Very Low Frequency transmitters used for communications with submarines modify the dynamics of energetic electrons in the inner radiation belt and the slot region.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics
Holistic Views of the Nighttime Ionosphere
The nightside ionosphere, at latitudes away from the auroral zone, should have very little charged particle density, but it doesn’t. A new comprehensive study of satellite data explains why.
The When and Where of Mesospheric Bores Revealed
In a new study, the enigmatic gravity waves were seen most frequently at equatorial latitudes and propagating from the winter to the summer hemisphere.
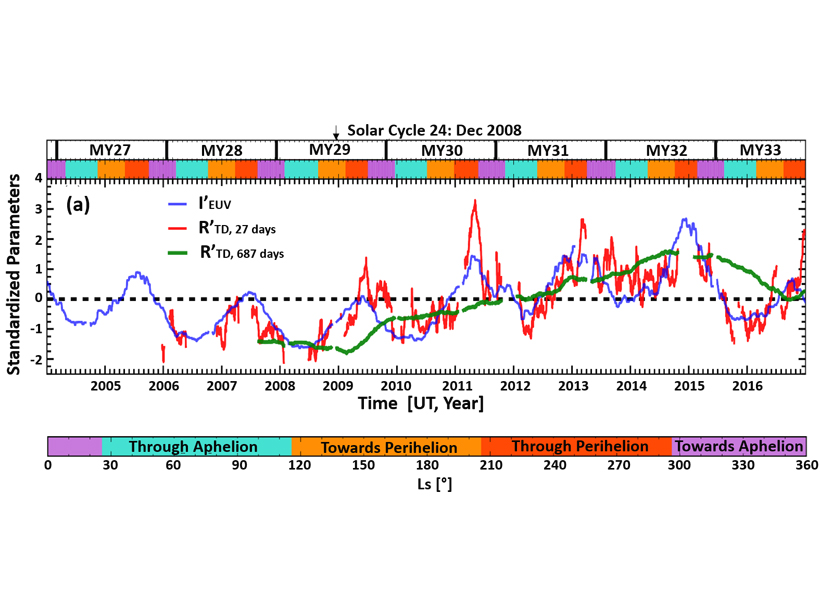
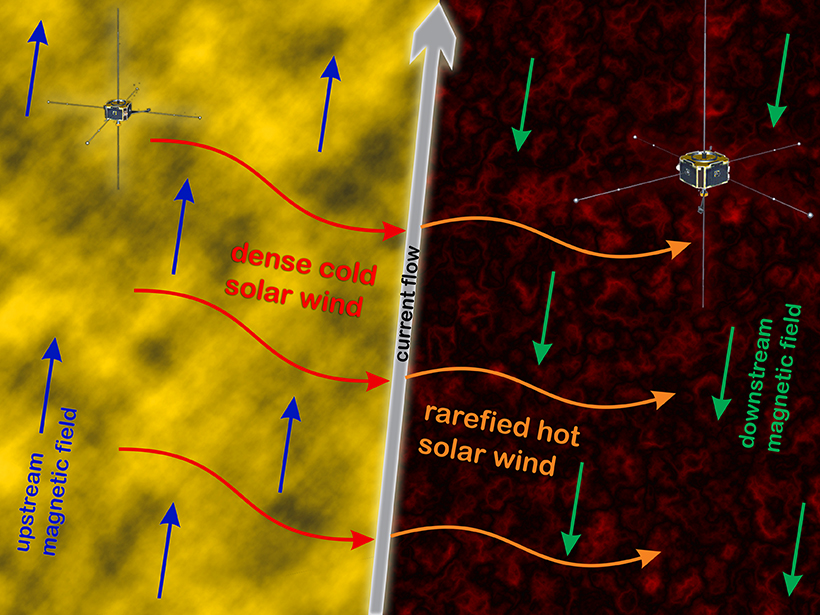
Solar Properties Rival for Control of Mars’s Bow Shock
While most planetary bow shocks are controlled by the solar wind, at Mars the solar EUV flux is equally important.
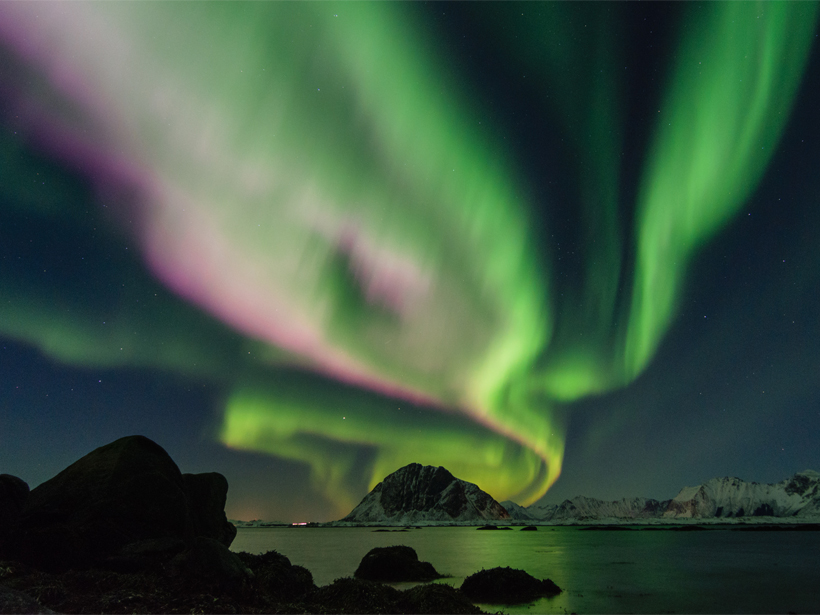
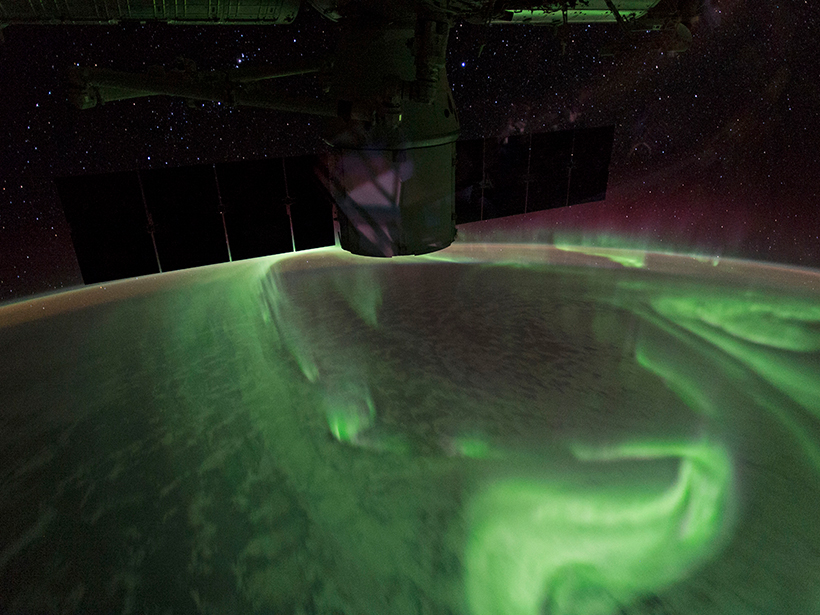
Red and Green Aurora Stop and Go for Different Reasons
Green-line arc is found to be embedded within large-scale upward field aligned currents while red-line-only arc is found to be associated with low-energy precipitation bursts.
Understanding the Turbulent Nature of the Solar Wind
Sometimes the conditions in the solar wind can change dramatically over short distances. Satellite observations of these features show that they’re more complex than previously thought.
Data Mining Reveals the Dynamics of Auroral Substorms
An analysis of 5 decades of satellite data has pieced together the most comprehensive picture yet of substorms, the magnetic disturbances that cause surges of aurora.
No Underground Magma Ocean on Jupiter’s Fiery Moon?
A new study suggests alternative explanations for Io’s unusual magnetic field.
Bringing Clarity to What Drives Auroras
A new classification scheme helps researchers distinguish what accelerates the electrons that create auroras.
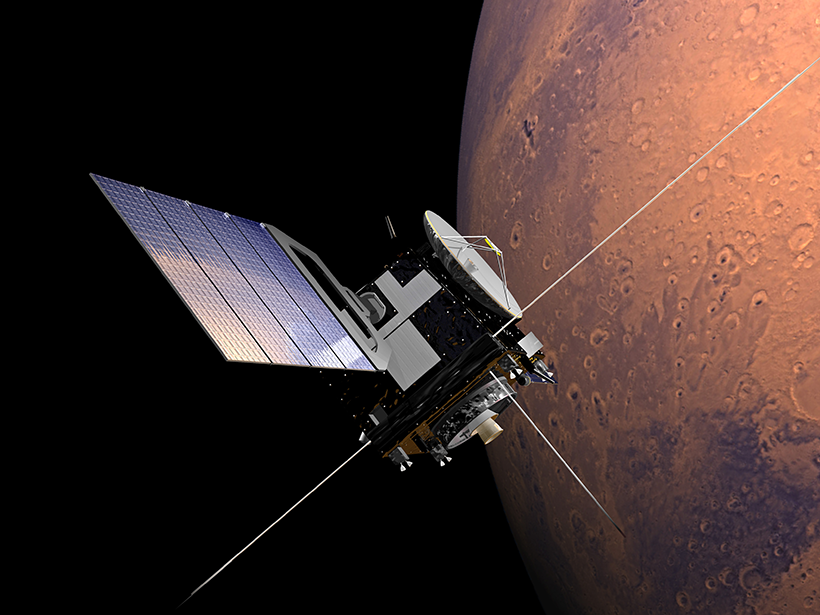
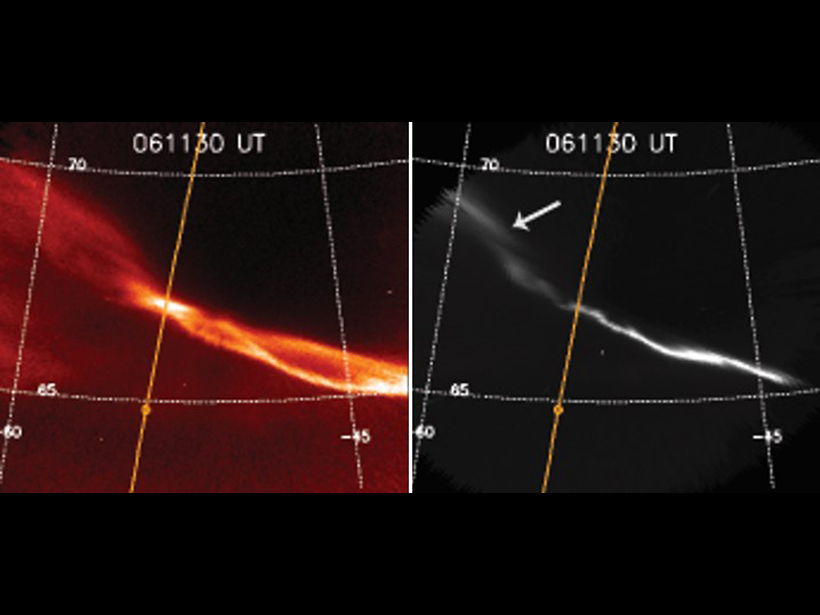
The Accidental Particle Accelerator Orbiting Mars
The radar aboard the Mars Express spacecraft can generate ion beams arcing through space above the planet, which could lead to a new way of studying the plasma surrounding it.