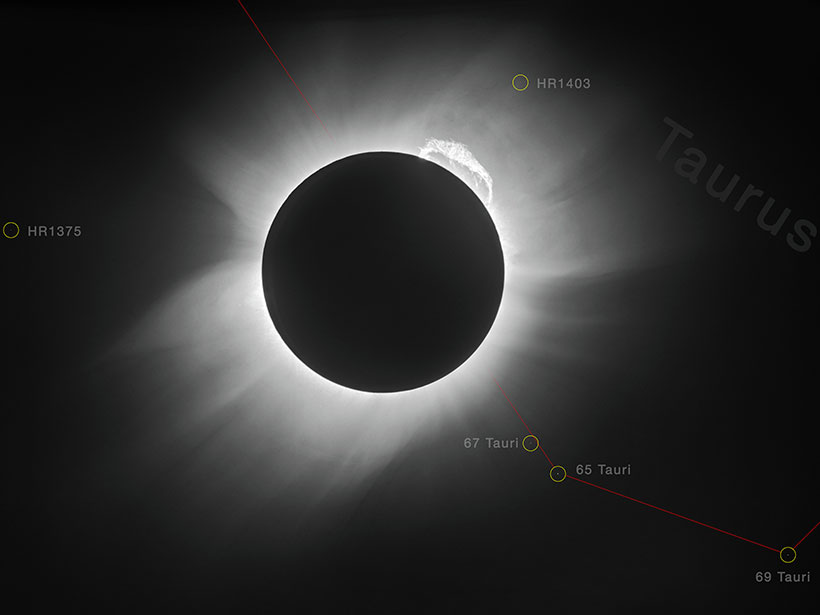
The first stopover site map for U.S. migratory birds reveals the attraction of urban light pollution.
light
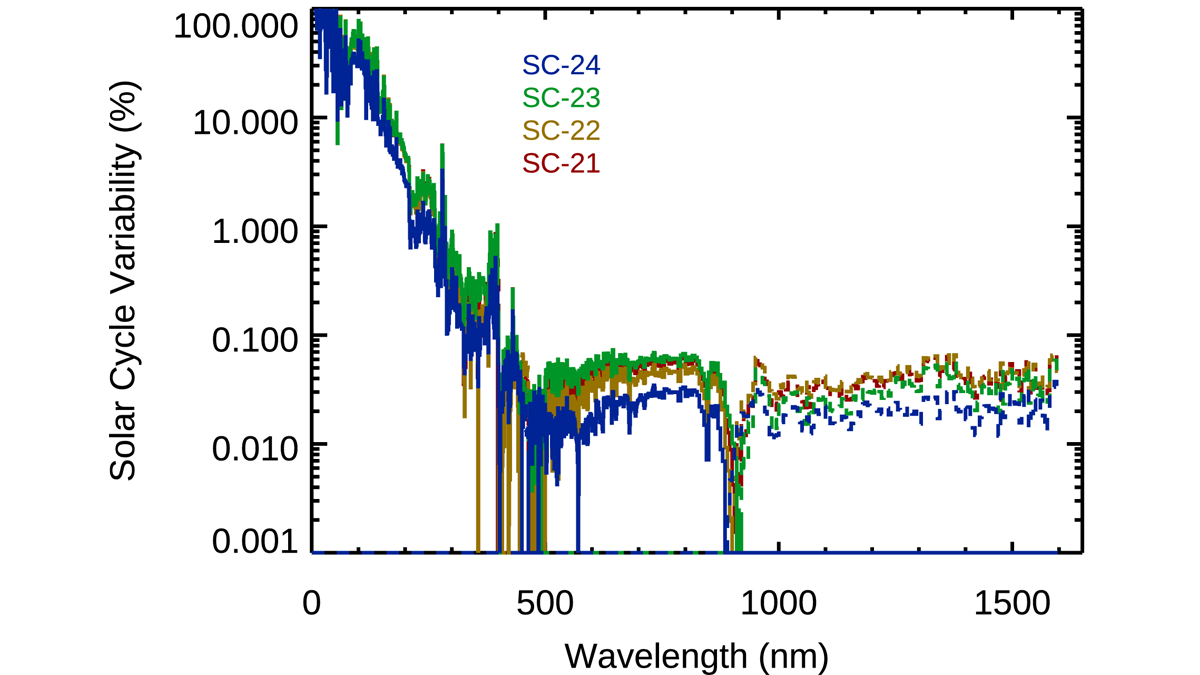
Newly Improved Solar Spectral Irradiance Composite Record
A new study accurately captures solar irradiance, which is crucial to understand the energetics and radiation balance of Earth and its influences on the cryosphere, atmosphere, and ocean currents.
Laser Flashes Shed Light on a Changing Arctic
An ongoing project in northern Alaska is using pulses of laser light to monitor anthropogenic activity, ice quakes, and marine wildlife.
Flying Saucers Could One Day Probe the Mesosphere
Researchers have created thin, levitating disks that could be used to study the mesosphere, a layer of Earth’s atmosphere that’s difficult to reach with conventional flyers.
Stratospheric Weather Impacts Light Species at Great Heights
Sudden stratospheric warmings in the high latitude wintertime can drive changes in light species (H, He and O) all the way though the thermosphere, likely influencing ion densities in the exosphere.
A Better Understanding of How the Sun Bends Light
Incorporating the refractive index of the Sun into models of gravitational lensing effects improves agreement with measurements of the phenomenon.
Exoplanet Earth: An Ultimate Selfie to Find Habitable Worlds
Aliens spying on us from afar is a common science fiction trope. Soon we might know what E.T. would see through a telescope. And that information could help identify other Earth-like planets.
Gravity Waves Leave Ripples Across a Glowing Night Sky
A thunderstorm made waves on a rare “bright night.”
¿Podría la Vida Estar Flotando en las Nubes de Venus?
Si están presentes, los microbios podrían explicar patrones de evolución en la atmósfera planetaria de Venus, al observarse con luz ultravioleta.
¿Por Qué la Luz Solar es Importante para los Derrames de Petróleo en el Mar?
Una década de investigación desde el desastre de Deepwater Horizon ha revelado cómo la luz solar—su importancia subestimada durante mucho tiempo en la ciencia de derrames de petróleo—altera sustancialmente el petróleo que flota en la superficie del mar.



![Two plots showing percent changes in TIME-GCM zonally averaged [O+] and [H+] as a function of latitude and altitude in the Northern Hemisphere between the “disturbed” and “pre-disturbance” time periods in 2012–2013](https://eos.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/2020JA028331-Figure-12-top-row-with-legend-sized-for-Eos.png)




