Christopher Paola will receive the 2016 G. K. Gilbert Award at the 2016 American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting, to be held 12–16 December in San Francisco, Calif. The award recognizes "a scientist who has either made a single significant advance or sustained significant contributions to the field of Earth and planetary surface processes, and who has in addition promoted an environment of unselfish cooperation in research and the inclusion of young scientists into the field."
planetary surfaces
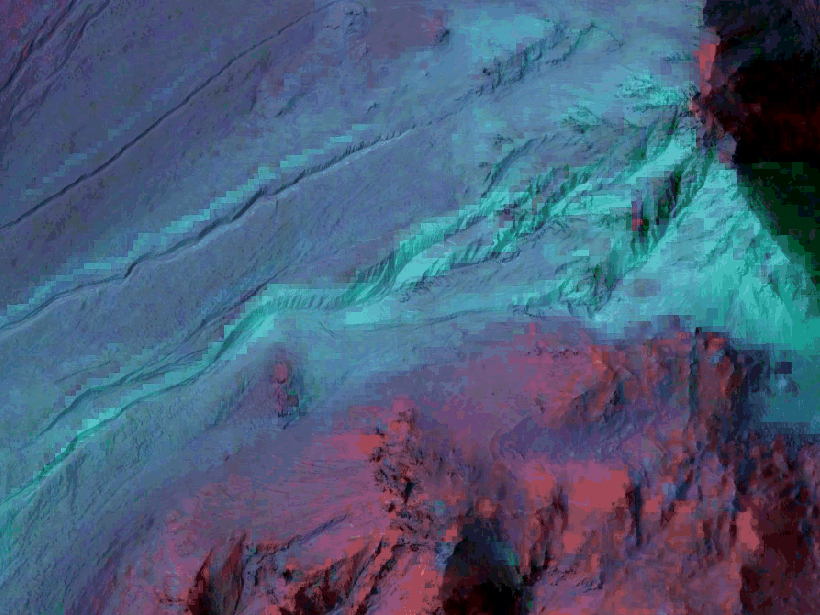
Mars’s Climate May Have Been Wet Much Later Than Thought
Water-carved valleys may be relatively young, challenging assumptions about the history of the Red Planet's climate.
How Do Gullies Form on Mars?
New orbiter data support an important role for seasonal frost—not liquid water—in the formation of Martian gullies.
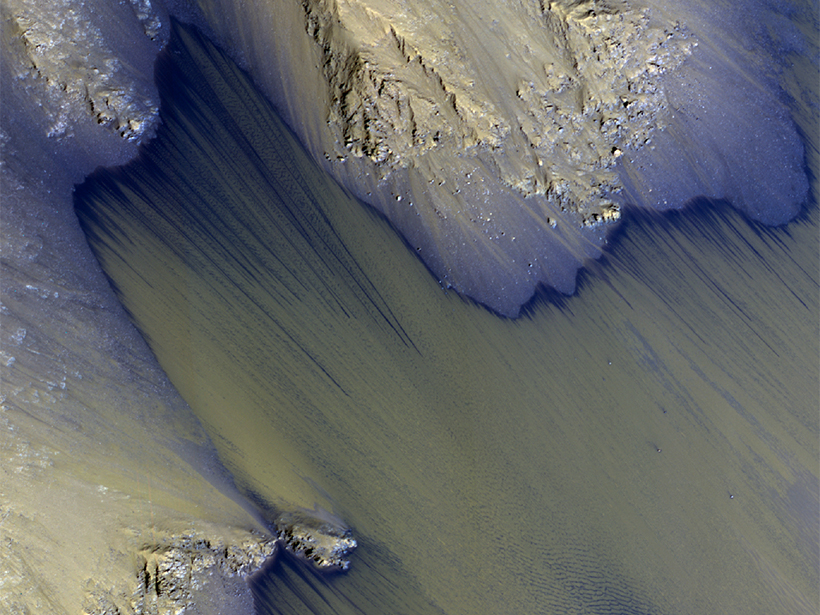
A Cluster of Water Seeps on Mars?
The discovery of dense concentrations of recurring flowlike features in two Valles Marineris chasms could aid in the search for life and influence future exploration of the Red Planet.
Curiosity Sends Curious Water Data from Mars
The rover's neutron spectroscopy instrument hints at an unexpected trend: The upper soil levels in the layers of Gale Crater's Kimberley formation seem to hold more water-associated hydrogen.
Tsunamis Splashed Ancient Mars
Massive meteorites likely slammed into a Martian ocean billions of years ago, unleashing tsunami waves up to 120 meters tall, a close study of a region of the Red Planet's terrain has found.
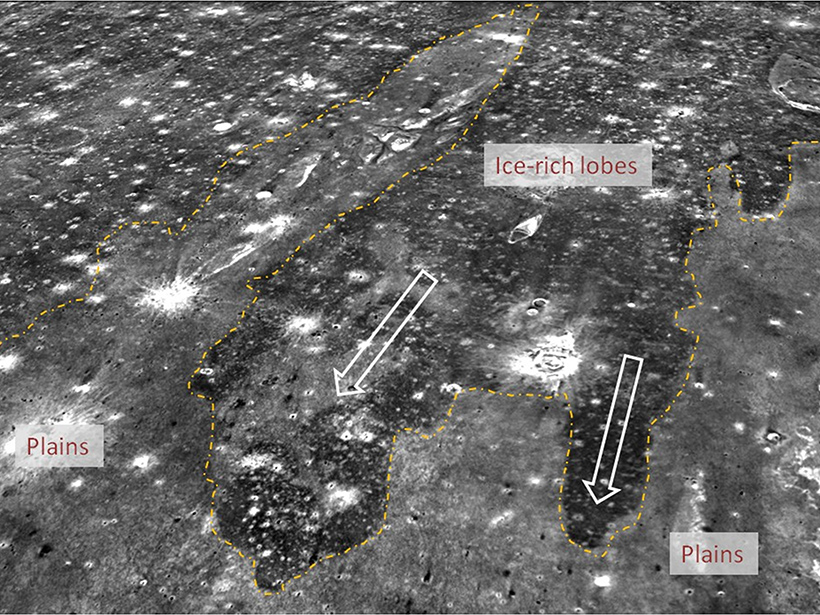
Demystifying Mercury "Hollows"
Spectral data from NASA's MESSENGER spacecraft indicate that the properties of the depressions on Mercury's surface can vary within a single crater and that these differences may correlate to age.
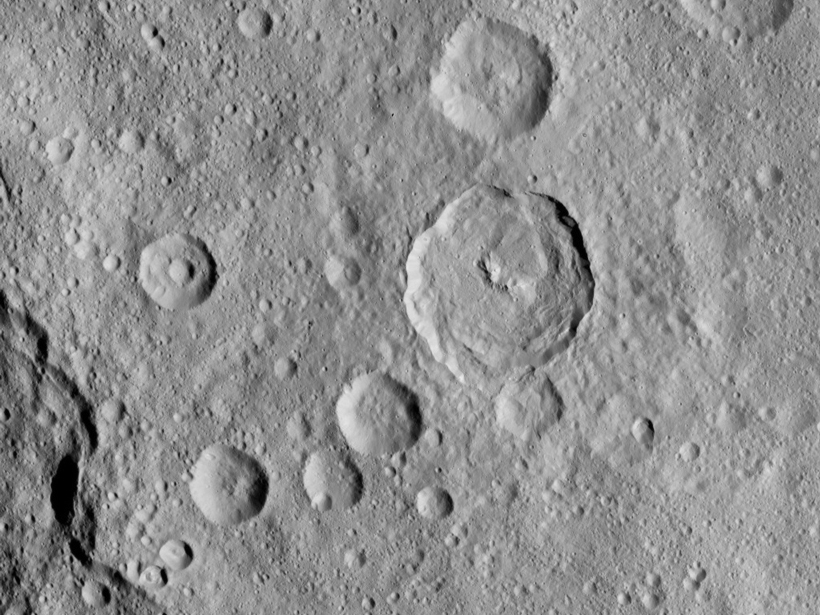
Objects That Slam into Ceres Remain on Its Surface
Hypervelocity impact experiments shed new light on the composition and evolution of the largest dwarf planet's little-known surface.
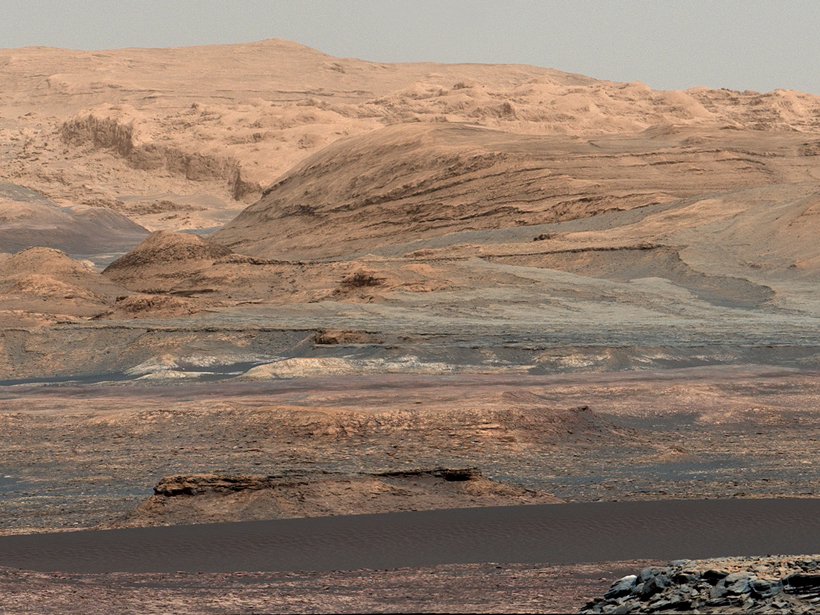
Where Curiosity Has Taken Us
The Curiosity rover, one of NASA's flagship missions, analyzes Martian geology, geochemistry, climatology, and radiation to assess whether Mars could have supported microbial life.
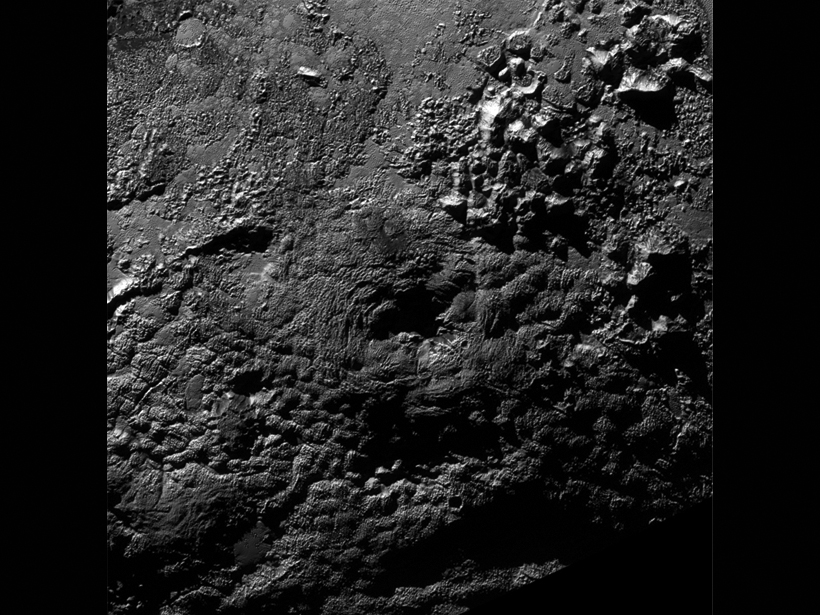
Pluto: In the Icebox but Maybe Still Cookin'
New evidence of ice volcanoes and of middle-aged terrains on Pluto's surface suggests that the dwarf planet has remained geologically active ever since it first formed billions of years ago.