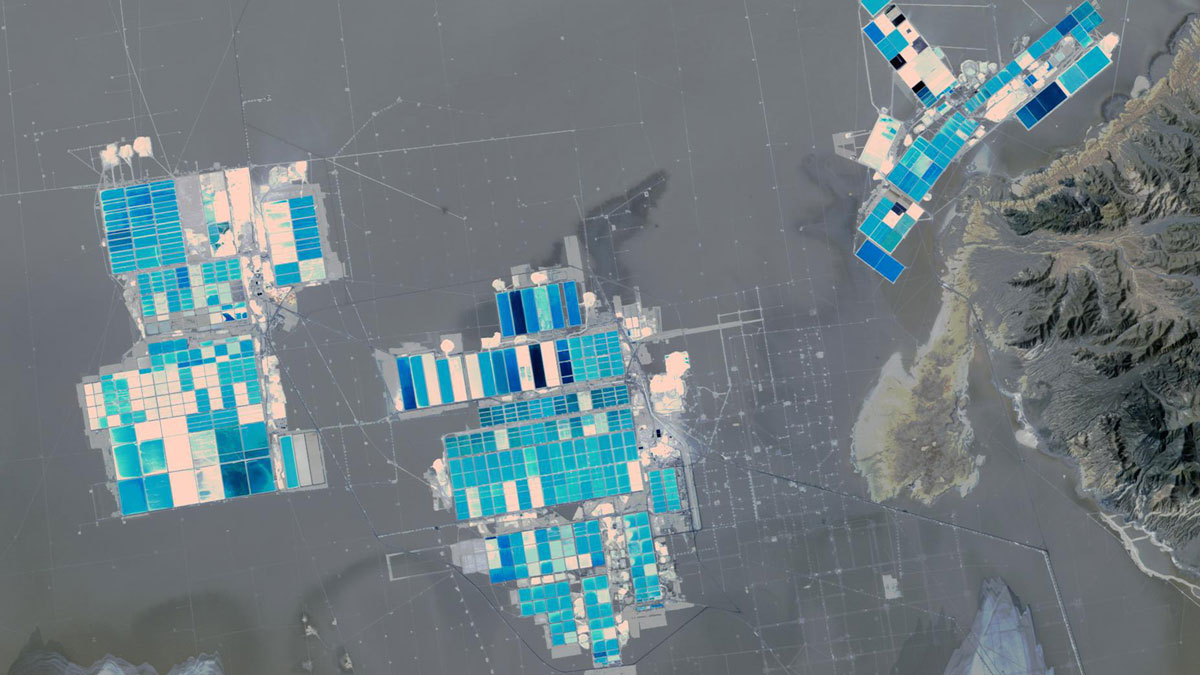
The new chemical solvent technique could cut water use, speed extraction, and unlock reserves like California’s Salton Sea.
pollution
The Olympics Just Saw Its First “Forever Chemical” Disqualifications
Waxes containing PFAS are banned at the Milan-Cortina Games. Three athletes already have been disqualified for using them.
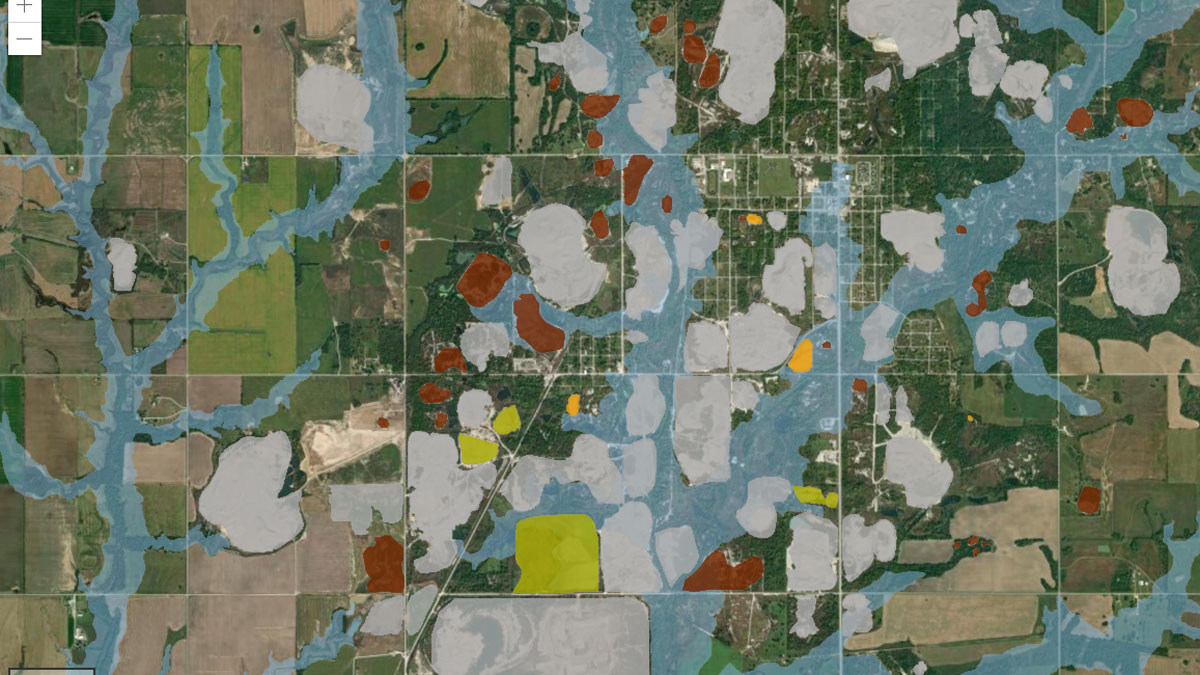
Making a Map to Make a Difference
A new study highlights the partnership between scientists and nonscientist community members in building an interactive GIS map to show flooding risk in a Superfund site.
Pollution Is Rampant. We Might As Well Make Use of It.
Human-made substances hold dangers for the environment, but they also give scientists a view into recent history.
EPA to Abandon Stricter PM2.5 Air Pollution Limits
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency moved this week to reduce limits on fine particulate air pollution, including soot, set by the Biden administration last year.
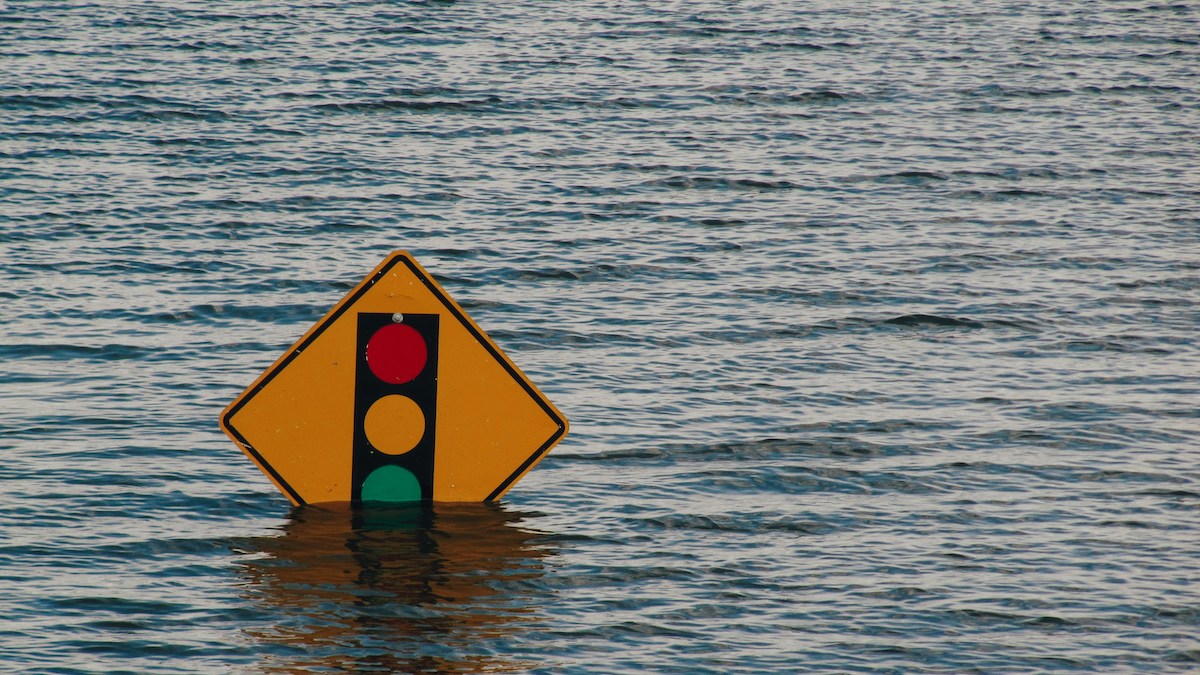
5,500 Toxic Sites in the U.S. at Risk of Flooding as Seas Rise
Rising sea levels have put thousands of facilities containing hazardous materials at risk of flooding this century, according to a new study published in Nature Communications.
EPA Proposes That Major Polluters No Longer Report Their Emissions
The EPA proposed today that approximately 8,000 polluting facilities, including oil refineries, power plants, and steel mills, should no longer be required to report their greenhouse gas emissions.
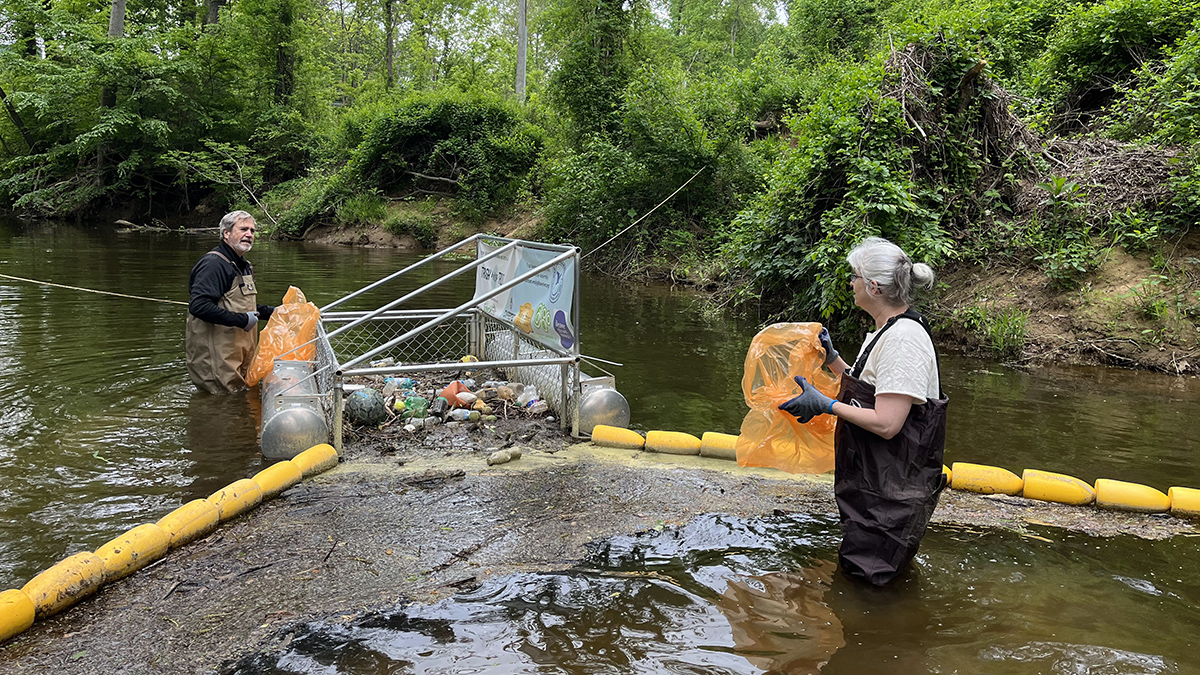
How North Carolina Trash Traps Could Help Inform Policy
Staff and volunteers at Waterkeepers collected and categorized more than 150,000 pieces of trash from the state’s waterways, the vast majority of which were plastic.
Protein-Powered Biosensors with a Nose for Environmental Ills
Odorant-binding proteins derived from pigs, bovines, and other animals are the next frontier in localized, climate-smart sensing of pesticide spills, greenhouse gas precursors, and more.
Artificial Light Lengthens the Urban Growing Season
New research shows that artificial light at night lengthens the plant growing season in cities, overshadowing the effect of high urban temperatures.