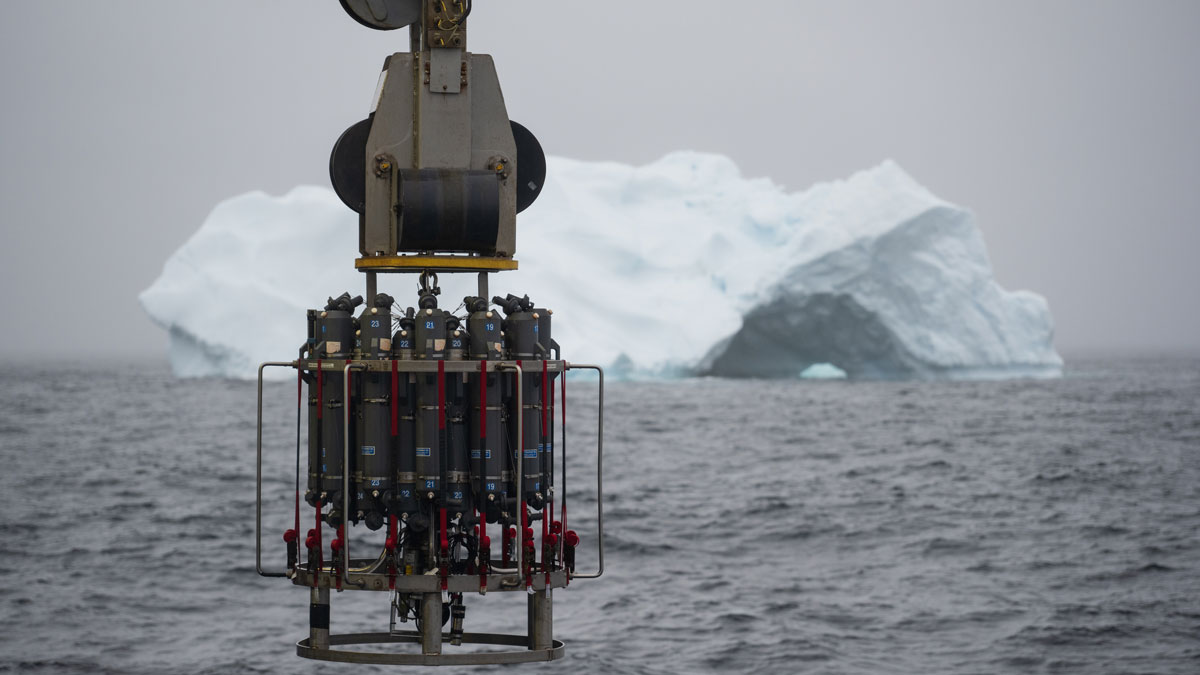
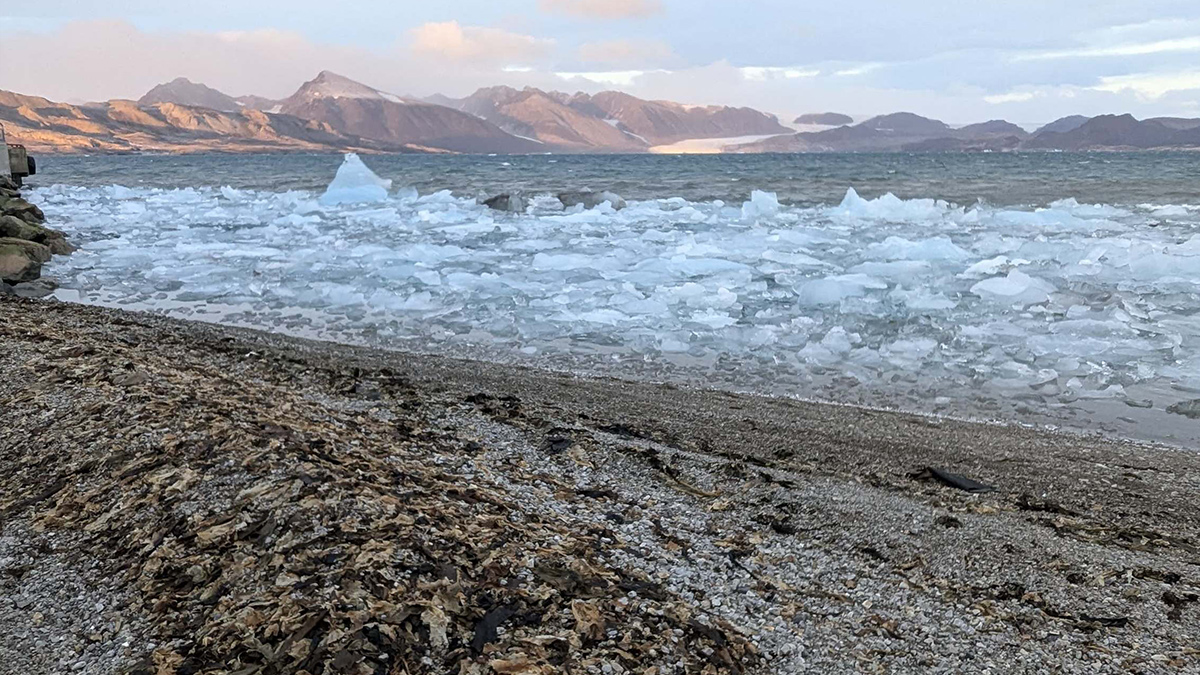
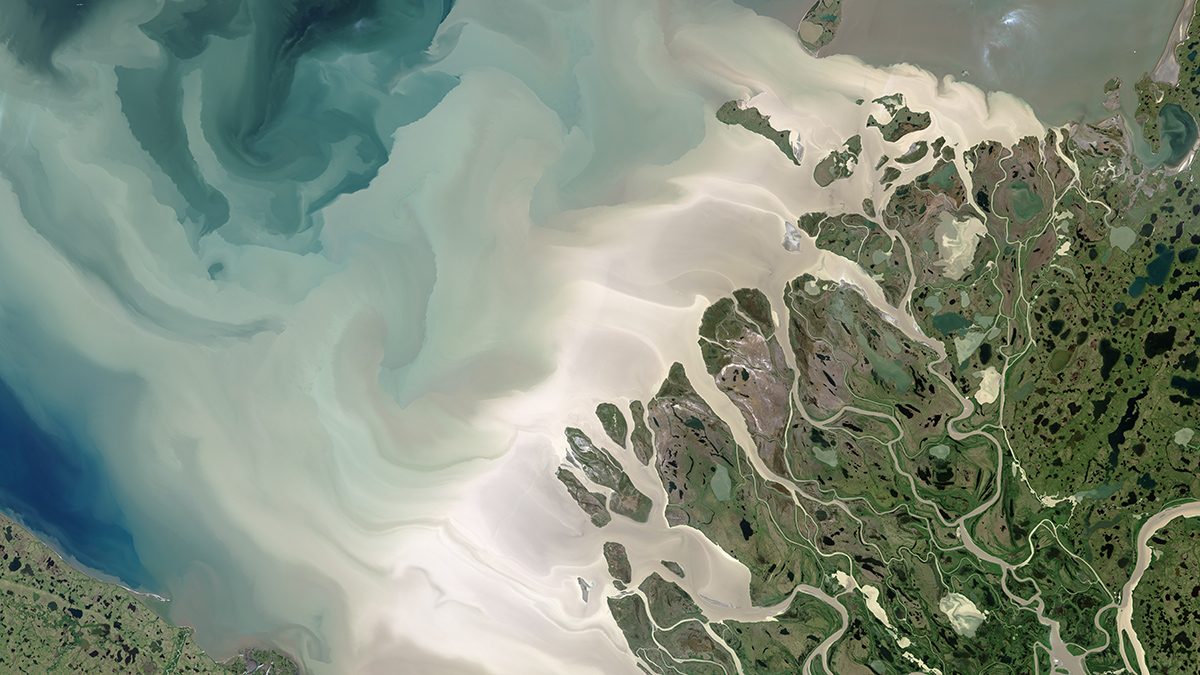
Existing theory underestimates the mixing of freshwater and seawater by up to 50%.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans
A First Look at How Sand Behaves Inside a Rippled Bed
A detailed numerical model shows how sediment particles experience wave-driven shear stress inside and above a sea bed with sand ripples.
Strong Tides Speed Melting of Antarctic Ice Shelves
Ocean currents along the underside of the ice are a major control over melting.
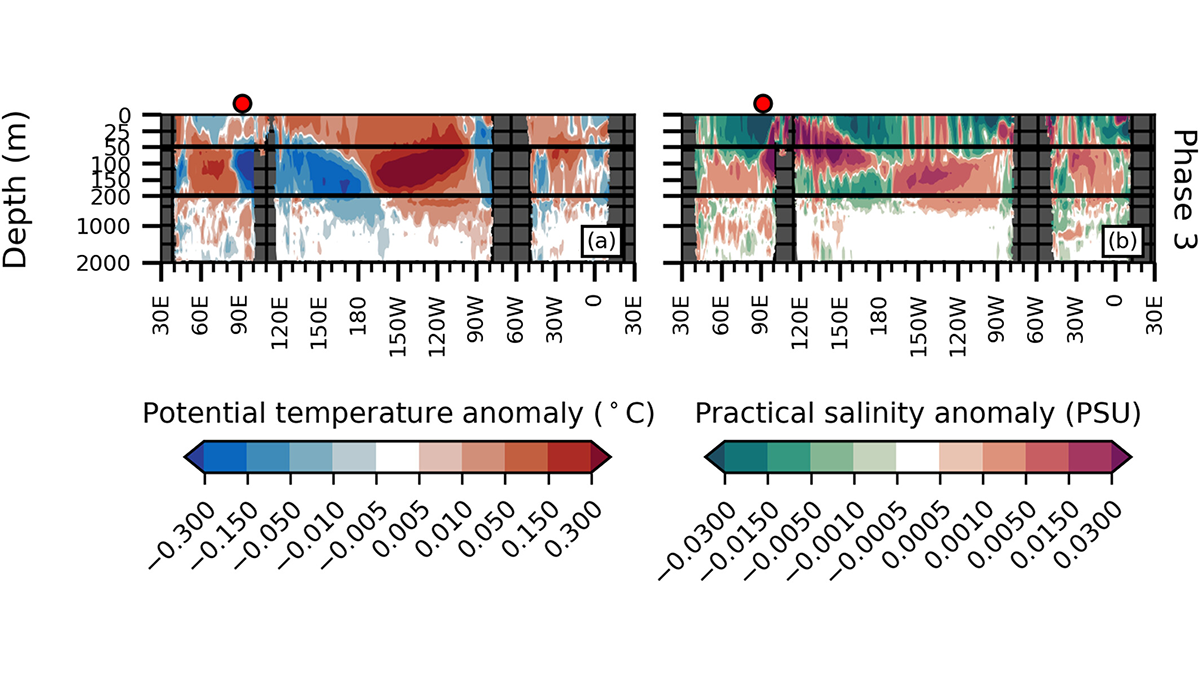
Equatorial Deep Ocean Response to the Madden-Julian Oscillation
The changes in Madden-Julian Oscillation wind can trigger a response in the deep equatorial Pacific and Indian Ocean.
Advances in Ecological Forecasting
AGU and ESA invite contributions to a cross-society special collection on ecological forecasting across ecosystems and scales.
Where Do Antarctic Submarine Canyons Get Their Marine Life?
A new study investigates how much of the phytoplankton in the Palmer Deep submarine canyon is homemade and how much is delivered.
Kuroshio Intrusions into Luzon Strait Increase Chlorophyll
Using in-situ observational data, scientists reveal that Kuroshio intrusions through the Luzon Strait increase small phytoplankton in the South China Sea.
How Greenland’s Glacial Troughs Influence Ocean Circulation
Glacial troughs in Antarctica promote mixing of warm and cold water, affecting global climate. A new study explores whether the same is true in troughs along Greenland’s coastline.
Seaweed Surges May Alter Arctic Fjord Carbon Dynamics
Climate change–accelerated seaweed growth could cause seaweed-dependent microbes to proliferate and consume more oxygen, leading to a rise in oxygen-starved zones.
The Uncertain Fate of the Beaufort Gyre
Climate models produce widely varying predictions for what will happen to this influential ocean current, but most models predict it will weaken or stop.