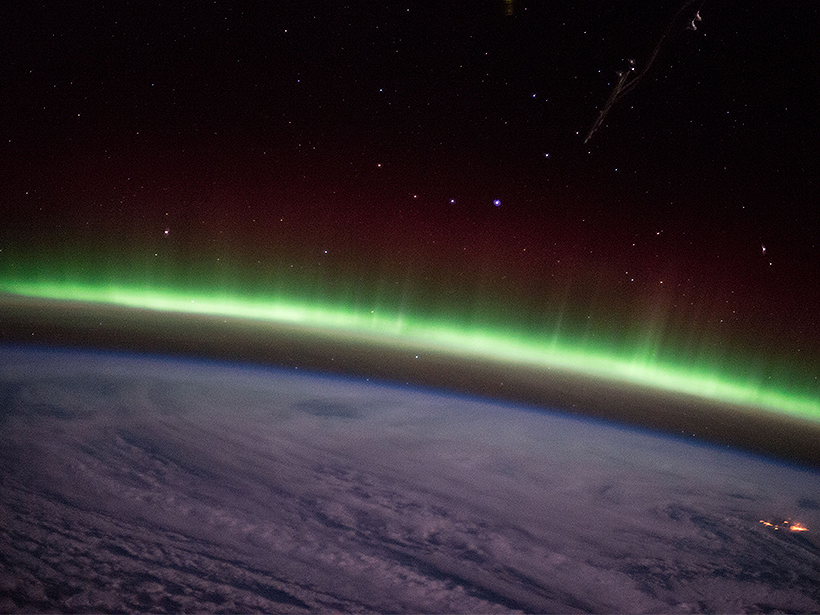
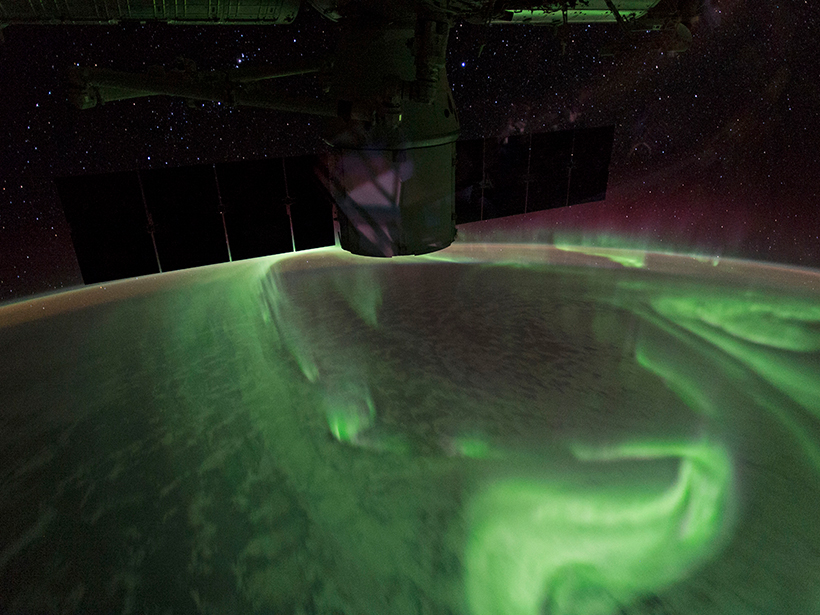
A new classification scheme helps researchers distinguish what accelerates the electrons that create auroras.
ionospheres
How Mars Lost Steam
Solar winds are not the main culprit in stripping the planet’s atmosphere, a new study suggests.
Probing the Origin of a New Celestial Phenomenon
The first statistical study of STEVE events suggests that the appearance of these narrow ribbons of light is closely correlated with violent disturbances in Earth’s magnetosphere.
How Did We Miss This? An Upper Atmospheric Discovery Named STEVE
Captured unknowingly by scientific instruments for years, a sky phenomenon is finally brought to the attention of researchers by eagle-eyed citizen scientists.
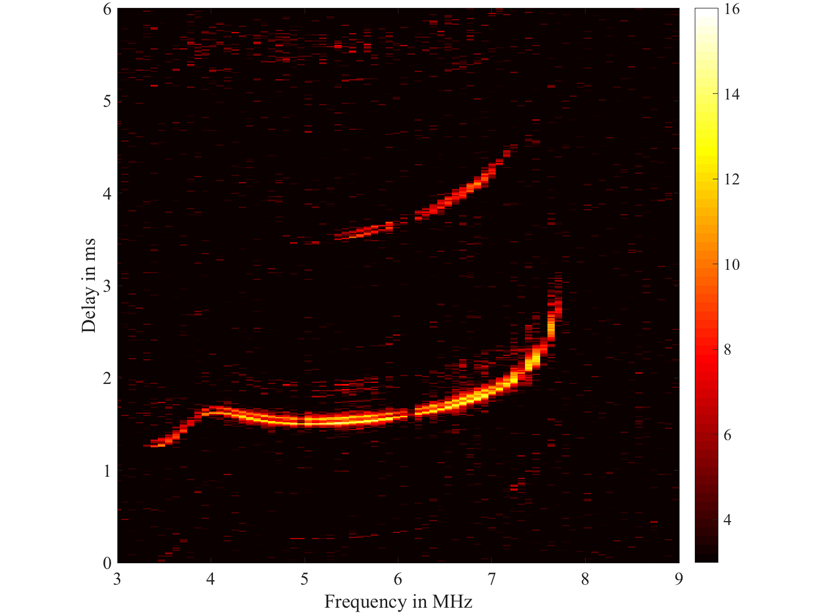
High Resolution Imaging of Ionosphere by Lightning
The three-dimensional distribution of electron density in the Earth’s ionosphere could be obtained using the broadband radiation of naturally occurring lightning discharges.
Energetic Electrons Can Penetrate the Stratosphere
Precipitations of electrons with energies greater than 30 kiloelectron volts from the slot region penetrate at low altitude and can contribute to destroy ozone.
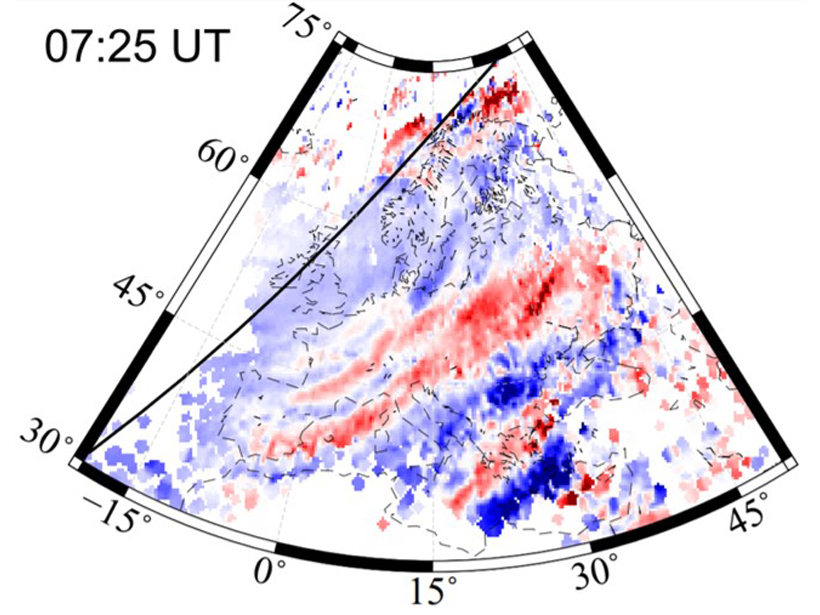
Seeing Waves: GNSS Tracking of Waves in the Upper Atmosphere
Dense GNSS networks enable scientists to track large-scale waves traveling through the upper atmosphere, away from sources in the auroral zone and the day/night terminator.
Equatorial Ionospheric Scintillation During Daytime
Scintillation—flickers and distortions in radio waves passing through the ionosphere—can happen during daytime and at much lower dip latitudes than previously thought.
Dramatic Stratospheric Warmings Carved a Hole in the Ionosphere
A new study of sudden temperature spikes in Earth’s stratosphere could improve space weather forecasting.
Mysterious Aurora Borealis Feature Explained for the First Time
High-speed particles cause indentations in the magnetopause to form “throat auroras.”