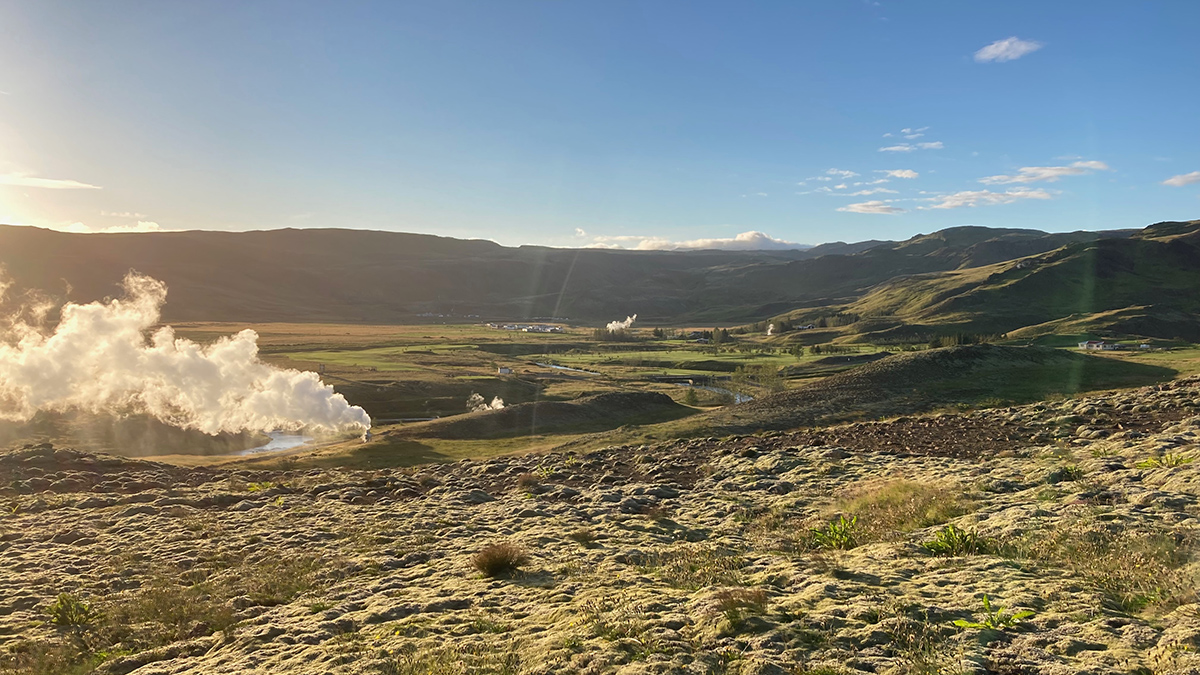
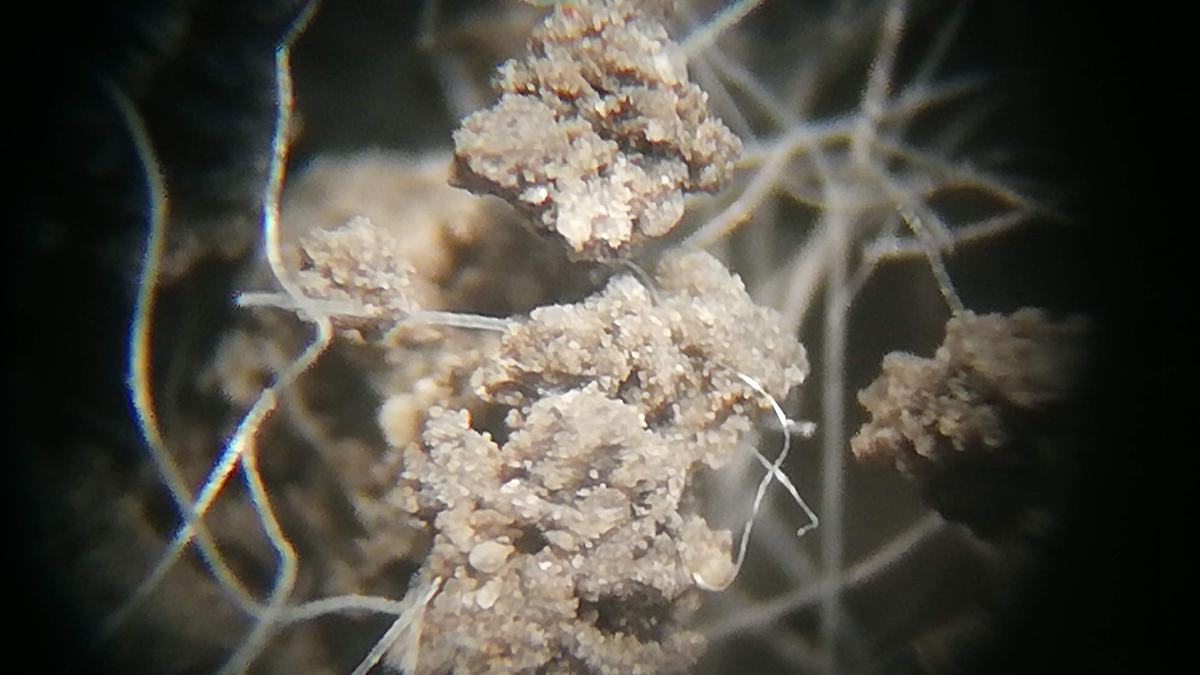
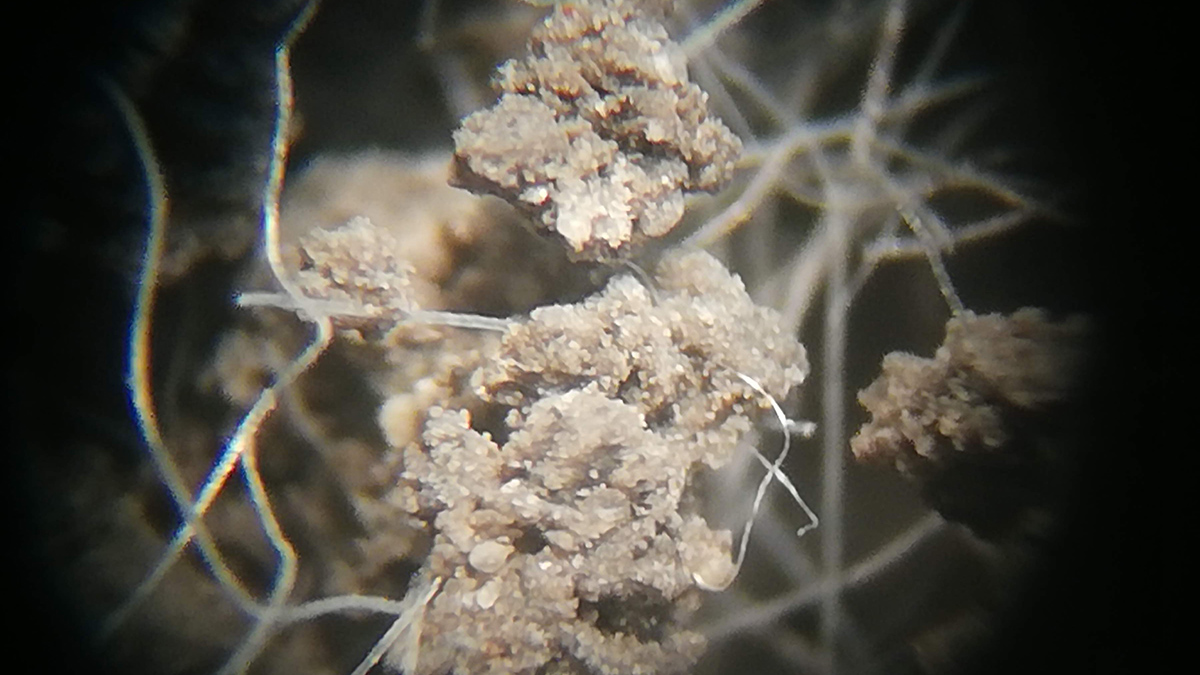
A study in Iceland found that microbes are hoarding more nitrogen for themselves, altering nutrient cycling and leaving less for plants.
plants
Los microplásticos tienen efectos muy variados en el suelo
Un nuevo estudio revela que una concentración de microplásticos de tan solo el 0,4 % altera el drenaje del suelo, lo que podría afectar al crecimiento de los cultivos y otras plantas.
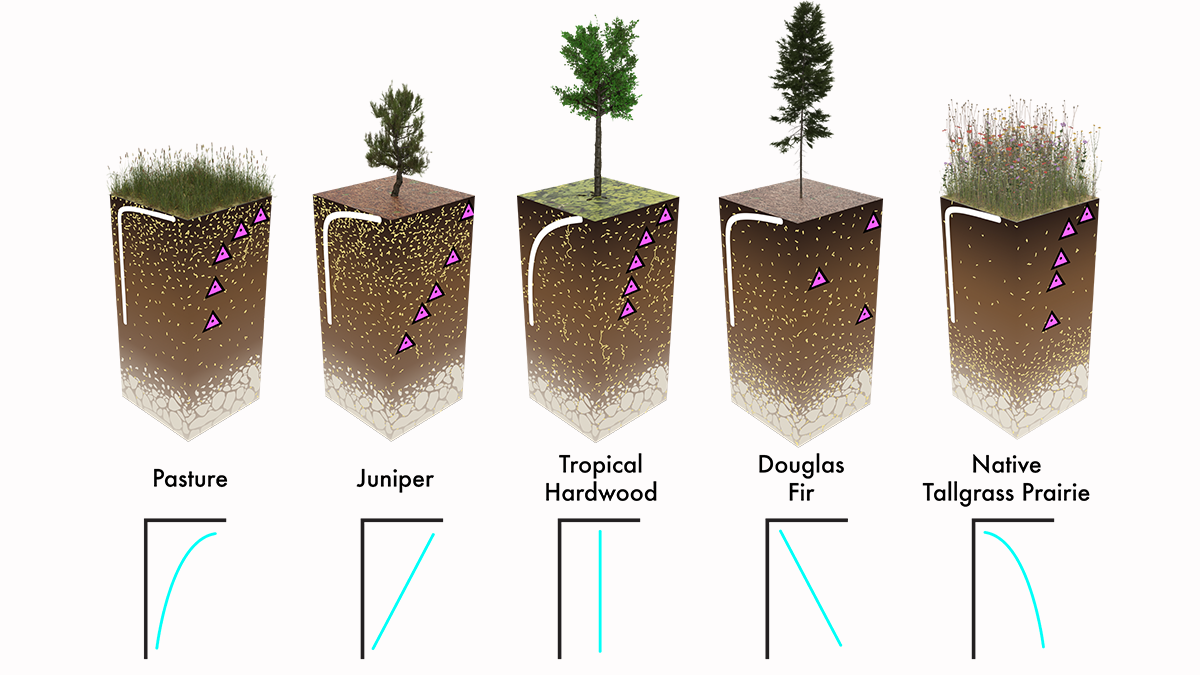
Rethinking How to Measure Roots
Researchers present a new method for determining depth-dependent patterns of the root-soil interactions that drive ecosystem functions in the critical zone.
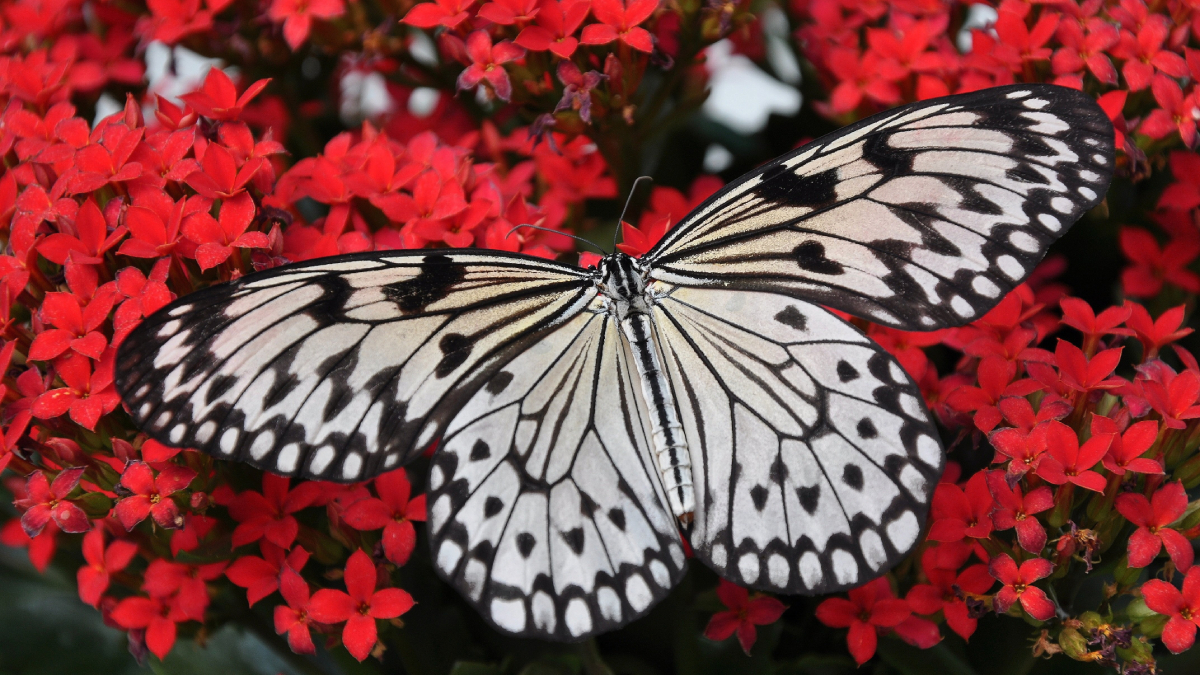
Climate Change Could Drive Butterflies and Plants Apart
Insects and the plants they depend on are migrating in response to climate change, but not always in the same way.
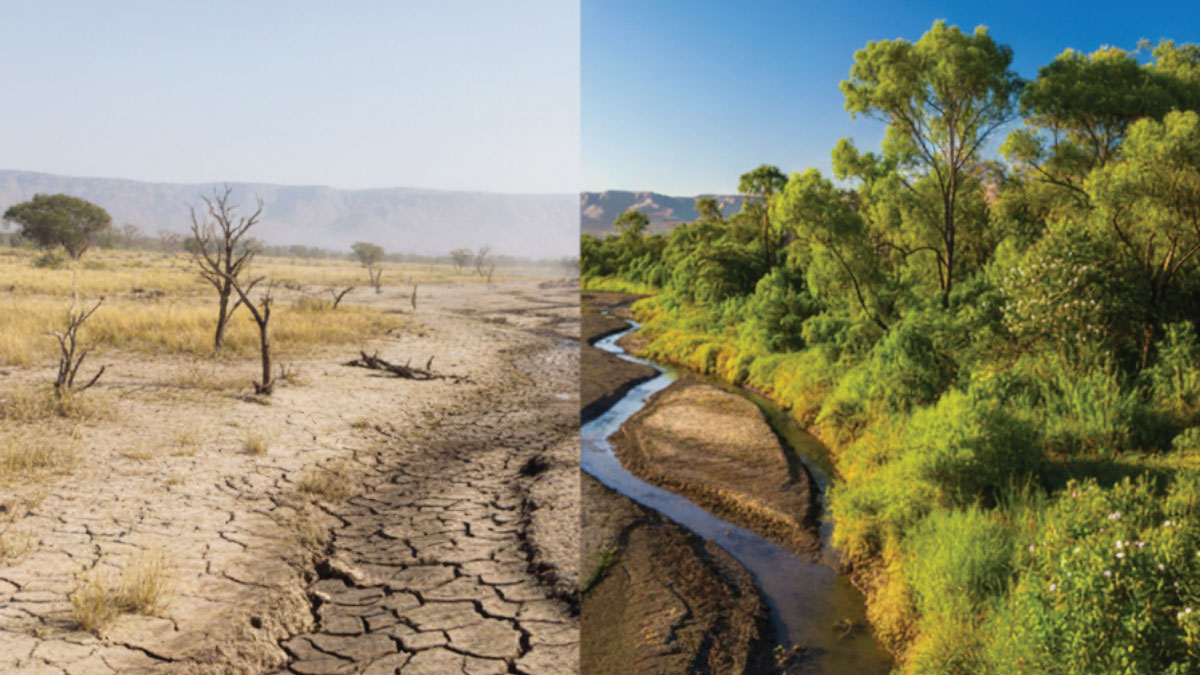
An Ecosystem Never Forgets
A new study in southwestern China shows how ecosystems may exhibit “hydrological memory,” which affects how they react to extreme climate events such as heat and drought.
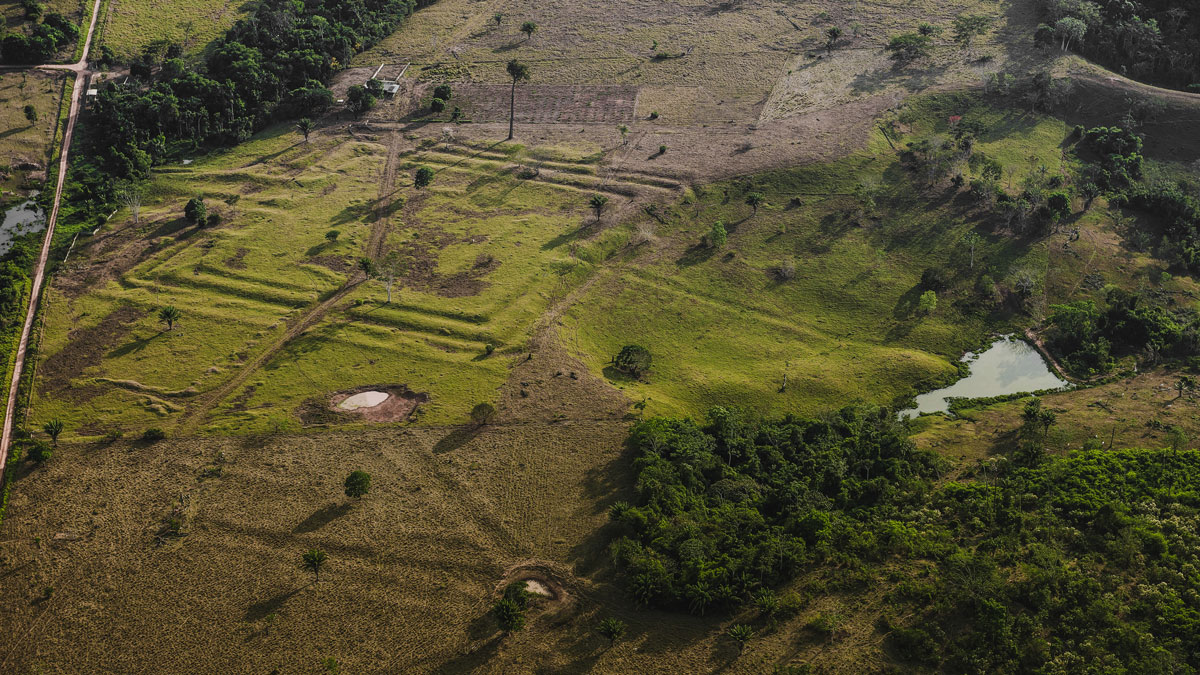
How Ancient Indigenous Societies Made Today’s Amazon More Resilient
Portions of the forest managed by pre-Columbian populations hold higher biomass and are more able to withstand climate change.
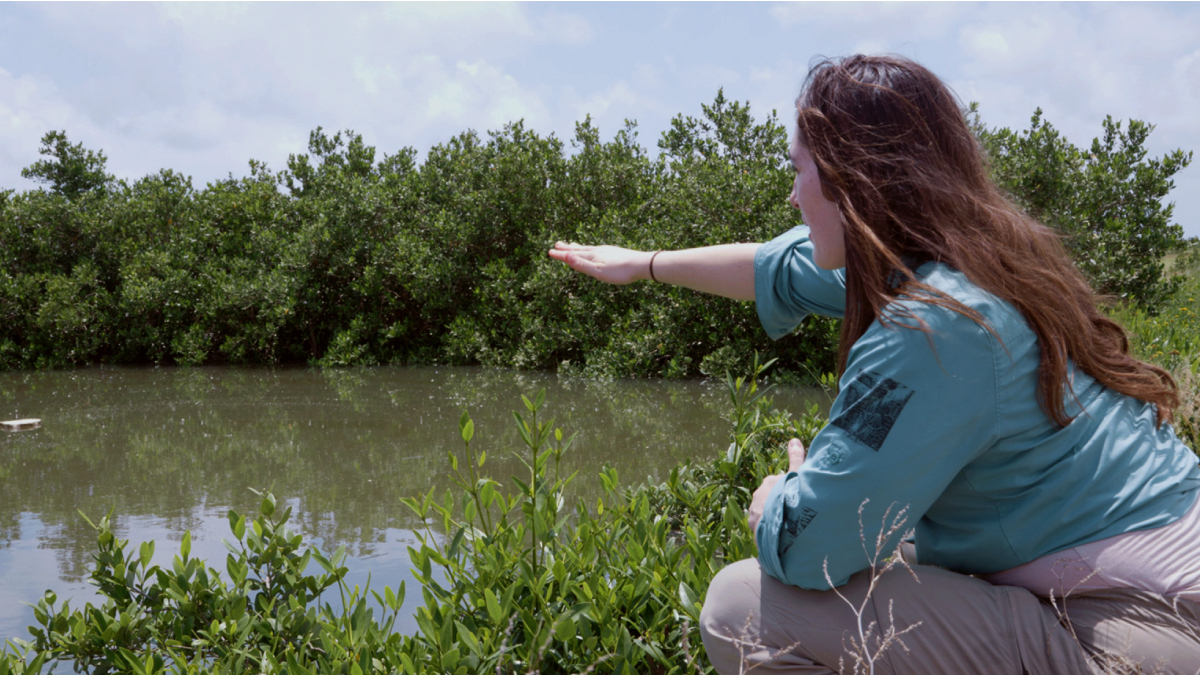
Glass Sand Grows Healthy Mangroves
In places with lots of glass waste, sand made from recycled material could be another tool in the coastal restoration toolbox.
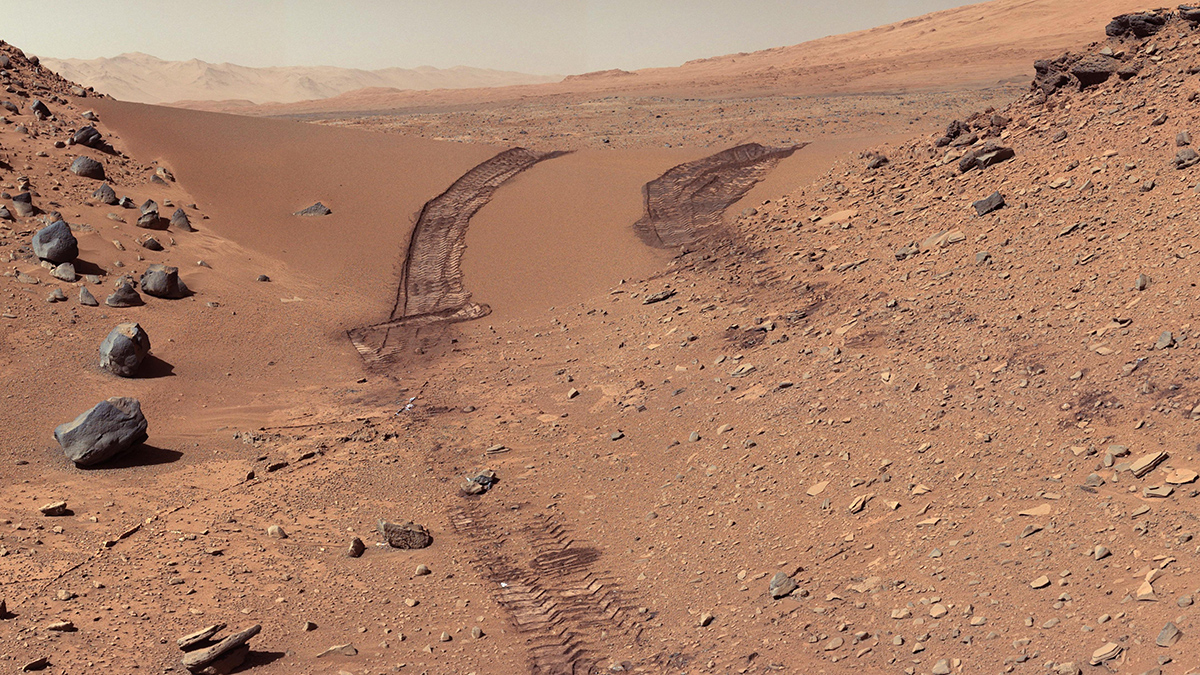
Fungi, Fertilizer, and Feces Could Help Astronauts Grow Plants on the Moon
A new study offers tantalizing evidence that filamentous fungi extending from roots, along with treated astronaut waste, could provide sufficient scaffolding to help plants grow in planetary regolith.
Microplastics Have Widely Varying Effects on Soil
A new study finds that a microplastic concentration of just 0.4% alters the drainage of soil, which could affect the growth of crops and other plants.
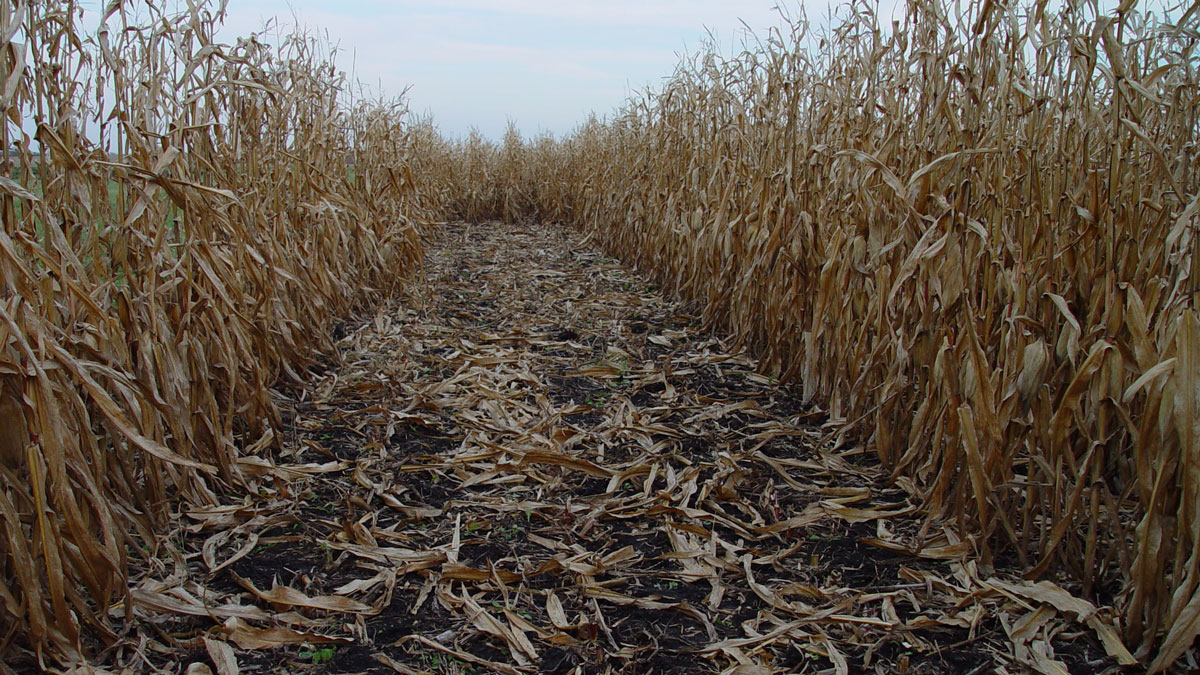
How Might Leftover Corn Stalks Halt Fugitive Carbon?
Bio-oil made from plant waste could help limit carbon emissions from orphaned oil and gas wells. But would it help or hinder farmers’ bottom line?