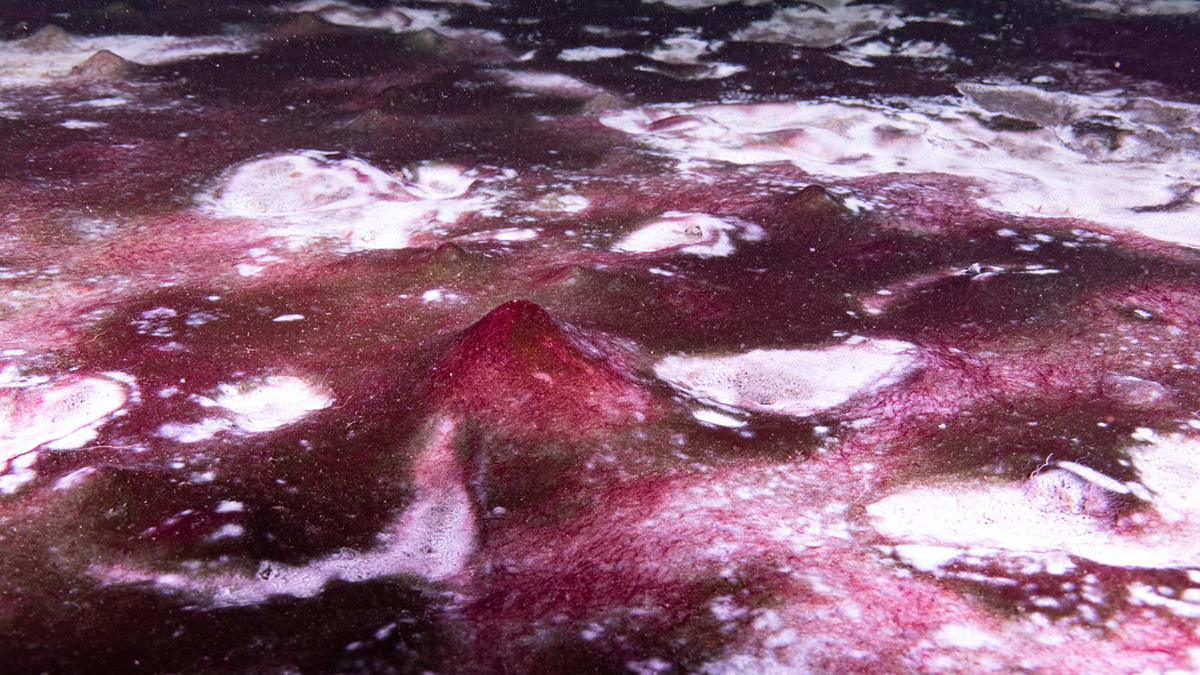
Comprising diverse groups of microbes, isolated but globally scattered mat ecosystems like those in Lake Huron may be analogues of life on early Earth and in other exotic environs.
life as we know it
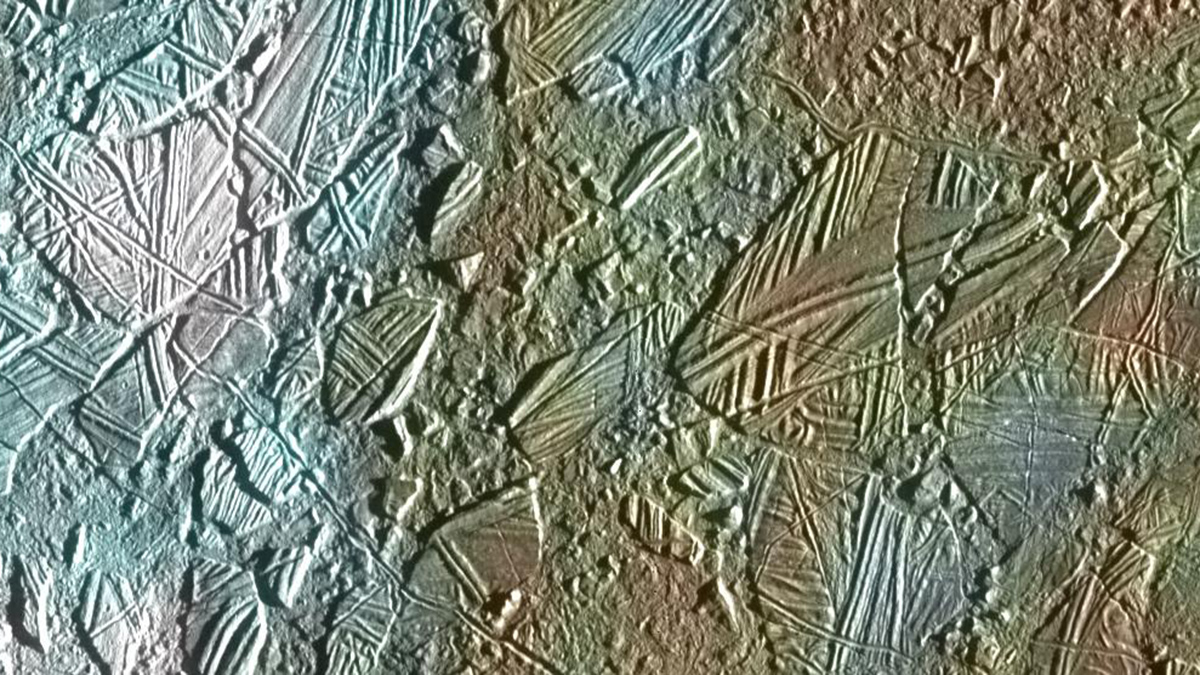
Scientists Investigate How Heat Rises Through Europa’s Ocean
A new study examines how heat may be transferred from the mantle, through the ocean, and into the icy crust of one of Jupiter’s moons—perhaps among the most promising places in our solar system to search for life.
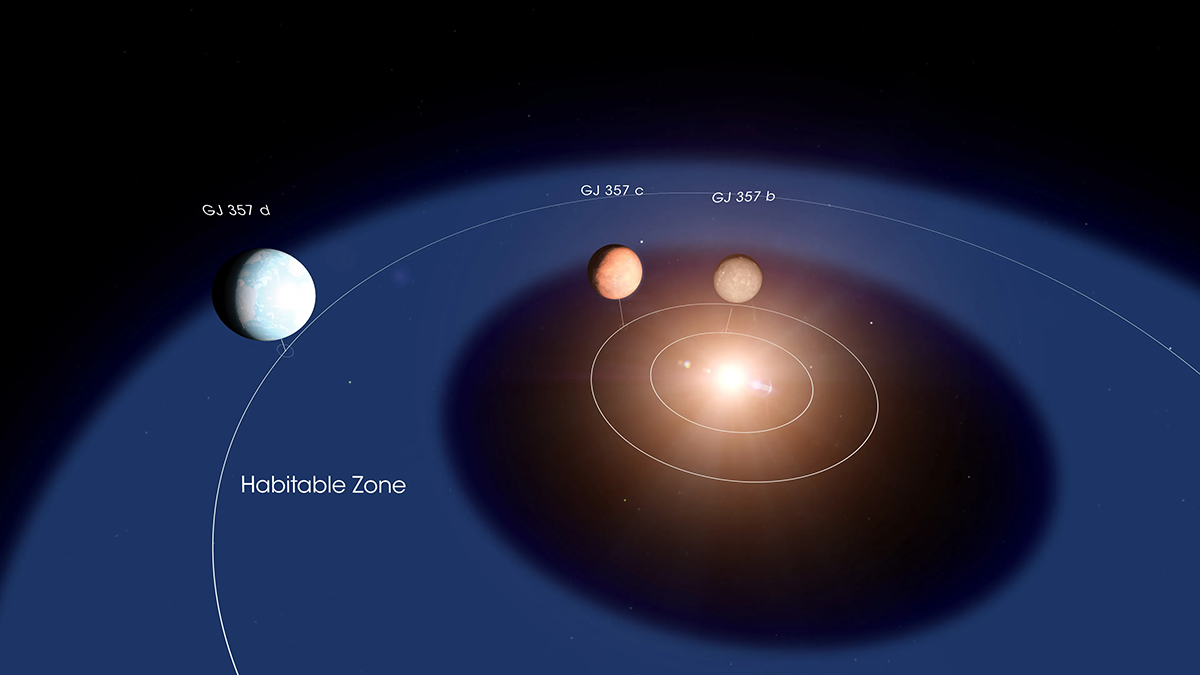
Giant Planets May Be “Agents of Chaos”
Two studies suggest that some giants could make it difficult or even impossible for terrestrial planets to remain in a star’s habitable zone.
Microbe Goo Could Help Guide the Search for Life on Mars
Sticky substances secreted by microbes may help create landforms on Earth. And new research shows that these substances are more preserved in iron-rich sediment. Mars is decidedly iron-rich (it’s the Red Planet, after all), so the new study adds to evidence that microbe goo could help researchers explain landform creation there. “I think this is […]
La canción de hielo y fuego del criovulcanismo
Las lunas oceánicas del sistema solar exterior nos dan pistas sobre volcanes de hielo, fuentes hidrotermales, y la tentadora posibilidad de habitabilidad.
Ancient Mars May Have Had a Cyclical Climate
Hexagonal structures in sediments are evidence of repeated wet and dry conditions on the Red Planet.
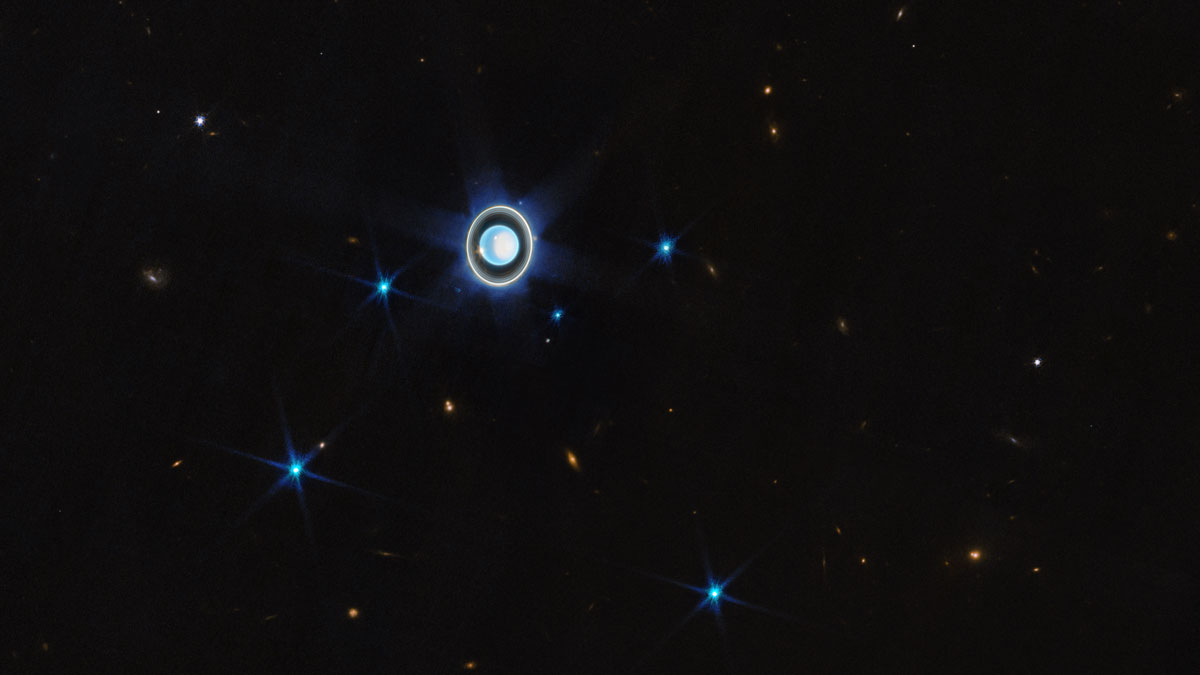
Uranus: Time to Boldly Go
Scientists say now is the time to unlock the secrets of Uranus and suggest a low-cost, low-risk way to do so.
Cryovolcanism’s Song of Ice and Fire
Ocean moons of the outer solar system hint at ice volcanoes, hydrothermal vents, and the tantalizing chance of habitability.
Subsurface Oceans Could Boost Exoplanet Habitability
Researchers have shown that oceans buried below layers of ice are more common than previously thought.
Essential Ingredient for Life Found on Enceladus
Icy plumes from Saturn’s moon Enceladus contain phosphorus, part of the biochemistry of life—the first time the element has been found in a liquid environment beyond Earth.