Better data and assessment metrics—and improved researcher involvement in communities—are needed to understand and redress inequitable vulnerabilities to and recoveries from flooding.
Modeling
Rainstorm Intensity Drives Desert Landscape Evolution
New mathematical models show that the persistence of near-vertical cliffs in arid landscapes is maintained by infrequent, but high-intensity rain storms.
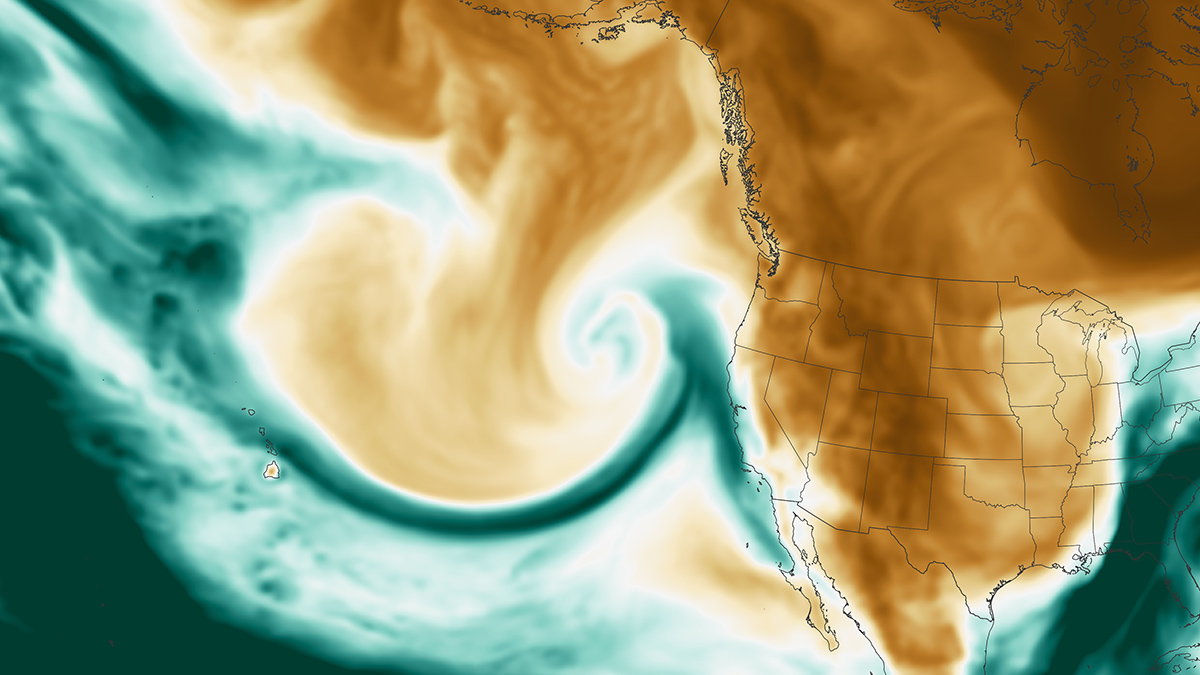
The Escalating Impact of Global Warming on Atmospheric Rivers
Climate change is set to intensify atmospheric rivers and exacerbate extreme rainfall worldwide.
Antarctica’s Ocean Acidity Set to Rise Rapidly by Century’s End
New research shows acidity levels could as much as double by 2100, imperiling fragile ecosystems in the frigid Southern Ocean.
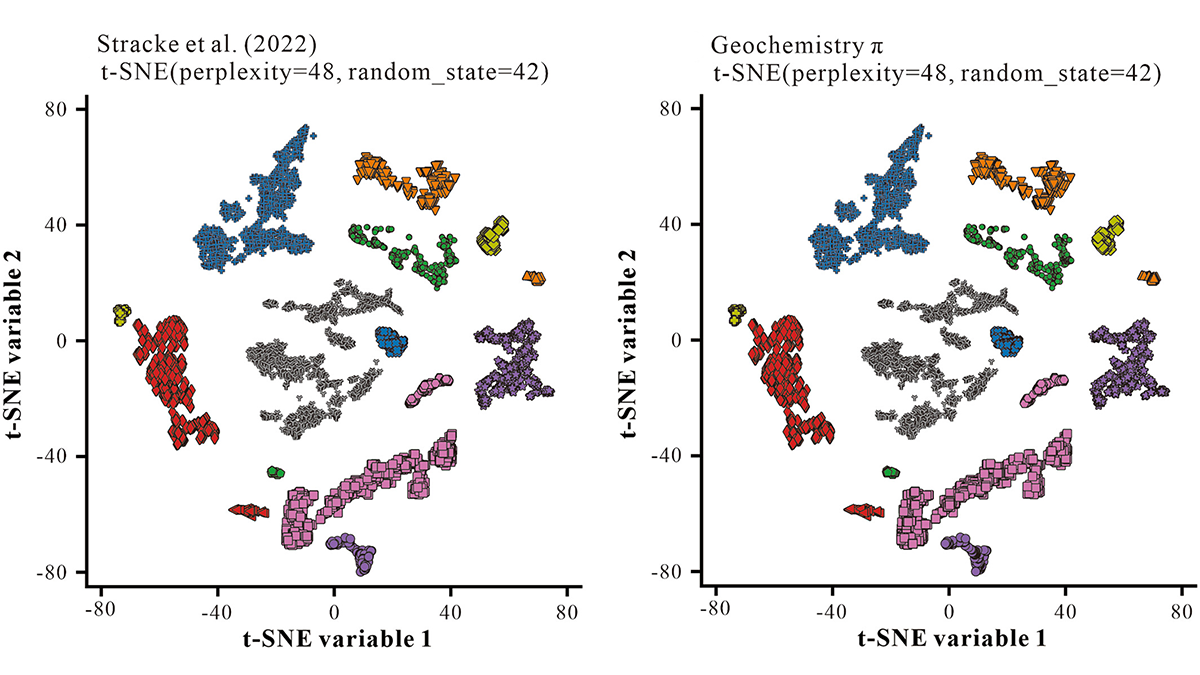
Machine Learning for Geochemists Who Don’t Want to Code
Geochemistry π is an easy-to-use step-by-step interface to carry out common machine learning tasks on geochemical data, including regression, clustering, classification, and dimension-reduction.
Poorer Countries Face Heavier Consequences of Climate Change
As forests shift to higher latitudes, nations to reckon with losses of both market and nonmarket ecosystem benefits.
Climate Models Often Miss How Plants Respond to Drought
New research suggests that Earth system models are underestimating the effect of low moisture levels on plants’ abilities to exchange carbon, water, and energy with the atmosphere.
OneHealth, Climate Change, and Infectious Microbes
AGU and ASM welcome submissions to a joint special collection focusing on the impacts of climate change and microbes on human well-being.
Deep Learning Tackles Deep Uncertainty
A new method based on artificial intelligence could help accelerate projections of polar ice melt and future sea level rise.
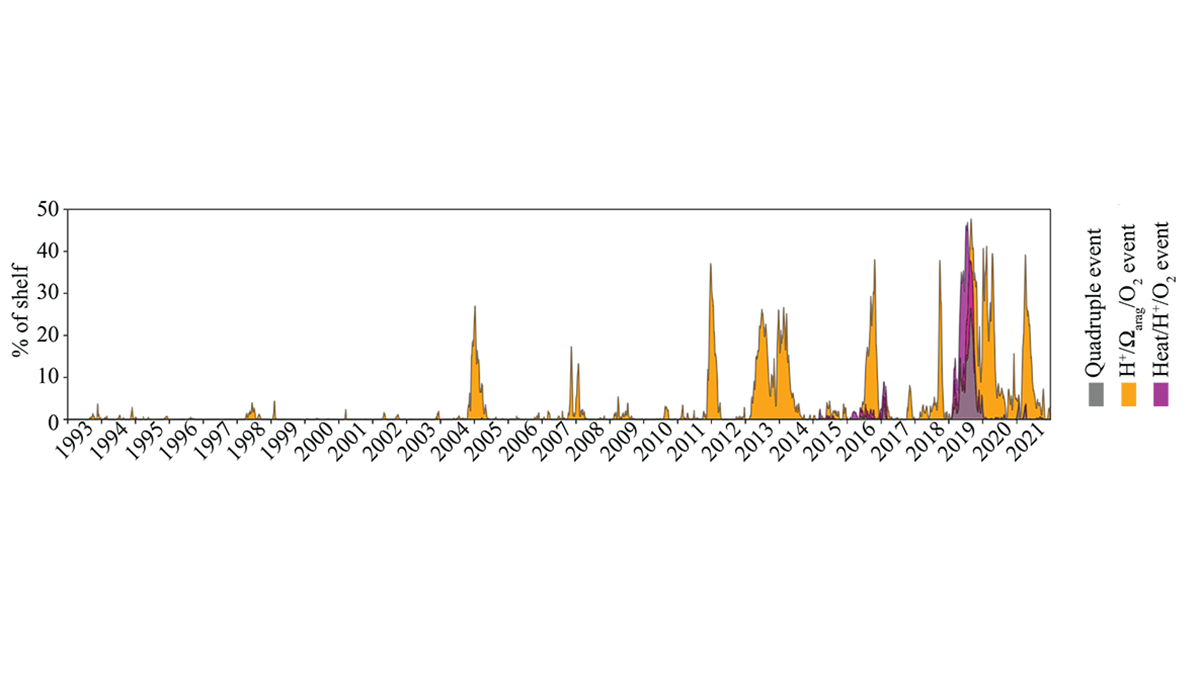
Compound Extreme Events Threaten Marine Ecosystems
Short-term extreme marine heat wave events superimposed on stressors from longer-term climate change produce compound extreme events that impact the Gulf of Alaska ecosystem.