Rainfall varies with elevation, and such precipitation gradients can have profound and often counterintuitive effects on topography.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface
Recovering Mantle Memories from River Profiles
Researchers use a closed-loop modeling strategy to validate regional uplift patterns recorded in river profiles across the African continent.
Grain Scale Dynamics During Barchan-Barchan Interactions
A new study pinpoints grain scale dynamics during binary interactions between barchan dunes.
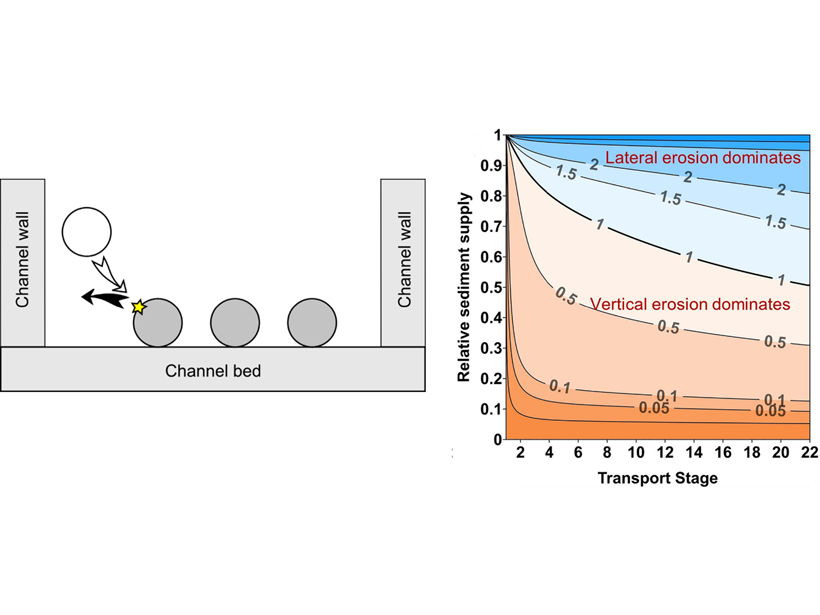
Impacts by Moving Gravel Cause River Channels to Widen or Narrow
A new analytical model describes how the amount and grain size of sediment transported by rivers influences bedrock channel width, which can be used to predict where rivers will widen or narrow.
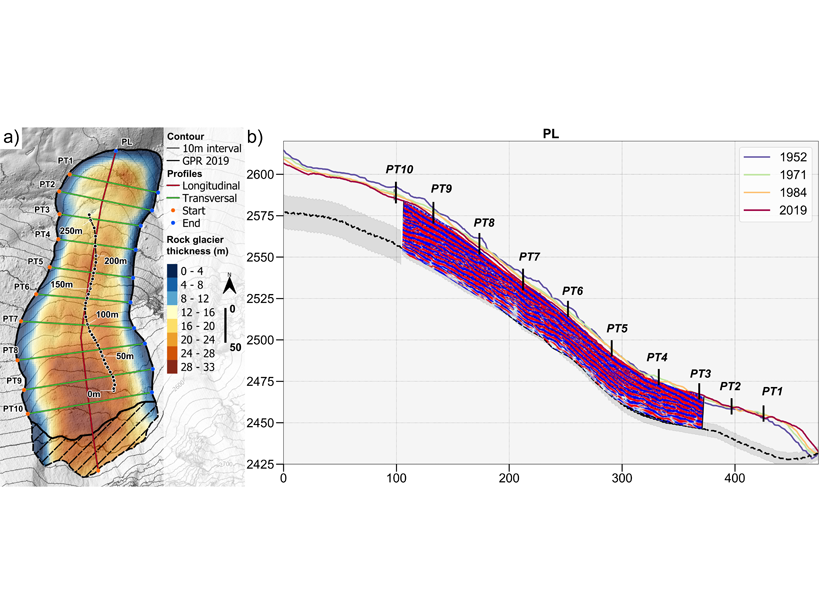
Revealing How Rock Glaciers Respond to Climate Change
Detailed measurements of the geometry and flow of Laurichard rock glacier over 67 years reveal the distinctive behavior of these landforms through periods of warming and cooling.
A New Model for Self-Organized Pattern Formation
Scale-dependent feedbacks in time, rather than in space, result in a new type of competition, explaining the regularly patterned landscape of Big Cypress National Preserve in South Florida.
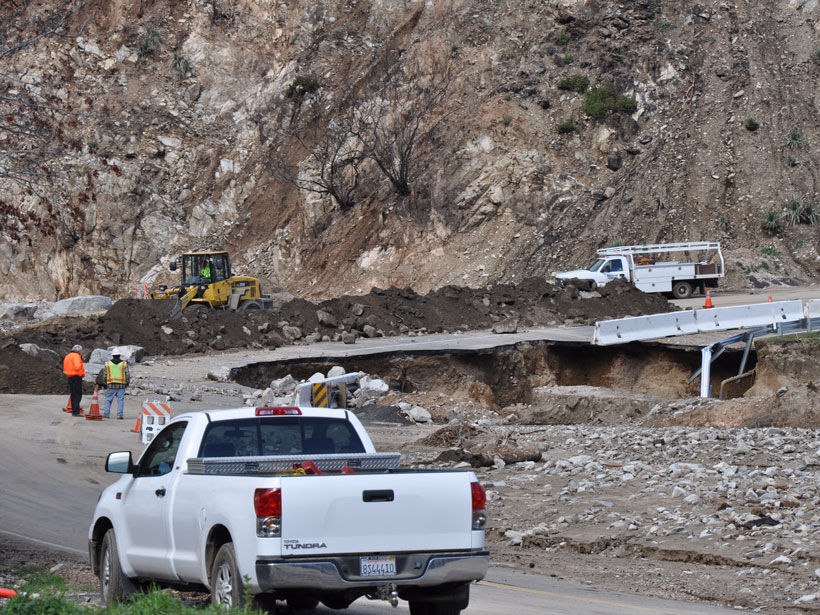
The Wildfire One-Two: First the Burn, Then the Landslides
Severe wildfires strip away plant cover and reduce the soil’s ability to hold water. A new study develops a model to better understand landslide risk following a burn.
Thickness and Strength of Slow-moving Landslides Revealed
Hundreds of slow-moving landslides’ deformation patterns were inverted to obtain their thickness and frictional strength, revealing that larger landslides are weaker and thinner than smaller ones.
Predicting the Next Big Frost Quake
Frost quakes occur in boreal regions when rapidly expanding ice underground causes frozen soils to fracture. A recent frost quake in Finland has given scientists a rare look into how they form.
Experimenting with Underwater Sediment Slides
Sediment-laden currents caused by breaching flow slides are hazardous to flood defenses and seabed infrastructure. New research shows that these phenomena must be accounted for in erosion simulations.