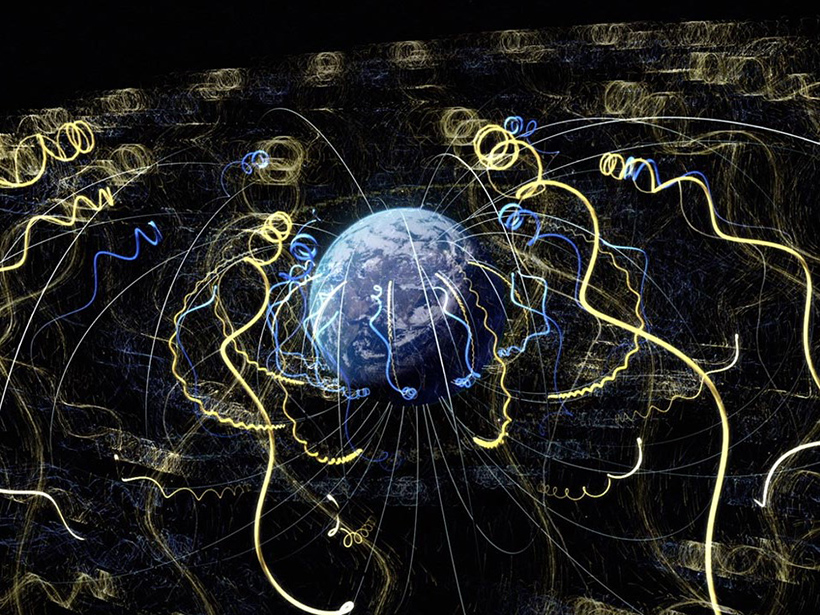
Energetic electrons are accelerated directly by magnetic reconnections and can act as tracers of large-scale magnetic field conditions.
plasmas
A New Approach to Characterizing Space Plasmas
When plasma particle velocity distributions have multiple, distinct parts, treating each as a separate beam may yield more intuitive results.
New Results Concerning Solar Wind Entry into the Magnetosphere
A new book describes recent results defining the many pathways and foreshock, bow shock, magnetosheath, and magnetopause phenomena connecting the solar wind to the dayside magnetosphere.
Terrestrial Radio Signals May Suppress High-Energy Electrons
Naval radio signals may cause the formation of a barrier observed during geomagnetic storms that is seemingly impenetrable by relativistic electrons.
Liu Receives 2019 Fred L. Scarf Award
Terry Zixu Liu received the 2019 Fred L. Scarf Award at AGU’s Fall Meeting 2019, held 9–13 December in San Francisco, Calif. The award is given annually to “one honoree in recognition of an outstanding dissertation that contributes directly to solar–planetary science.”
A Whistle Here, There, and Everywhere on the Giant Planet
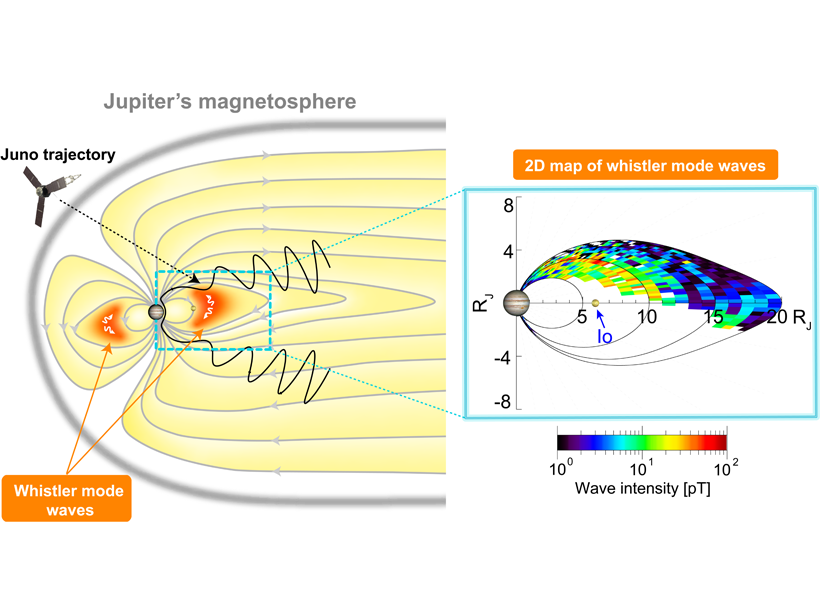
NASA’s Juno spacecraft is “hearing whistles” all over the place on Jupiter, a type of natural plasma waves called whistlers that are sometimes associated with atmospheric lightning.
All Hands on Deck to Catch Ion Cyclotron Waves
An international armada of orbiting satellites and ground VLF network join forces to form a “magnetosphere-ionosphere observatory” to size up electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves in the magnetosphere.
Explaining the Missing Energy in Mars’s Electrons
Electrons energized and trapped at Mars were thought to lose energy inside the planet’s magnetosheath, but new research suggests a different explanation of spacecraft data.
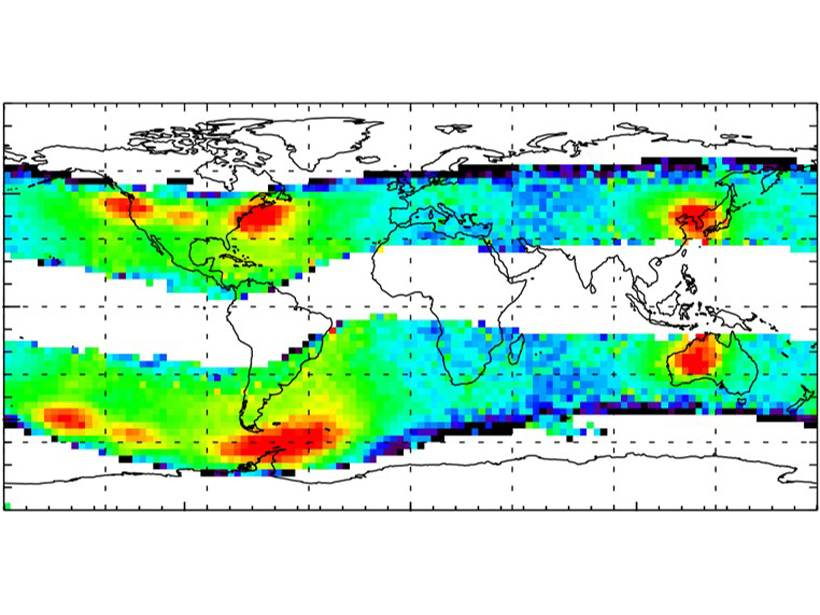
Human-made Emissions Modify Electron Space Environment
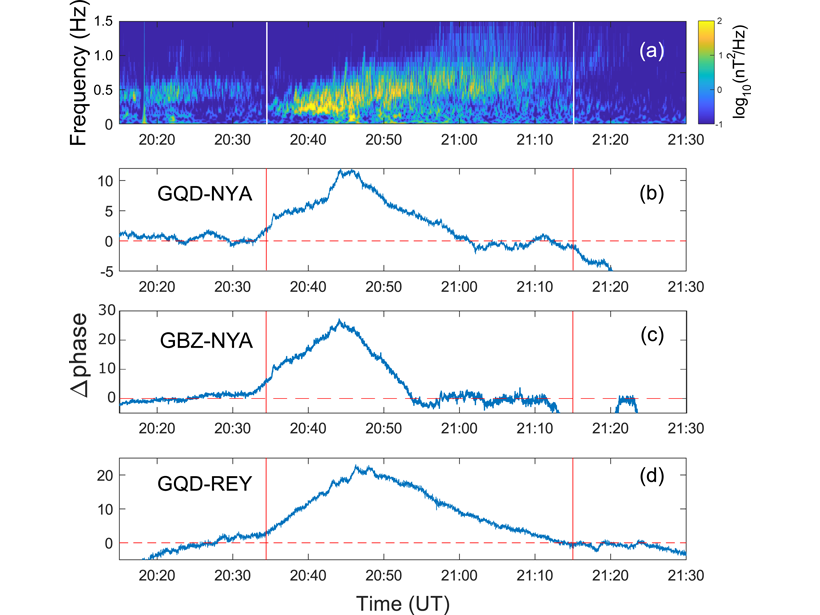
Very Low Frequency transmitters used for communications with submarines modify the dynamics of energetic electrons in the inner radiation belt and the slot region.
Holistic Views of the Nighttime Ionosphere
The nightside ionosphere, at latitudes away from the auroral zone, should have very little charged particle density, but it doesn’t. A new comprehensive study of satellite data explains why.