在中国的西北部,沙漠条件保存了长城最偏远的部分。科学家们正在探索着2000年前的建筑材料,以寻找该地区过去气候的迹象。
plants
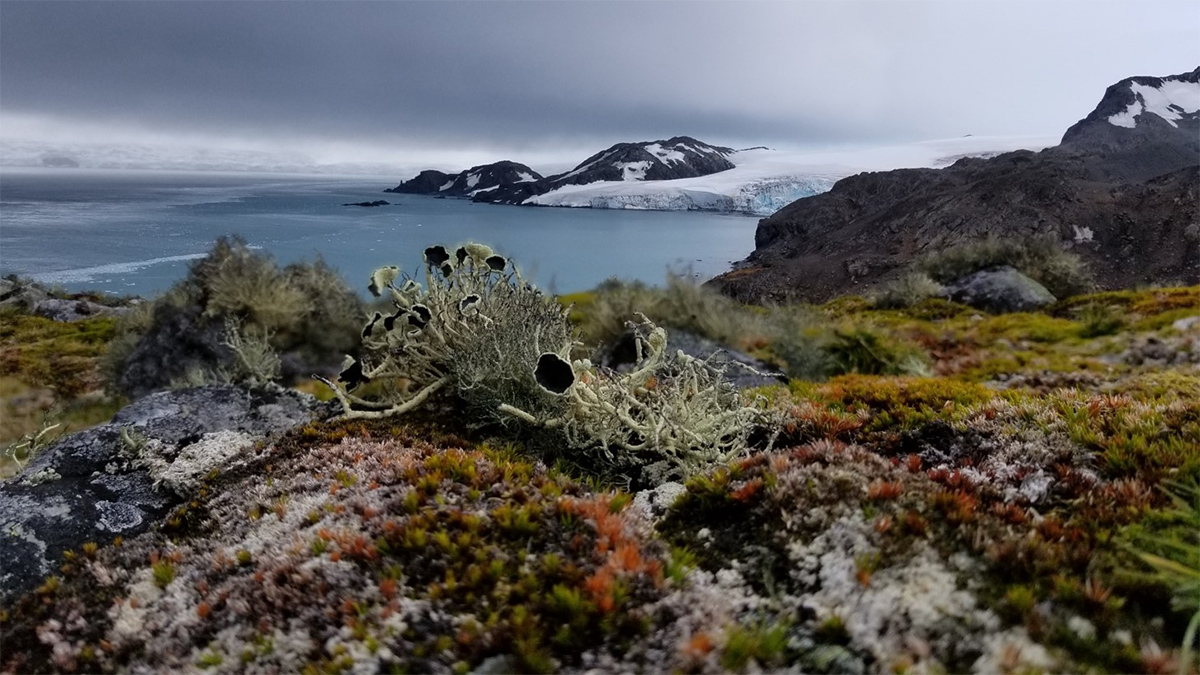
New Map Reveals the Extent of Vegetation in Antarctica
More than 40 square kilometers of vegetation cover Antarctica, including in previously unknown areas. A new map offers fresh insights for conservation amid climate change.
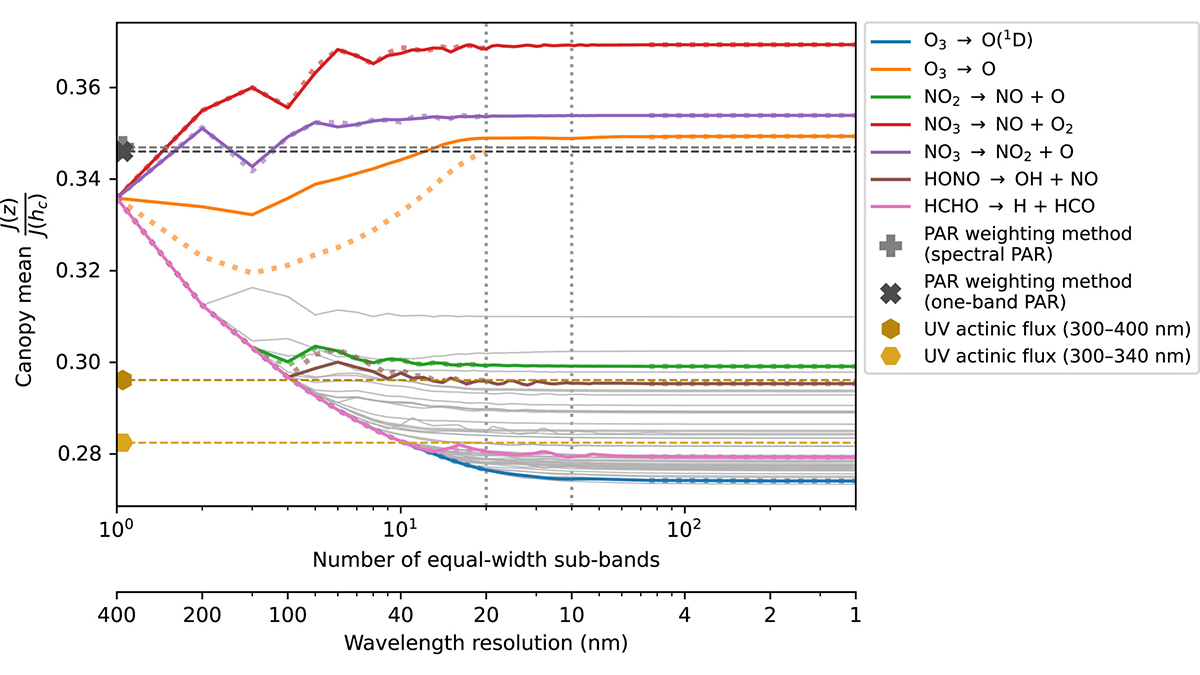
Spectral Solar Radiative Transfer in Plant Canopies
Spectrally resolved radiative transfer is needed to compute reliable estimates of sunlight transmission and photolysis of molecules within plant canopies.
Ancient Pines Could Reveal the Heat of Thousands of Past Seasons
A novel 3D CT scan approach unlocks temperature records preserved in the gnarled wood of bristlecone pines.
Carbon Cycles Through Plants More Quickly Than Expected
A radioactive isotope produced by nuclear weapons reveals that plants take up more carbon—but hold on to it for less time—than current climate models suggest.
How Soil Symbionts Could Unlock Climate-Smart Agriculture
By tracing the evolutionary history of beneficial soil microbes, scientists hope to unearth a sustainable solution for producing food to feed a growing global population.
Sand’s Role in Rerouting Meandering Rivers Is Bigger Than We Thought
Researchers delve into the dirt causing rivers to migrate.
Kansas Prairie Streams Are Getting Choked, Maybe for Good
A herculean effort to fight back woody plants in the Konza Prairie has largely failed. The outcome shows how difficult it can be to retore these ecosystems.
Discounting Carbon Gain to Prevent Water Loss Today
A new study introduces a timescale for optimizing tradeoffs between carbon gain and water loss to improve estimates of photosynthesis during prolonged dry spells.
Extra Carbon Dioxide Helps Lower Layers of the Amazon Thrive—for Now
Plants living in the shadows grew faster when exposed to excess carbon dioxide. But this short-term effect could vanish in a high-emission-induced warmer future, making the forest a carbon source.