A study of nightglow over India reveals that gravity waves are less important than previously thought.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics
Probing the Origin of a New Celestial Phenomenon
The first statistical study of STEVE events suggests that the appearance of these narrow ribbons of light is closely correlated with violent disturbances in Earth’s magnetosphere.
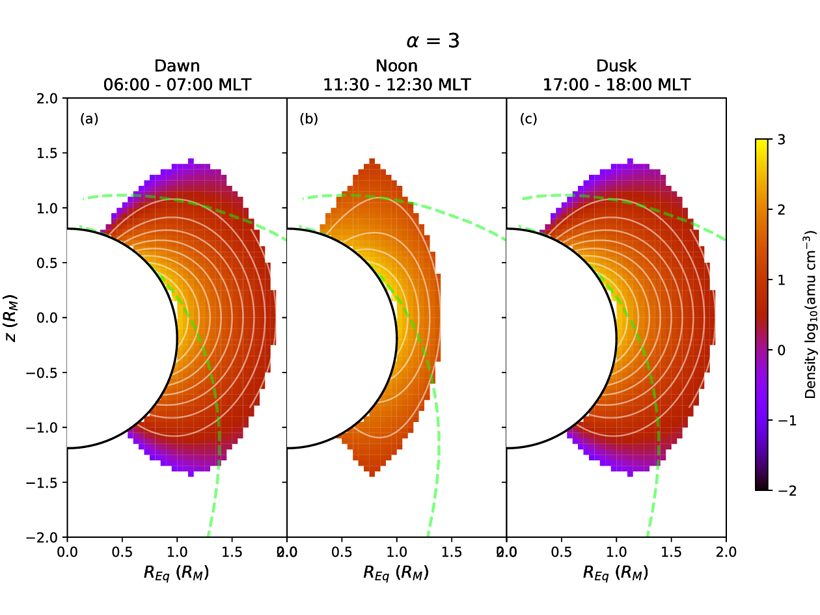
Plasma Density Distribution in Mercury’s Magnetosphere
A new measurement of plasma density distribution in Mercury’s magnetosphere obtained from observations of field line resonance events provides necessary constraint for many planetary science issues.
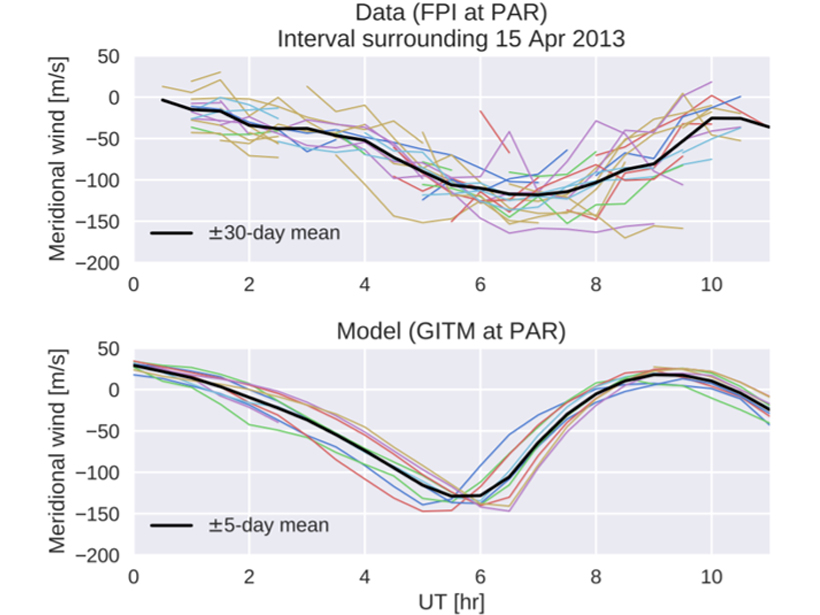
Windy Weather in the Thermosphere
The weather in the thermosphere includes winds that buffet spacecraft as they orbit the Earth, but how well can these winds be modeled?
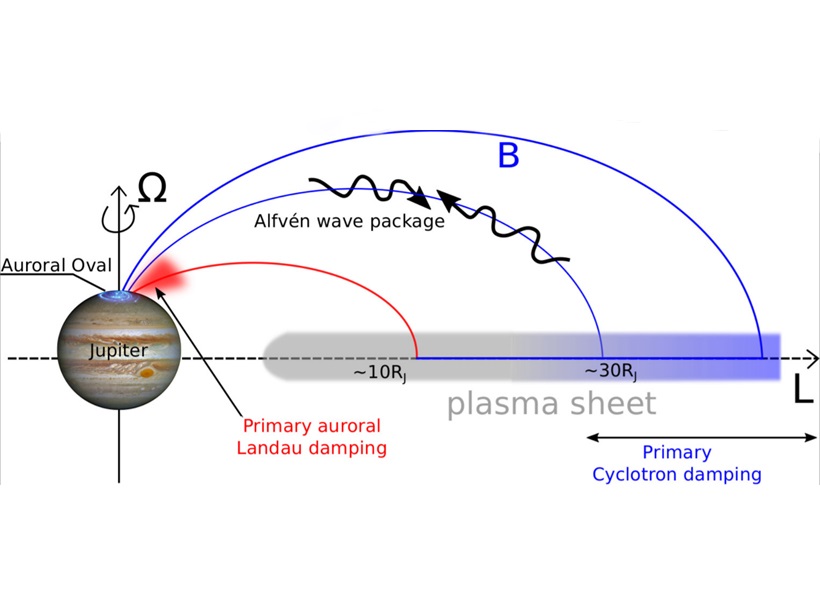
Jupiter’s Stressed Out Magnetosphere Causes Aurora and Heating
Force imbalance between Jupiter’s ionosphere and magnetosphere leads to wave generation to release this stress, but the waves also accelerate particles, causing aurora and heating.
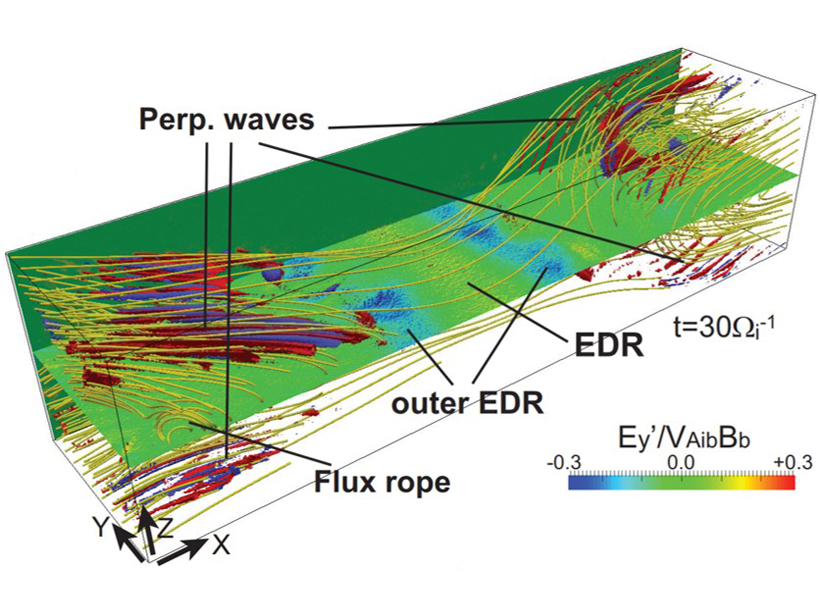
Measuring the Magnetic Reconnection Rate in the Magnetotail
Both simulations and observations are used to measure the magnetic reconnection rate in the Earth’s magnetotail, suggesting that the rate is correlated with the intensity of a magnetic substorm.
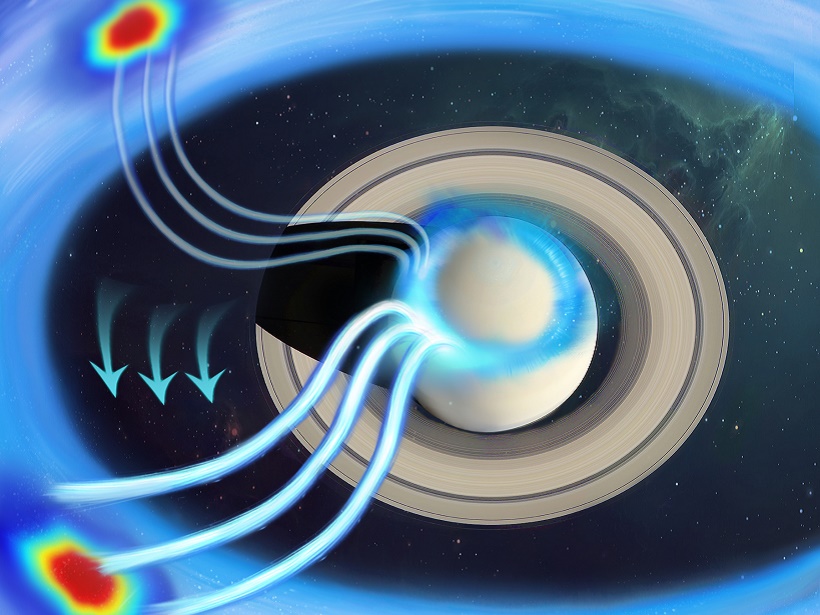
Cassini Reveals a Missing Link on Saturn’s Rotating Aurora
The bright aurorae dancing in the sky are produced by charged particles traveling along the magnetic field lines from tens of planetary radii. By why do aurorae rotate at Saturn but not at Earth?
Energetic Electrons Can Penetrate the Stratosphere
Precipitations of electrons with energies greater than 30 kiloelectron volts from the slot region penetrate at low altitude and can contribute to destroy ozone.
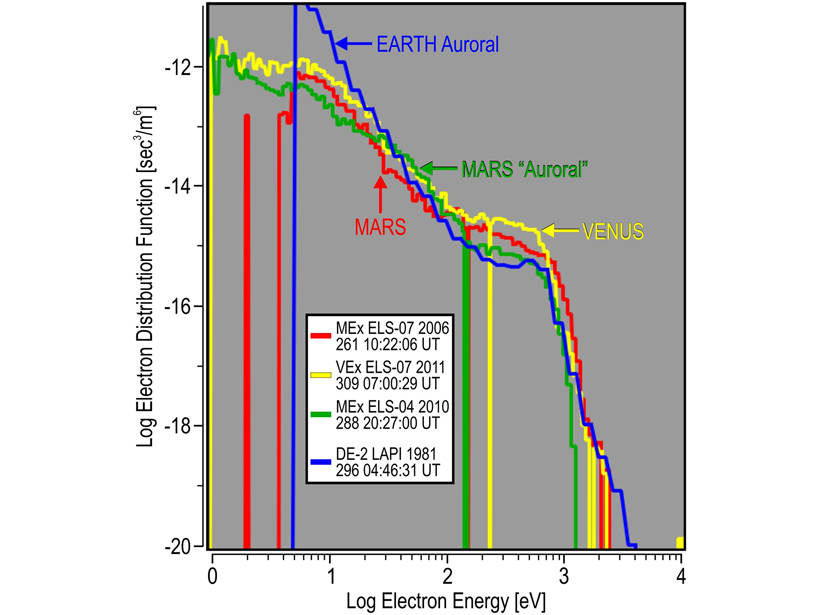
Extreme Space Conditions at Mars: The 10 Largest Electron Events
A solar cycle of data was scoured for the biggest electron energy fluxes seen in the Mars space environment.
Dramatic Stratospheric Warmings Carved a Hole in the Ionosphere
A new study of sudden temperature spikes in Earth’s stratosphere could improve space weather forecasting.