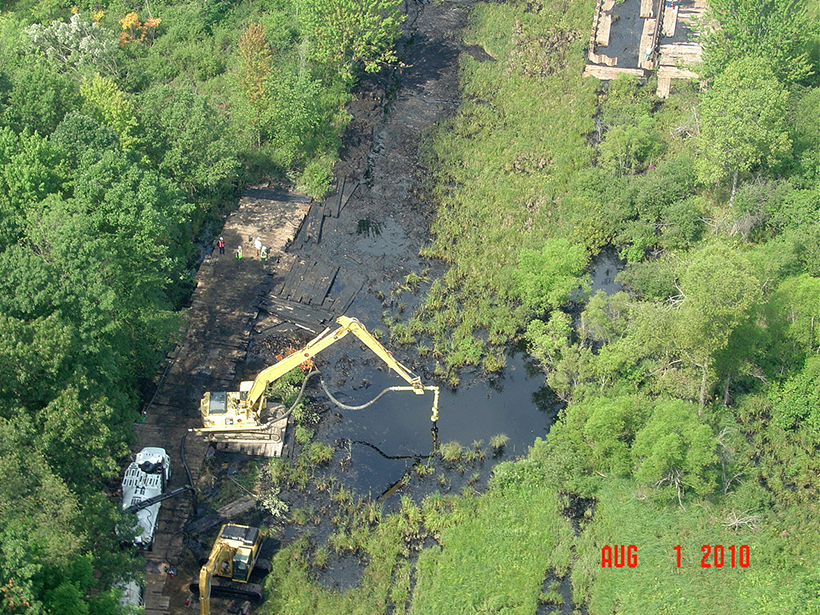
New experiments at an old oil spill site in Minnesota suggest that nonbiological processes alone may not account for decreased magnetization.
oil & gas
Forecasting Geohazards in the Age of Gas Hydrate Exploitation
A curious breath-like pattern exhibited by gas hydrates may help forecast hazards associated with extracting them from the seafloor.
America’s Natural Gas Pipeline Routes and Environmental Justice
Pipeline infrastructure disproportionately burdens America’s most vulnerable communities.
El Oleoducto Keystone Derrama 9,120 Barriles de Petróleo en los Humedales de Dakota
La fuga tuvo lugar en una sección pre-existente del oleoducto Keystone. Este es el cuarto derrame del oleoducto en 9 años.
¿Por Qué la Luz Solar es Importante para los Derrames de Petróleo en el Mar?
Una década de investigación desde el desastre de Deepwater Horizon ha revelado cómo la luz solar—su importancia subestimada durante mucho tiempo en la ciencia de derrames de petróleo—altera sustancialmente el petróleo que flota en la superficie del mar.
More Gas Wells Linked to More Symptoms in Pennsylvania Residents
Natural gas production has been booming in southwestern Pennsylvania, but it may also yield multiple health complaints, especially for residents surrounded by oil and gas facilities.
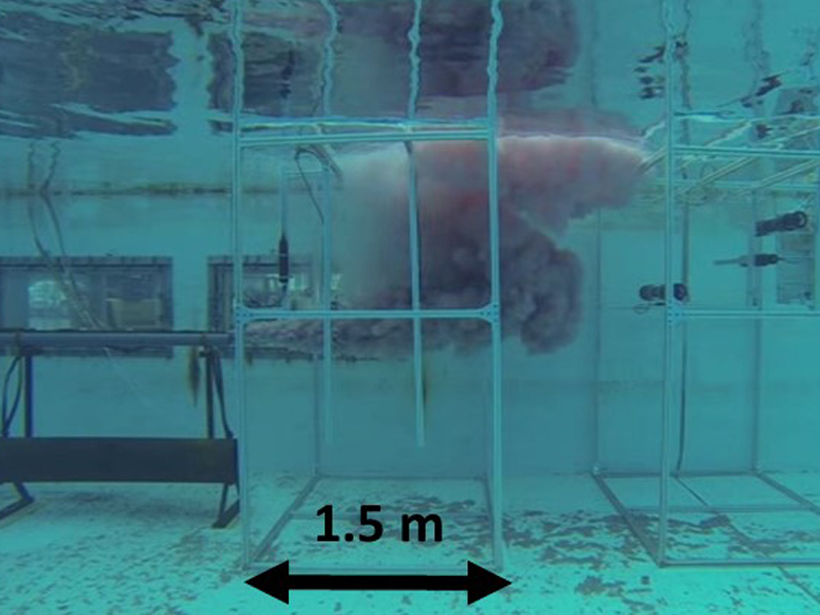
The Underwater Behavior of Oil and Gas Jets and Plumes
Exploring how the multiscale interaction between underwater oil and gas plumes and the environment impacts plume composition and trajectory.
Los Costos Ecológicos de Remover las Plataformas Petroleras Mar Adentro en California
Las plataformas de perforación de petróleo- y gas-mar adentro son hábitats ricos para peces. Eliminarlas por completo resultaría en una pérdida del 95% de biomasa de peces, revela una nueva investigación.
Understanding Earthquakes Caused by Hydraulic Fracturing
A better understanding of how earthquakes are caused by hydraulic fracturing is an important part of building better practices to manage and mitigate their risks.