Source: Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics
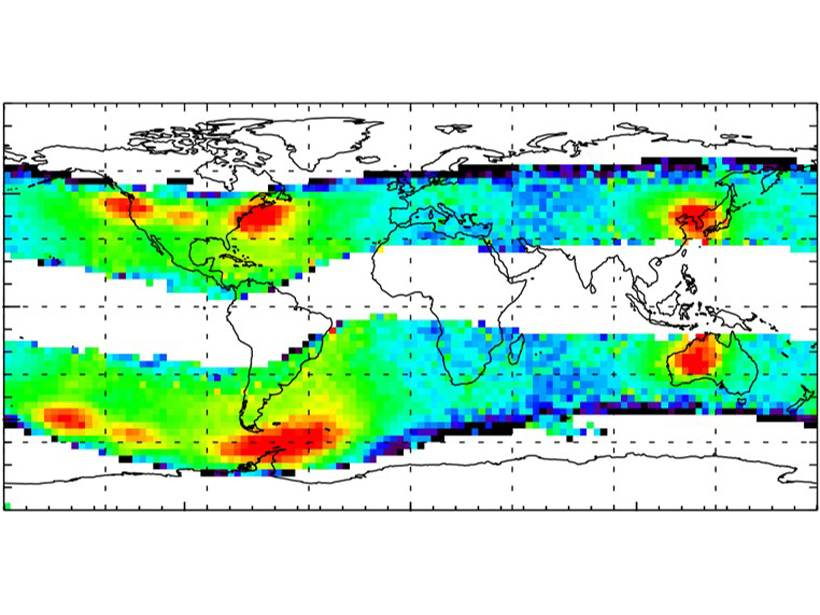
Human-made emissions have important effects on the geospace environment. Very Low Frequency (VLF) transmitters used for communications with submarines modify the dynamics of energetic electrons in the inner radiation belt and especially cause the formation of the slot, the region usually devoid of electrons separating the inner and the outer radiation belts.
The behavior of energetic electrons in the inner radiation belt and slot region is becoming increasingly important, because the satellite industry exploits more and more new satellites through this region. Meredith et al. [2019] constructs new models of the wave power from VLF transmitters in the inner magnetosphere and shows that half of the total wave power between 1.3 and 3 Earth radii comes from three specific VLF transmitters from Australia, USA, and Germany.
Citation: Meredith, N. P., Horne, R. B., Clilverd, M. A., & Ross, J. P. J.. [2019], An investigation of VLF transmitter wave power in the inner radiation belt and slot region. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 124. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JA026715
—Viviane Pierrard, Editor, JGR: Space Physics
Text © 2019. The authors. CC BY-NC-ND 3.0
Except where otherwise noted, images are subject to copyright. Any reuse without express permission from the copyright owner is prohibited.