replacing lawns with native plants that need less water could lead to hotter days and cooler nights.
Geophysical Research Letters
Tide Gauge Records May Underestimate 20th Century Sea Level Rise
Tide gauges can help measure sea level change, but their limited locations and short records make it hard to pinpoint trends. Now researchers are evaluating the instruments' limitations.
Mapping Water and Heat Deep Under Long Valley Caldera
Researchers use electrical resistivity to find the heat source and reservoir feeding Long Valley Caldera's labyrinthine hydrothermal system.
Jupiter's Auroras Recharge Between Solar Storms
New research suggests that Jupiter's magnetic field replenishes its stock of plasma during lulls in solar activity, creating spectacular displays when a solar storm hits.
All Earthquakes Are Created Equal
A study of the development of earthquakes shows that the size of the initial rupture does not determine its intensity or range later on.
Air-Sea Interactions Influence Major Southern Wind Belt
Ocean and atmospheric data provide evidence for how sea surface temperatures affect the Southern Annular Mode.
Melting Ice Could Reveal Toxic Cold War Era Waste in Greenland
Unforeseen political disputes could arise as countries assess who's responsible for the cleanup of the Cold War relics.
Mysterious Anomaly Interrupts Stratospheric Wind Pattern
For the first time, scientists have observed a deviation from the typical alternating pattern of easterly and westerly winds in the equatorial stratosphere.
The Role of Seafloor Methane in Ancient Global Warming
New research suggests that release of methane from seafloor hydrates was much slower than hypothesized during a period of rapid global warming about 56 million years ago.
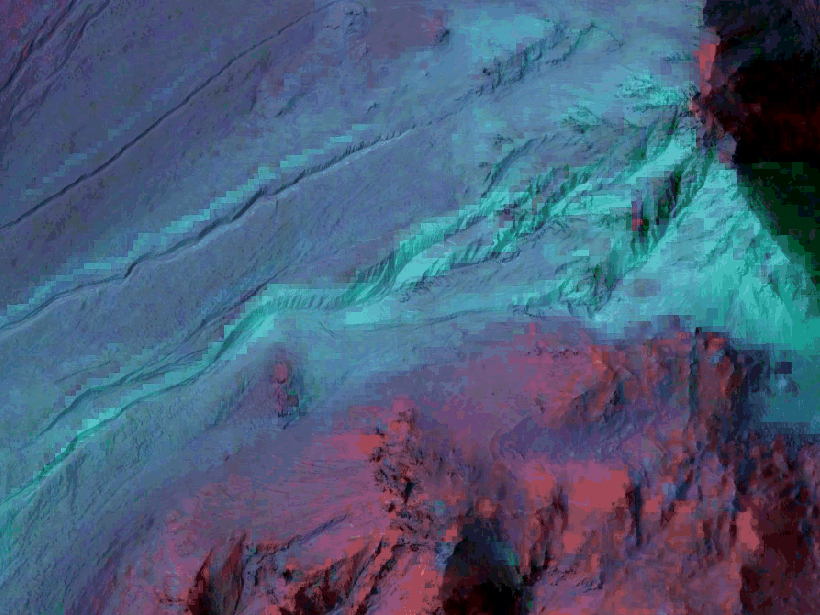
How Do Gullies Form on Mars?
New orbiter data support an important role for seasonal frost—not liquid water—in the formation of Martian gullies.